Greetings to our curious tree lovers. If you are here today you are probably interested in learning about what kind of trees occur or grow in America. Types of American Trees
So, let’s get started!
Red Maple – Acer Rubrum
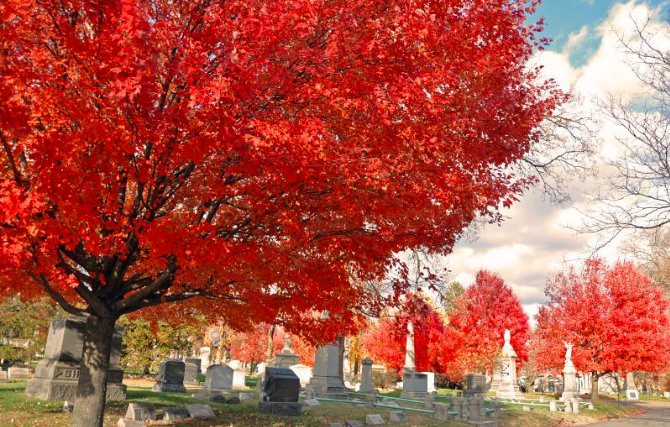

Acer rubrum, sometimes called the red maple or sugar maple in North American English, is one of the most common trees found throughout North America and Europe. It can grow to heights up to 50 feet tall but typically grows to 20-25 feet.
The tree has a broad crown with spreading branches that produce upright shoots that sprout from the base of the trunk. They are usually 4-7 inches wide when they first appear.
This species produces sweet sap which was used by Native Americans for making maple syrup and other products.
Loblolly Pine – Pinus Taeda
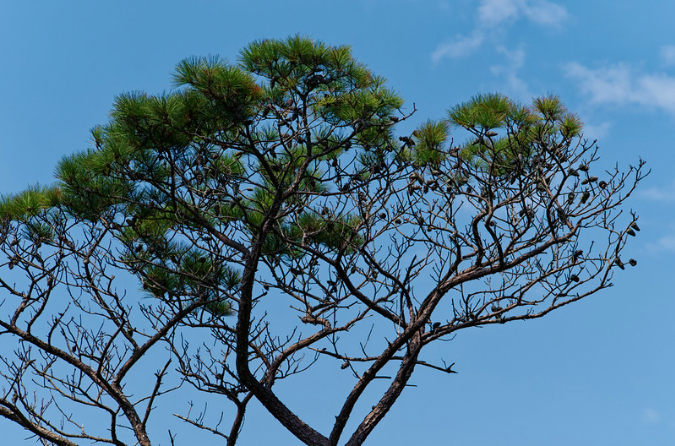

The loblolly pine is an evergreen coniferous shrub or small tree native to much of the southern United States, Mexico, Central America, northern South America, and tropical regions of Africa.
In its natural environment, it is often planted as a windbreak or hedge along roadsides, or as a specimen plant near buildings.
Sweetgum – Liquidambar Styraciflua
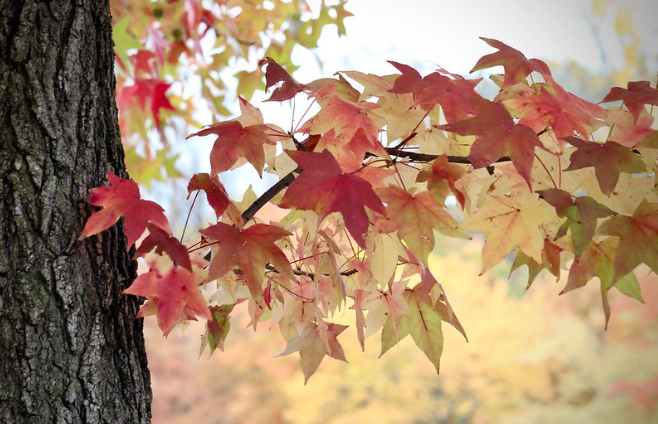

Liquidambar styraciflua, commonly known as the sweetgum, is a deciduous tree native to eastern North America. It is also called the sourgum because the leaves contain tartaric acid, which gives them their characteristic bitter taste.
The leaves are alternate, dark green on both sides, and have long pointed tips. The flowers are white and borne singly at the end of slender panicles.
Douglas Fir – Pseudotsuga Menziesii
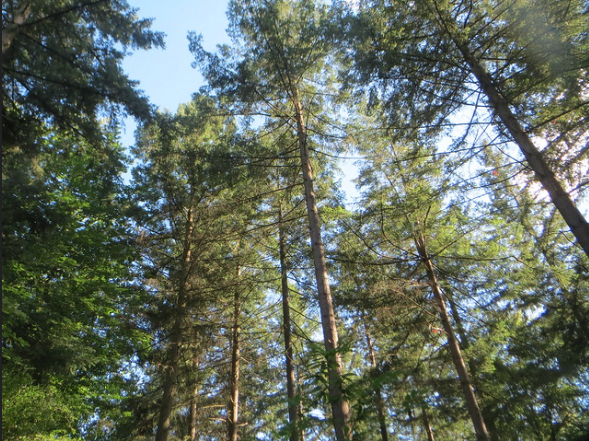

Pseudotsuga menziesii, commonly known as the Douglas fir, is a coniferous evergreen tree native to western North America. Its range extends from British Columbia across Canada and into the United States west of the Great Plains.
Quaking Aspen – Populus Tremuloides
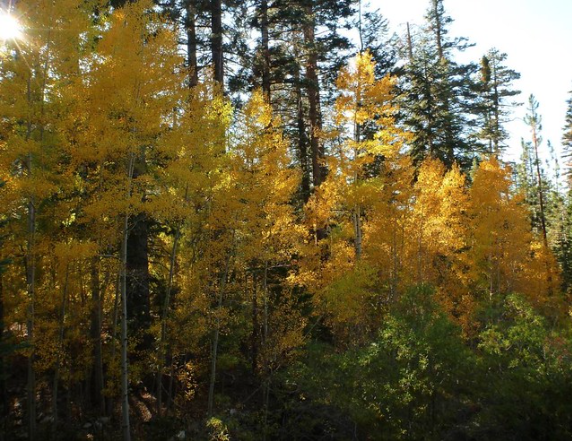

Populus tremuloides, the quaking aspen, is a medium-sized deciduous coniferous tree native to central North America.
It is widespread from Manitoba southward through the Canadian provinces of Alberta, Saskatchewan, and Ontario; eastwards to New York and Michigan; and northwards to Minnesota and
Sugar Maple – Acer Saccharum
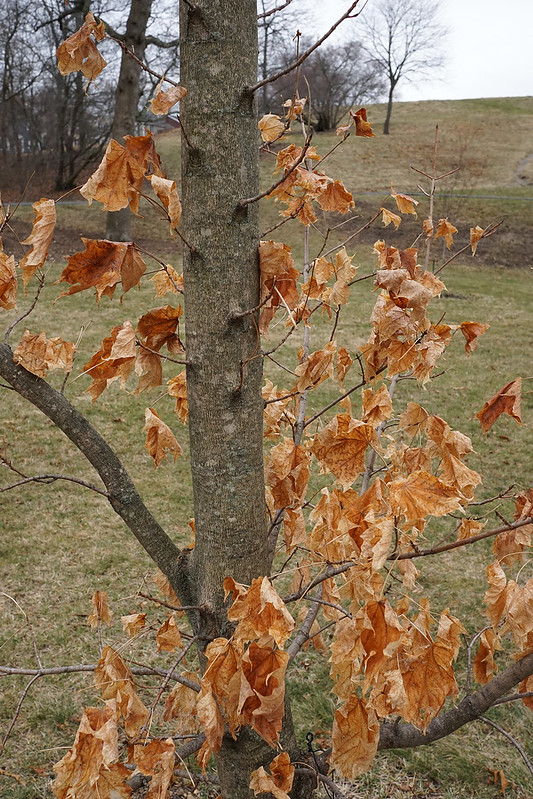

Acer saccharum, commonly known as the sugar maple, is a large deciduous tree native primarily to eastern North America, growing in moist areas such as swamps and bogs. It is also widely grown as an ornamental tree.
Balsam Fir – Abies Balsamea
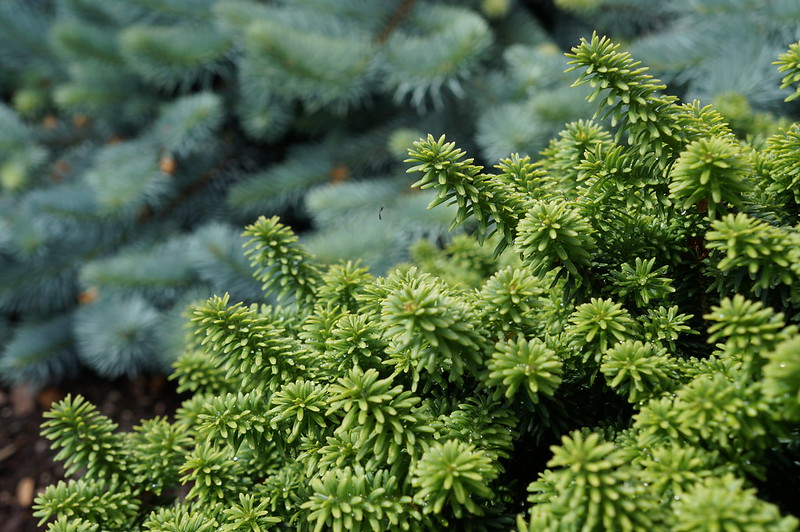

Abies balsamea (also known as silver fir) is a very large coniferous tree native mainly to Quebec, Maine, the Adirondack Mountains of New York State, and Nova Scotia.
It is not quite as massive as some other species of Abies, and so is more likely to be seen as a single tree rather than a densely packed group of trees or stands.
Flowering Dogwood – Cornus Florida
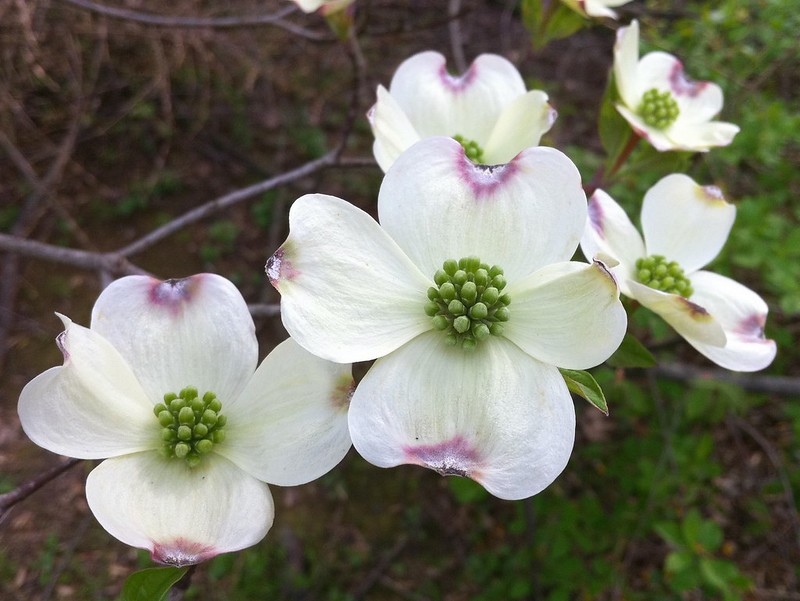

Cornus florida, commonly known as the flowering dogwood, is an erect flowering shrub or small tree. It is native to eastern North America from Newfoundland and Labrador to Georgia and Alabama, west to Illinois and Missouri.
Lodgepole Pine – Pinus Contorta
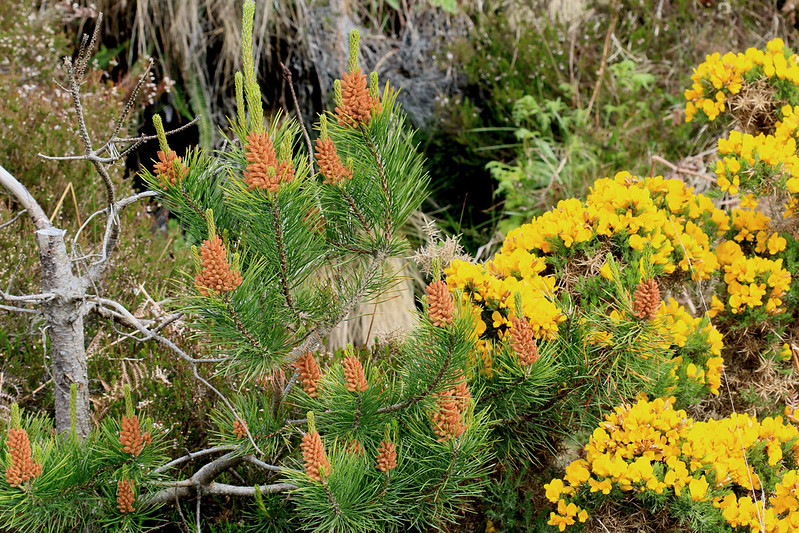

Pinus contorta, commonly known as the lodgepole pine, is a conifer in the family Pinaceae native to the Northern Hemisphere including all of Canada and the United States. It is the largest member of the genus Pinus.
White Oak – Quercus Alba
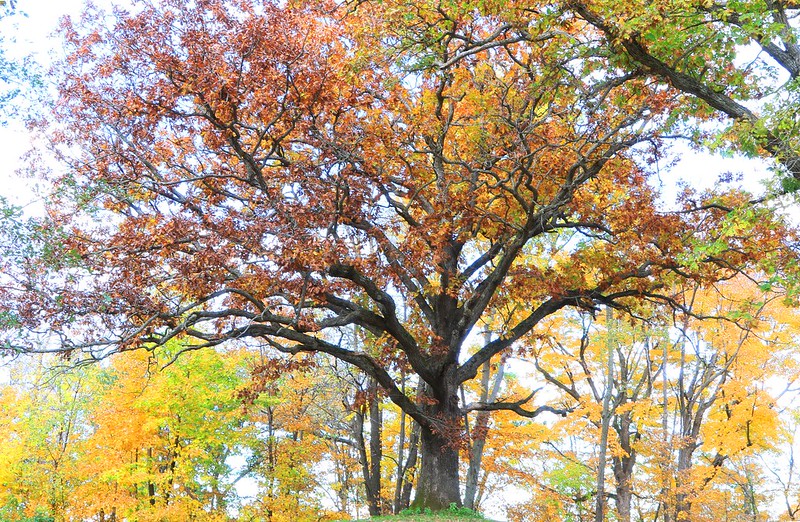

Quercus alba, commonly known as the white oak, is a deciduous-branching tree native to Eastern North America. It is found in forested habitats from sea level to elevations over 6500 ft.
Red Alder – Alnus Rubra
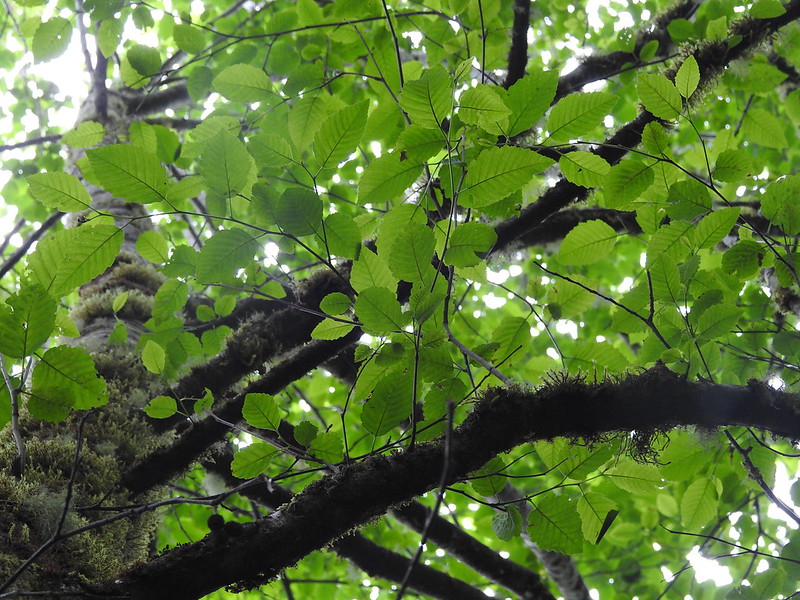

Alnus rubra, commonly known as the red alder, is a deciduous-branching tree that grows in wetlands and along streams throughout temperate North America. It has been introduced around the world for use in landscaping.
Green Ash – Fraxinus Pennsylvanica
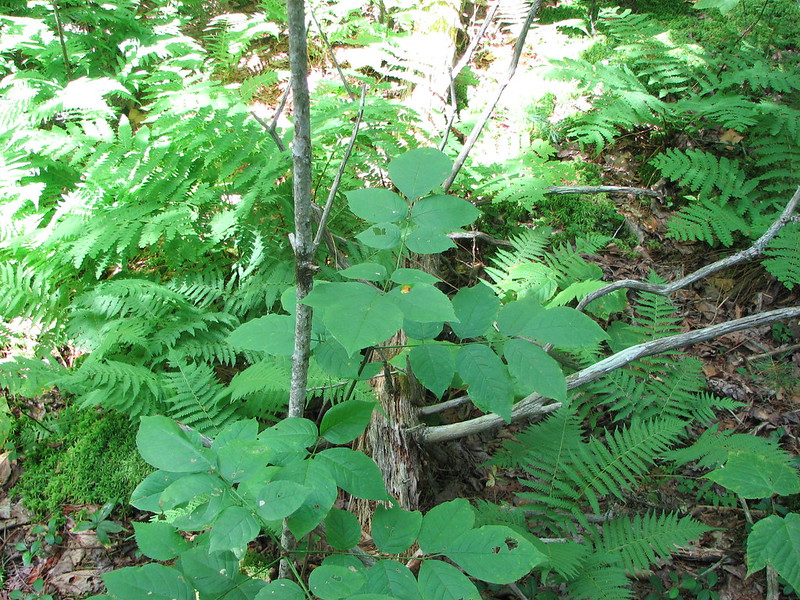

Fraxinus pennsylvanica, commonly known as the green ash, is a deciduous-branched tree that grows in moist habitats from sea level to 4939 ft, typically in forests but sometimes in open woodlands.
It is native to most of eastern North America, ranging from southernmost parts of Canada to the Midwestern states, with isolated populations farther west.
American Beech – Fagus Grandifolia
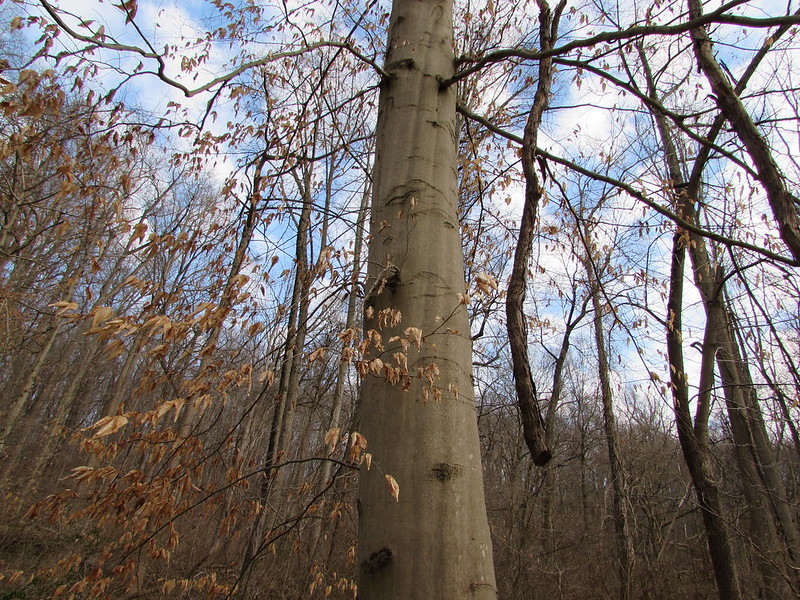

Fagus grandifolia, commonly called the giant beech, is a large deciduous coniferous tree native generally to North America, especially eastern North America. It is often referred to by its scientific name, Fagus grandifolia.
The bark is dark brown, smooth, and scaly. Leaves are alternate, simple, oblong, 1–3½ inches long, 2–4½ inches wide, with 3 distinct lobes.
Related: So Darn Delicious! 13 Different Types Of American Vegetables
American Basswood – Tilia Americana

Tilia Americana, commonly known as basswood, is a deciduous tree native to eastern North American forests, preferring wet soils. It is one of the dominant trees of lowland hardwood forests. In the United States, it is widely planted as an ornamental tree.
It is also used in landscape architecture. The leaves are opposite, leathery, 5–8 inches long and 4–6 inches broad; they have three rounded lobes on each leaf blade.
Paper Birch – Betula Papyrifera

Betula papyrifera, commonly known as paper birch, is a deciduous tree native to Eurasia and North America. Its range extends across Canada and the United States, where it occurs mainly in moist areas. Paper birch is very common in the boreal regions of both continents.
White Ash – Fraxinus Americana

The white ash, Fraxinus americanus, is a deciduous tree native to eastern North America, especially the Appalachian Mountains. It is widely naturalized elsewhere in the Northeastern U.S., such as in gardens.
The species was first described by Linnaeus in 1753. The tree’s foliage turns yellow in autumn. The fruit is similar to that of the blackberry, although somewhat smaller.
Butternut Tree – Juglans Cinerea
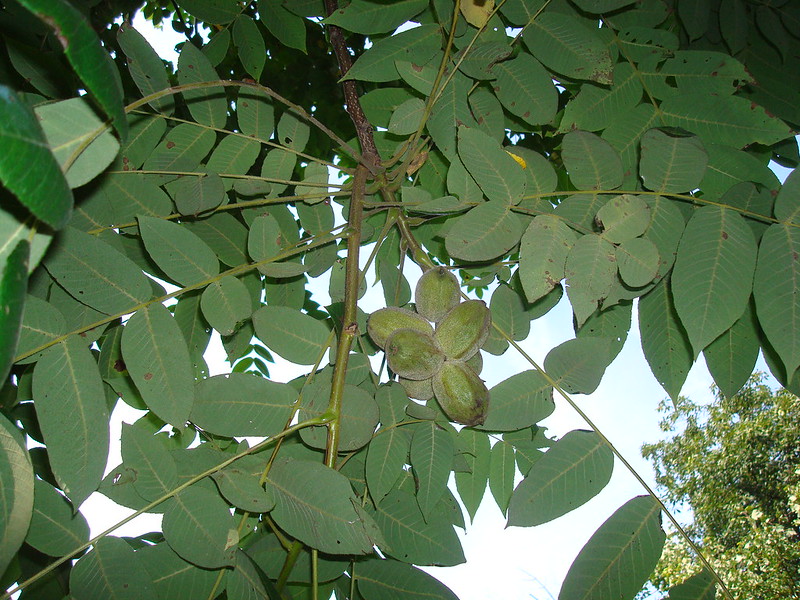

The butternut, Juglans cinerea, is a deciduous tree native to eastern North America, mostly in the Appalachians. It is widely cultivated as an ornamental tree because of its attractive fruits.
The leaves are compound, 6–12 inches long, 3–5 inches wide, and divided into seven leaflets. The flowers appear in early spring before the leaves. The fruit ripens in late fall or winter and is edible when raw. The seeds are eaten roasted like chestnuts.
Black Cherry – Prunus Serotina

Prunus serotina, commonly called the black cherry, is a deciduous-branching tree native to northeastern North America, primarily the Atlantic coast. It is often found growing along stream banks and other river floodplains.
Large colonies may form during periods of drought. The leaves are lanceolate, ovate, or linear, and arranged alternately on the stem.
The flower is pinkish purple, about ½ inch long, with five petals. Fruit is typically small, round, red, sweet cherries.
Black Cottonwood – Populus Balsamifera

Populus balsamifera, known as black cottonwood, is a decidable tree native to northern temperate North America. It ranges from Alaska to Labrador, south to Mexico and Central America. It is a medium-size tree reaching 98 feet tall.
The trunk can grow up to9 inches in diameter. The bark has lenticels, which allow water vapor to escape. Leaves are deciduous, oval, 2.5–6 inches long, usually asymmetrical.
Cucumber Magnolia – Magnolia Acuminata
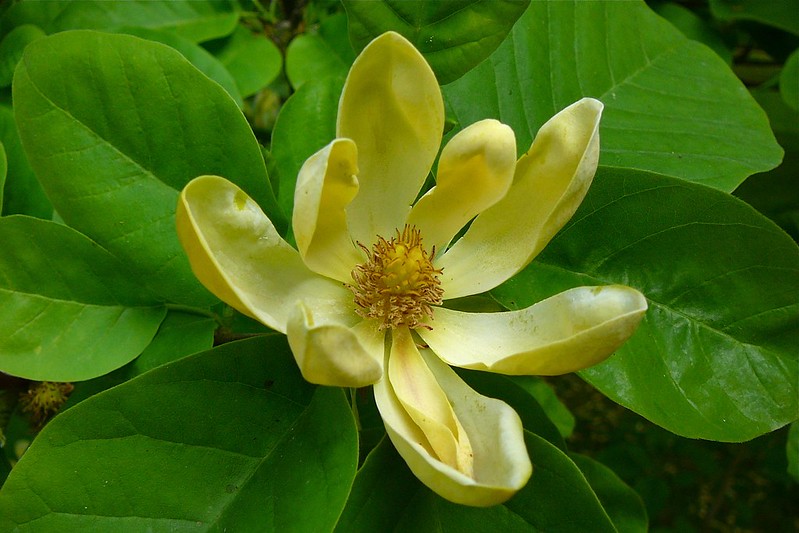

Magnolia acuminata is a deciduous-branching tree native to North America, occurring from Newfoundland westward to western Montana.
It prefers well-drained soil and full sun. It is sometimes considered a weed since it grows vigorously in disturbed or abandoned land. The cucumber magnolia is widely grown for its fragrant pink and white flowers in late summer.
Hackberry – Celtis Occidentalis

Celtis occidentalis, commonly referred to as hackberry, is a deciduous-branched tree native to North America. It is widespread throughout the continent, ranging from the plains to mountains and ocean shores.
In addition, it is one of only two trees (the other being the bald cypress) capable of surviving temperatures below freezing. It has been planted successfully across Europe and Asia. Its wood is used to make furniture and musical instruments.
Shagbark Hickory – Carya Ovata
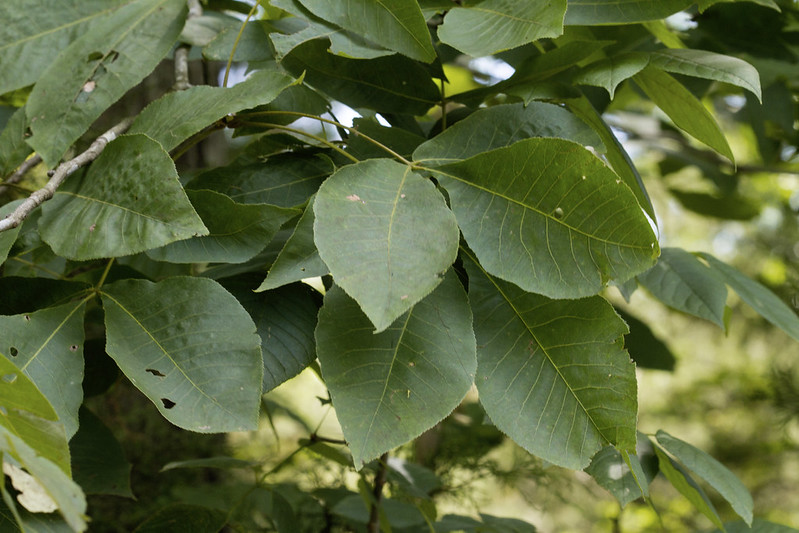

Carya ovata, also called shagbark hickory, is a deciduous tree native to eastern North America, mainly along the Atlantic Coast. It occurs from Nova Scotia to Florida. It is most common between the coastal plain and piedmont regions.
This species is an important source of food for wildlife such as deer, wild turkeys, and raccoons. It produces nuts that have high levels of fat content.
Black Locust – Robina Pseudoacacia
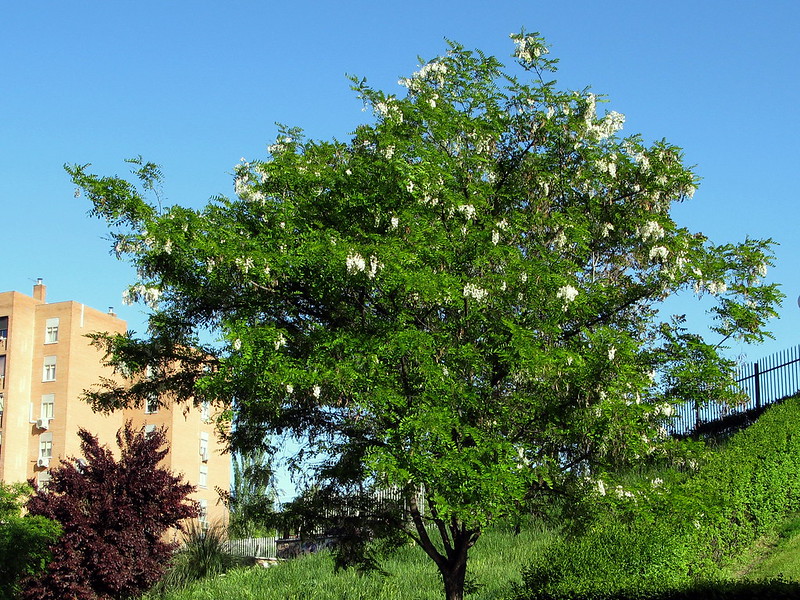

Robina pseudoacacia is a deciduous shrub native to Eastern North America; it is widely cultivated as an ornament. It was first described by Linnaeus in 1753. The foliage has opposite pairs of dark green, oblong leaves.
The flowers are produced in clusters at the ends of branches. They are pale blue, 1 ¼ inch long, with five petal-like sepals. It bears fruit that is edible but bitter. It also produces abundant seeds that float in the wind.
Osage Orange – Maclura Pomifera
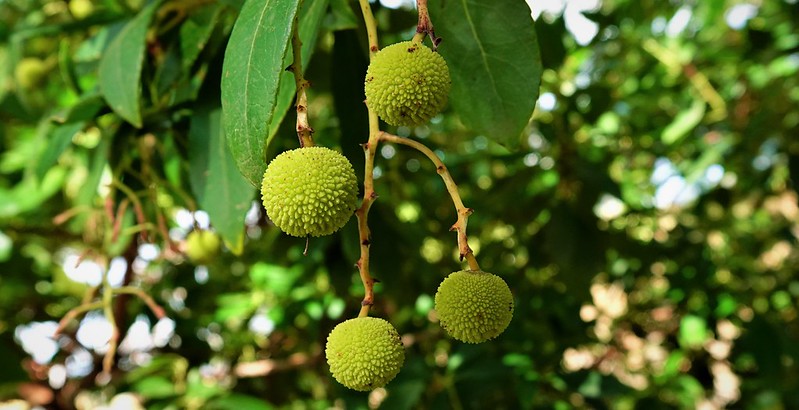

Maclura pomifera, commonly called osage orange, is a deciduous tree native to eastern North American prairies. It is widely naturalized elsewhere in the world. The tree reaches heights of 40–80 ft. and develops thickets.
The leaves are alternate, entire, 5–12 cm long, dark green above, lighter underneath. The flowers are yellow, 3 mm wide, borne in pendulous panicles. The fruit is a large, rounded drupe that is orange, 1.5–3 inches in diameter, containing a single seed.
Royal Paulownia – Paulownia Tomentosa
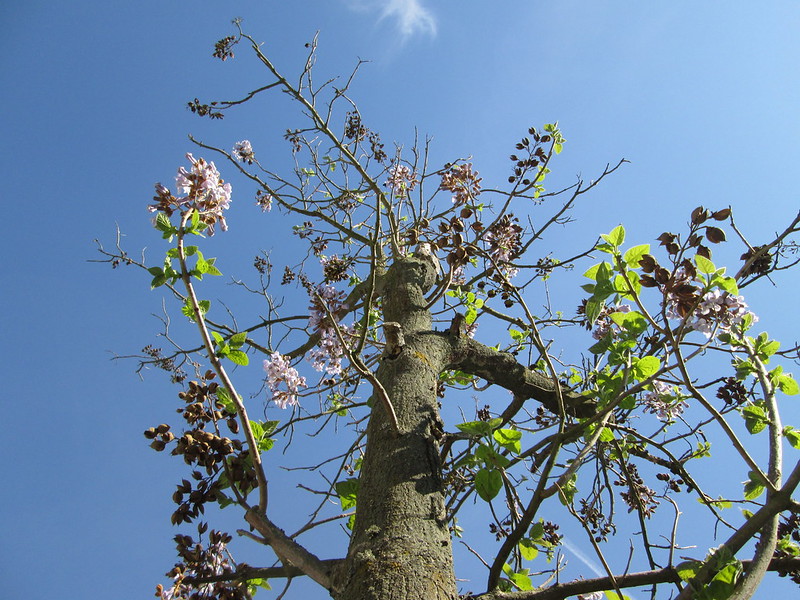

Paulownia tomentosa is a deciduous coniferous evergreen tree found on rocky slopes in mountainous areas of Canada and the United States. It is characterized by its very dense crowns of stiffly erect needle-shaped branches.
It reaches heights of 60 m and forms thickets. The branches bear small, scale-like leaves, which grow densely in tufts. The small, inconspicuous flowers appear in spring before new shoots emerge.
Pecan – Carya Illinoinensis
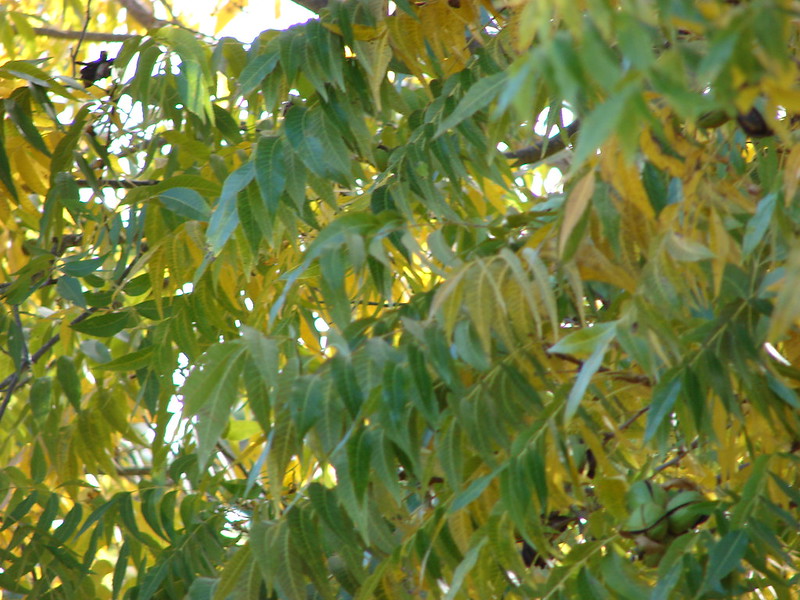

The pecan is a large tree, growing up to 30 meters tall, with a trunk diameter of about 2 meters. It can live for hundreds of years. With age, the outer bark becomes soft and grayish brown. When mature, the pecans produce edible fruits, known as “hullnuts”.
These nuts contain more oil than any other nut. The hard inner shell of the hullnut contains a sweet kernel. It grows best in well-drained soil in full sun or partial shade.
Redbud – Cercis Canadensis
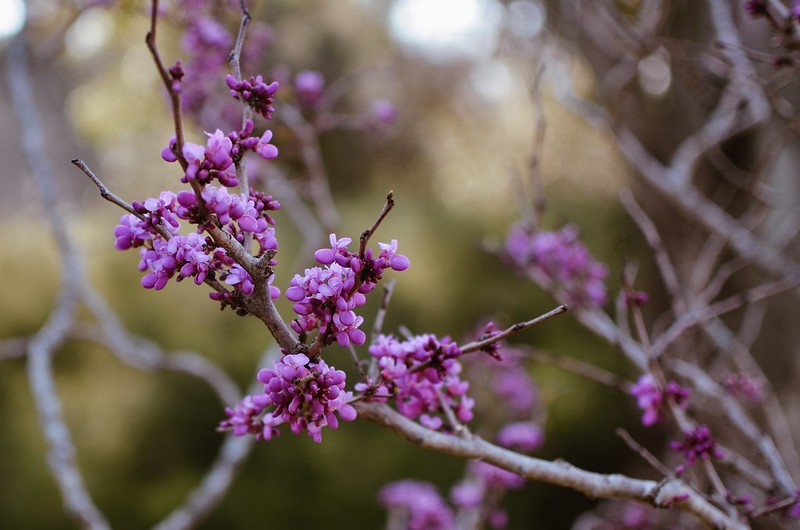

A deciduous tree native primarily to the Appalachian Mountains and Ozarks, redbuds are among the earliest spring bloomers in the Northern Hemisphere, often flowering before snow melts.
The leaves are alternate and compound, composed of three leaflets, each leaflet divided into three lobes. Each lobe is made up of three leaflets, also divided into three segments.
Sourwood – Oxydendrum Arboreum
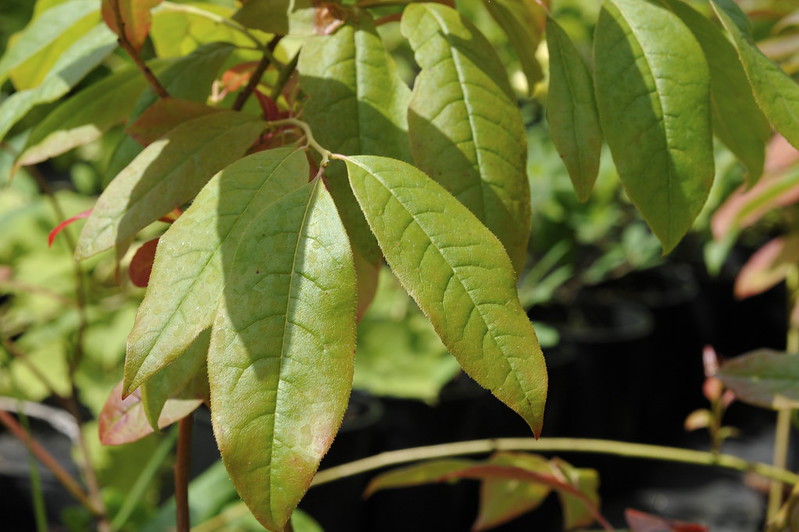

Oxydendrum arboreum is a deciduous forest tree native to eastern North Carolina, Virginia, and West Virginia. Its range extends south to Georgia and north to New Jersey. In all cases, this is a rare tree, confined to moist woodlands.
The leaves are opposite, simple, oval, pointed, finely serrated, and bright green. The flower is a star-shaped cluster of tiny white blossoms, 1/2 inch across. The fruit is a round berry, pink when ripe, 1/4 inch in diameter.
Final Thoughts
That is all for this article, we hope that you have enjoyed learning about trees that you might see in America. There are plenty more where this came from. Because of this, there is always something new to learn about the wondrous variety of trees all around the world.