Japan is an interesting country when it comes to its geography. Made of thousands of islands, different types of Japanese trees have a lot of the flora and fauna that live in this part of the world are unique to these isolated pockets of land and life.
However, because it is off the coast of another ecologically diverse place, South East Asia, it also receives plenty of new life both by natural and by unnatural means.
And that’s not even touching on how many plants have been brought to and from the country thanks to trade and other peoples!
With so many different forms of plant life, it can be hard to keep track of it all.
That’s why we’ve compiled this list of some of the most iconic trees that you can find in Japan today, both native to the area, and those that have come from further afield but have made a home for themselves nevertheless.
There’s plenty to cover, so let’s get started!
1. Monarch Birch
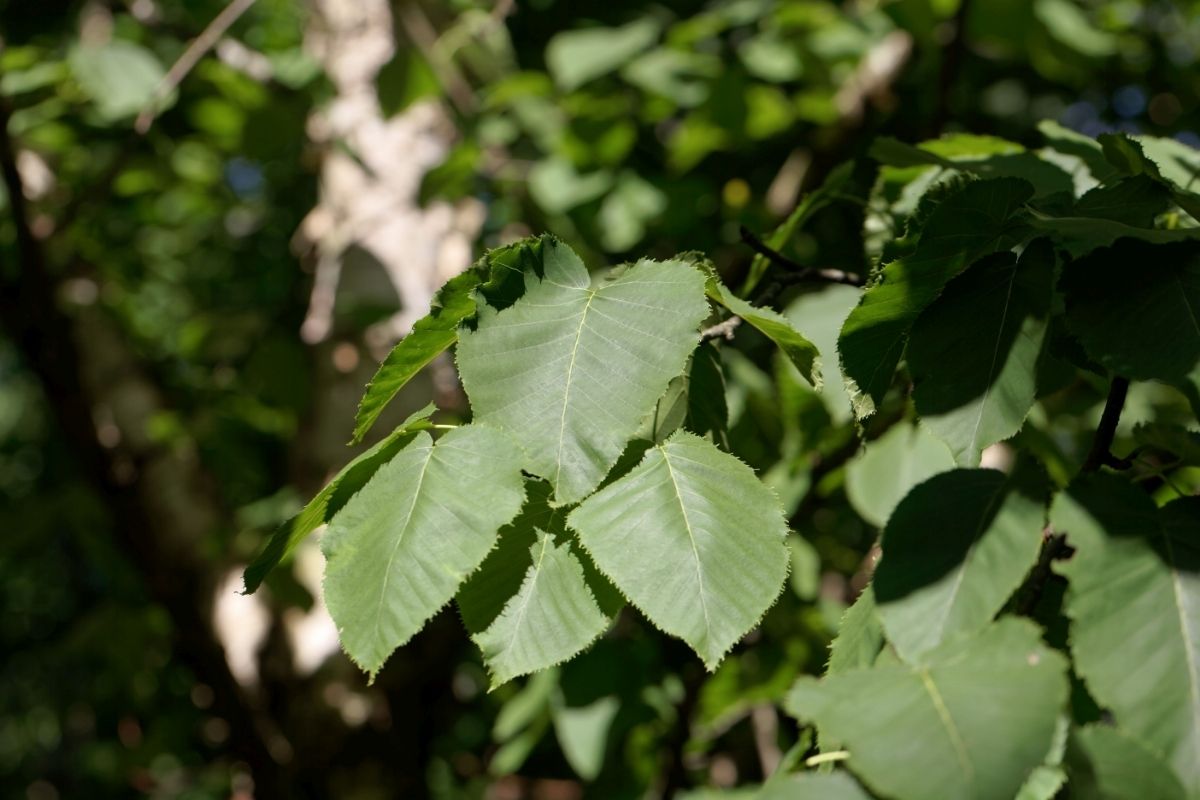

A native tree of the Northern and Central Islands of the country,
Monarch Birches grow mainly along rivers and streams. This species of the birch tree is called Japanese white birch.
The leaves of this tree are smooth and shiny. The trees usually live between 40 and 100 years.
In Japan, there are many types of birch trees such as red birch, black birch, silver birch, and Japanese white birch. Monarch birch trees grow up to 30 meters tall.
Japanese white birch trees grow well in wetter areas. This tree does not grow well in a dry area. The roots of this tree do not grow deep into the ground.
Therefore, it is not suitable for use in urban areas.
Japanese white birches are used for construction purposes. They can also be used for landscaping. These trees are often planted near ponds and lakes, and the seeds of the Japanese white birch are edible.
The pollen of this tree contains proteins, vitamins, minerals, amino acids, and lipids. It also contains calcium, iron, potassium, and magnesium.
2. Chinese Elm
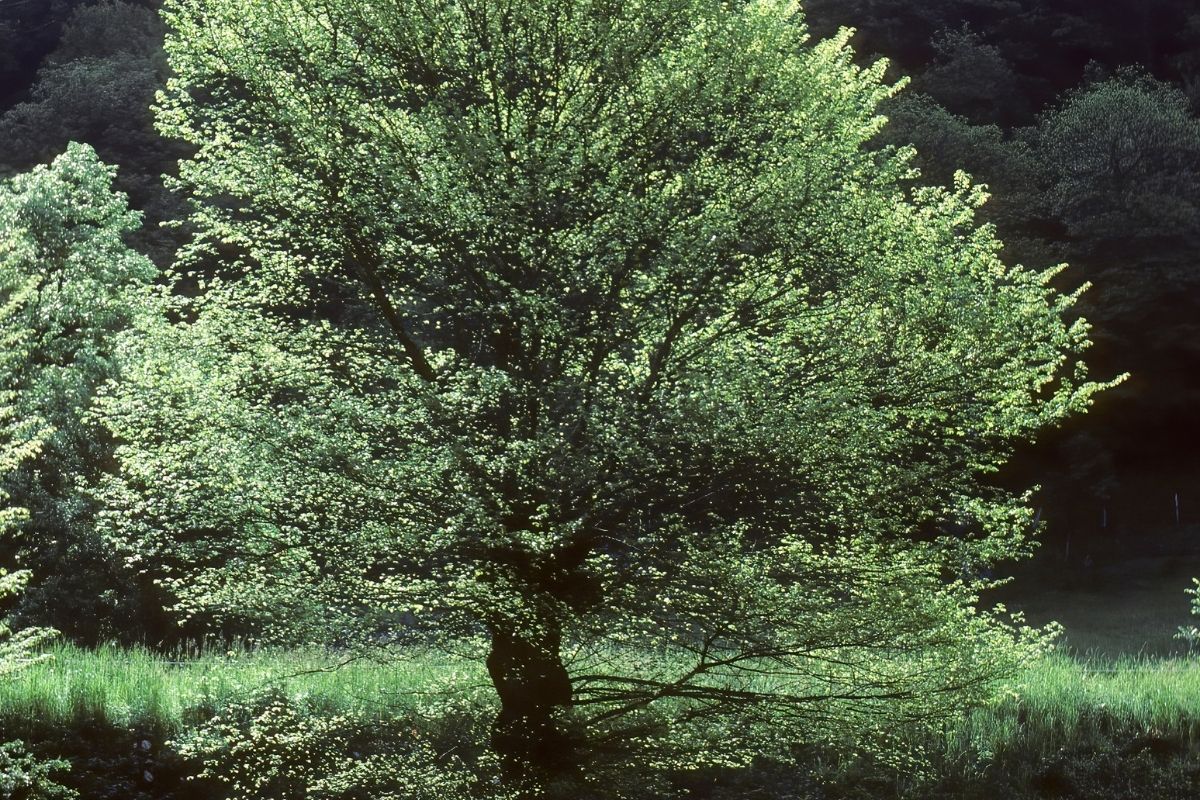

Although not a native of Japan, Chinese Elm trees have been grown in and around Japan for centuries,
partly due to their distinct leaves and bark patterns, but also because it is considered an excellent tree to grow and cultivate as part of the tradition of bonsai plant gardening.
It is considered a perfect specimen for newcomers to the hobby and art to start training their skills with, such as pruning, shaping, and general care and maintenance.
Because of the popularity of this art in Japan, it is often seen as a symbol of Japanese culture and is widely planted in many cities and towns across Japan.
Since it is a deciduous tree, its flowers bloom in early spring. However, its seeds ripen in late autumn. Therefore, the trees do not produce fruit every year.
This tree grows well in areas where there is little or no frost. It does not tolerate waterlogged soil.
Its roots grow deep down in the ground. Thus, the soil must be excavated to remove the roots before planting.
Afterward, the area should be compacted to minimize water infiltration.
The ideal temperature for growth is between 20 degrees Celsius and 25 degrees Celsius. As the weather gets colder, however, the tree will grow slower.
3. Japanese Spruce
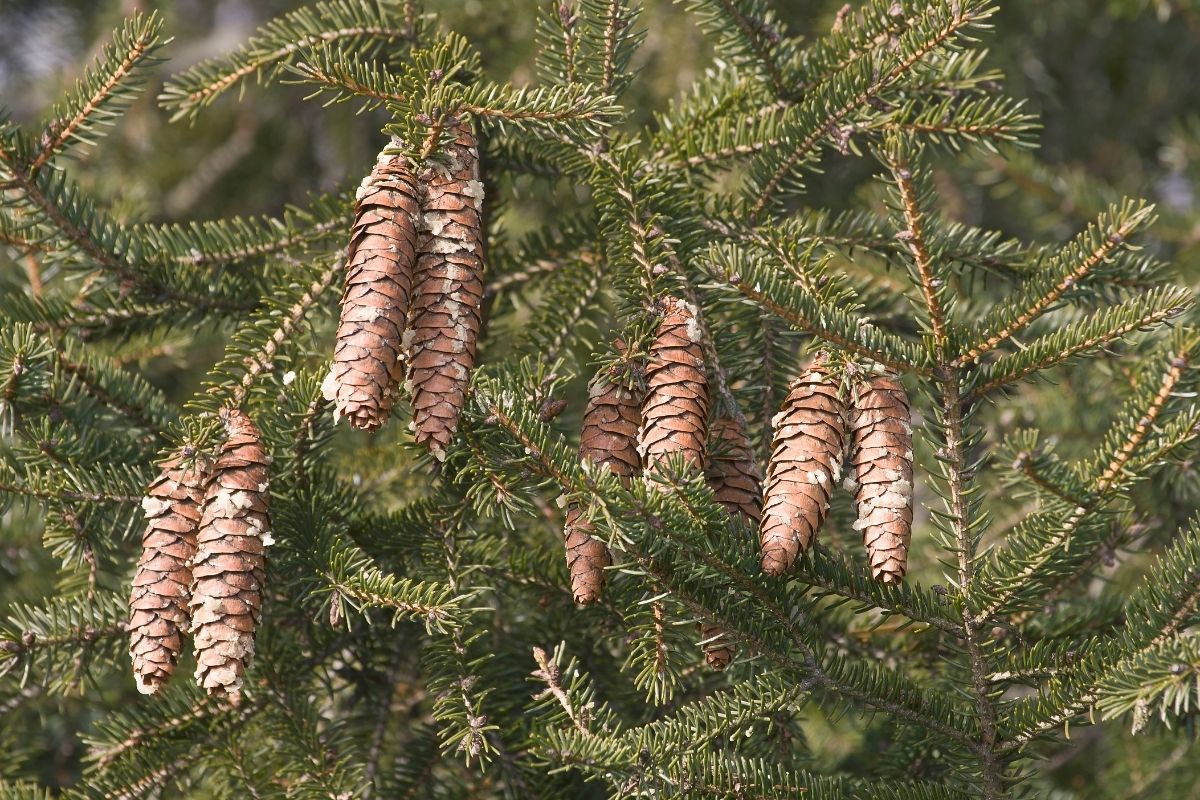

Japanese Spruce is a tree native to the islands of Japan.
Japanese spruce is an evergreen coniferous tree belonging to the pine family Pinaceae.
Conifers are characterized by needle-like leaves and cone-shaped structures known as cones, which contain seeds.
The needles are arranged spirally along with the shoots and twigs. Each shoot bears several needles.
This species of spruce can grow up to 20 meters tall, with some growing even as tall as 25 meters. The branches are usually straight and stiff.
They are used as garden ornamentals and for building materials.
However, in recent years, the tree is only found in Honshu, Central Japan, in the Akaishi and Yatsugatake mountains.
Despite this rarity, the Japanese spruce is one of the most popular tree species in Japan.
Its popularity with many botanical and gardening enthusiasts stems from its ability to withstand harsh winter weather conditions and its relatively fast growth rate.
4. Japanese Cherry Blossom
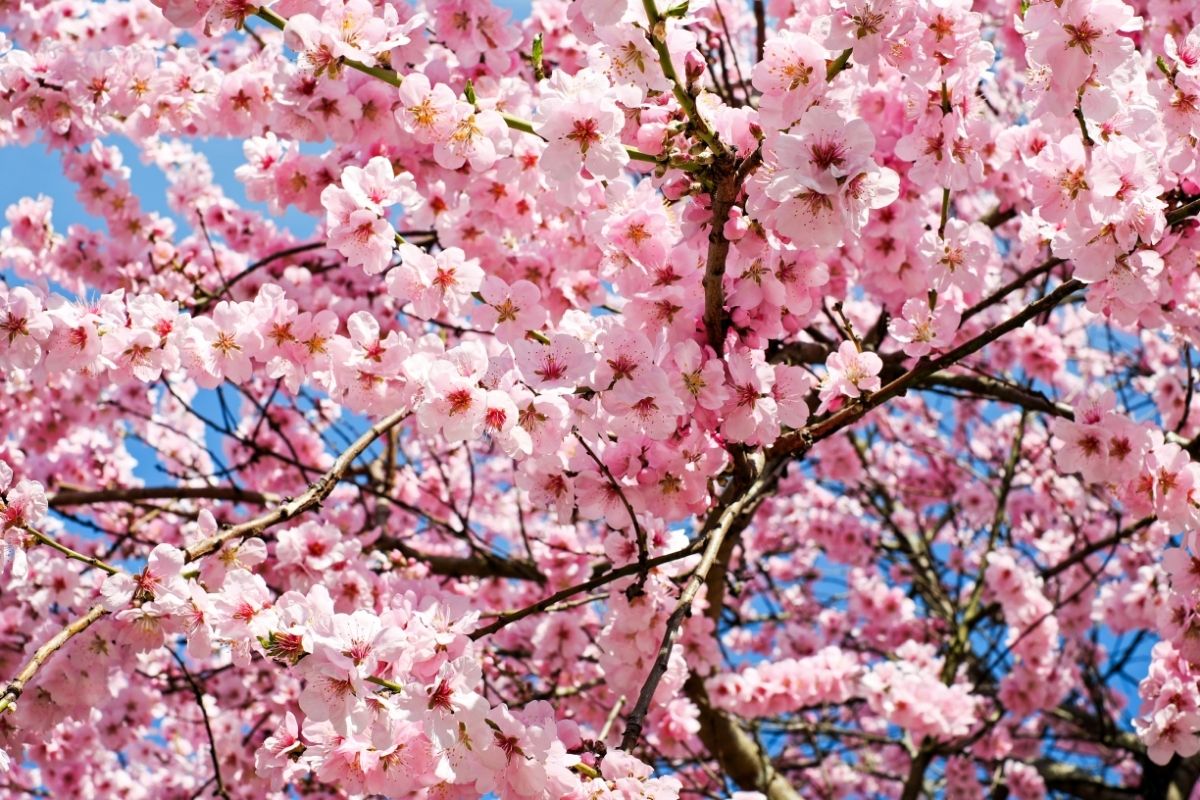

One of the most iconic trees from Japan, the Cherry Blossom is synonymous with the country’s flora.
Flowering into their iconic flowering display early in the year, cherry blossoms are one of the most popular spring events in Japan, and they are celebrated across the country every year.
They represent the hope and joy of spring, and people visit the areas where they bloom each year to experience the beauty of nature.
These beautiful flowers open early in April and last until late May.
To reach the peak of their flowering season, many varieties of trees are planted along rivers and streams so that they provide shade for the blossoms.
Some of the most famous places to view the cherry blossoms include the Kamogawa River in Tokyo, the Suzaki river in Kyoto, and the Hozugawa river in Osaka.
People travel from across Japan and other parts of the world to see the spectacular blooming of these flowers.
5. Japanese Zelkova
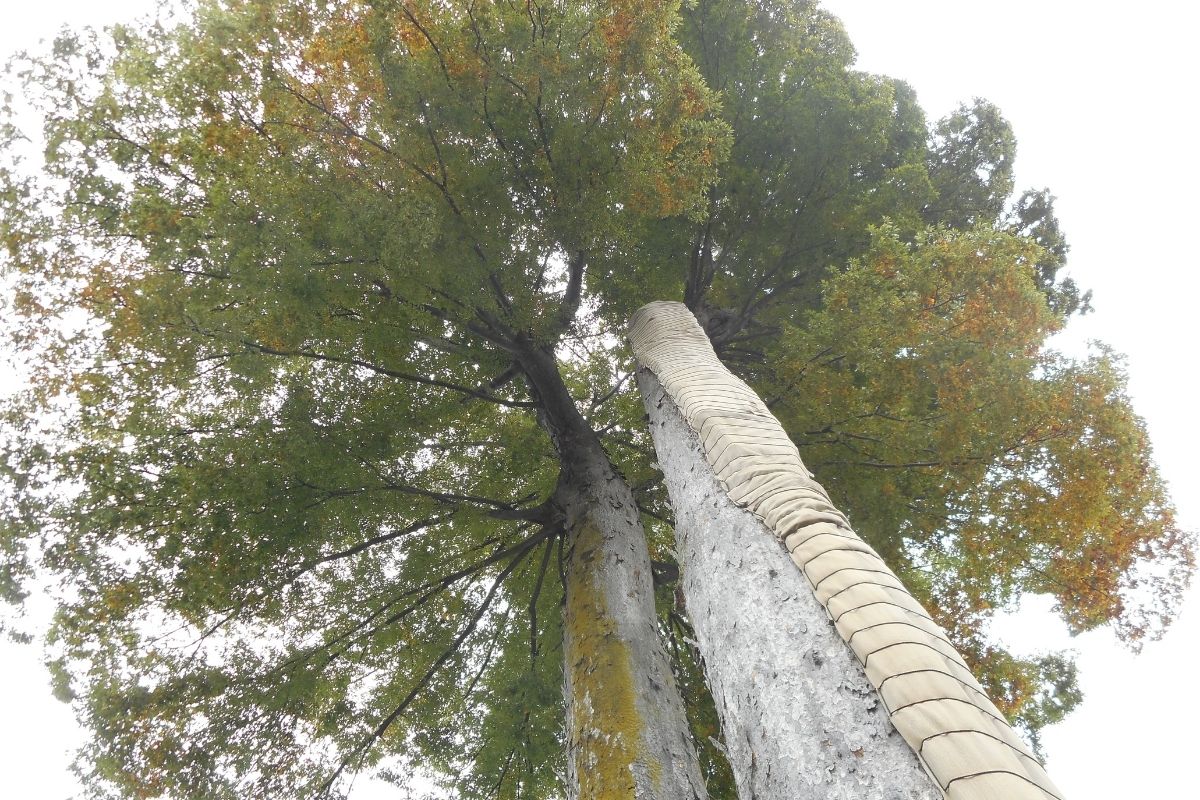

Zelkova trees are native to China, Korea, Japan, and Kazakhstan. They grow well in cold climates, especially in the Northern Hemisphere.
Zelkova trees are often used for ornamental purposes, such as for street trees, park trees, and landscaping.
The Japanese Zelkova tree has an incredibly long lifespan, able to live for hundreds of years if left uninterrupted.
There is a famous example of a Zelkova tree in Osaka that has been growing there for over a thousand years!
There are many different types of Zelkova trees growing in Japan. Each type has unique characteristics.
Historically, this tree was mainly used for house construction.
Wood is cut into planks, beams, posts, and so forth. For example, wooden fences, bridges, gates, doors, and steps are made from Zelkova wood.
Wooden tables, chairs, beds, desks, and cabinets are also made from this wood.
6. Sawara Cypress
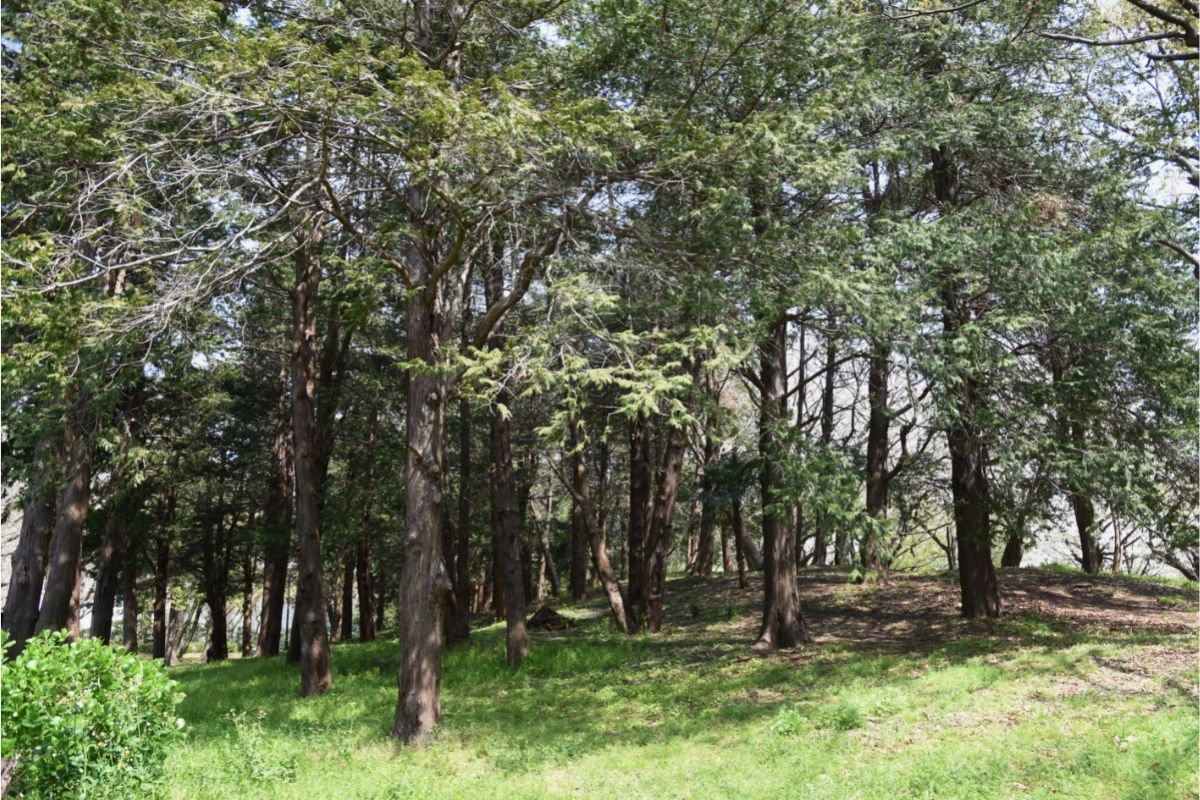

Sawara Cypress trees are native to Japan. They are found mostly in the north part of Japan where there are many mountains and forests, where they grow in sandy soil along rivers.
The tree has been used in Japanese culture since ancient times.
It was mentioned in the Heian period record “Kokin Wakashū” (Compendium of Ancient Matters) written by Fujiwara no Takafuji.
They grow well in areas where it gets cold. The main characteristic of the sawara cypress is the beautiful sprays of leaves that this tree produces as it grows.
In early modern Japan, people believed that the tree had healing properties. People came from far away to see the tree and take its leaves.
Today, the tree has gained popularity among those who appreciate the traditional floral nature of Japan.
Because of its unique shape and color, the tree is often featured in art exhibits and photographs.
7. Japanese Red Pine
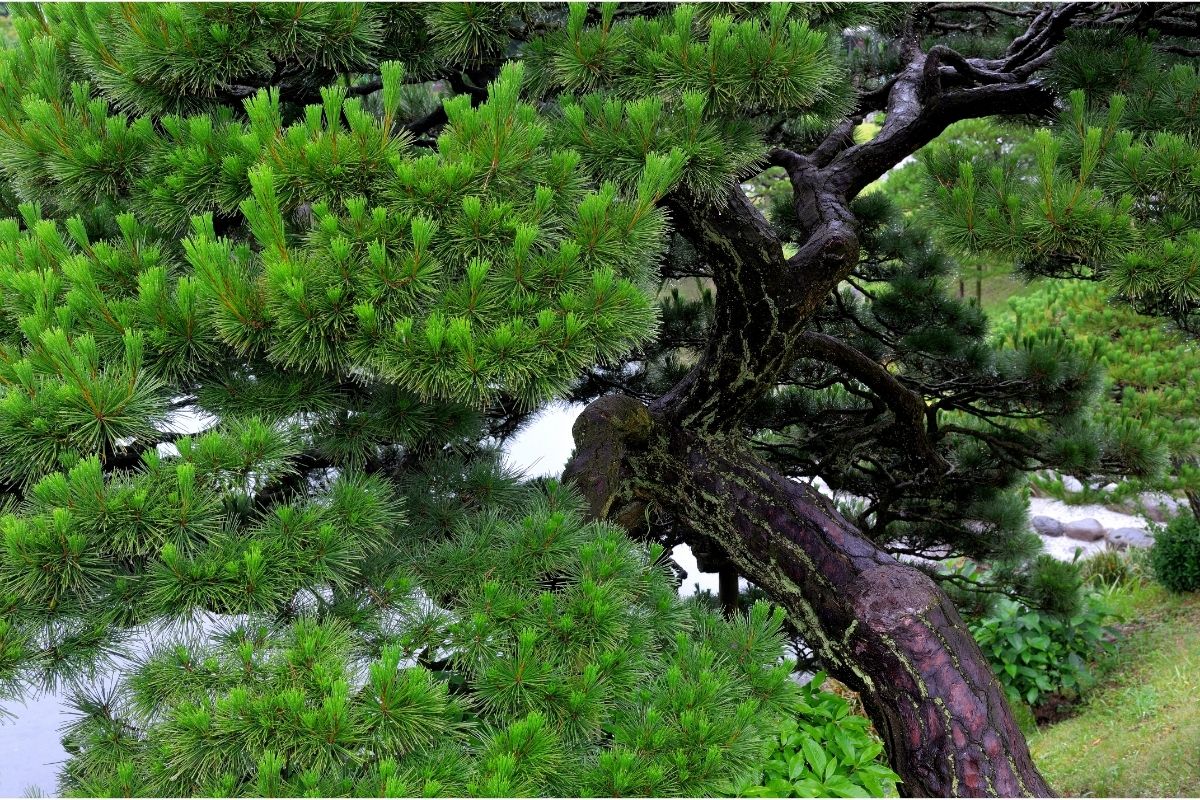

Japanese red pines grow well in many climates, especially temperate climates. They do best in full sunlight, though they tolerate partial shade too. The soil pH should be between 6 and 7.5.
A well-drained site is best. Pests such as scale insects cause damage to trees. These pests can be controlled by spraying insecticides.
Japanese Red Pine seeds germinate readily under moist conditions. Germination is at its slowest in cool temperatures. Seeds must be planted no later than March 15th, or April 1st in colder areas.
After planting, seedlings should be watered daily until they sprout. Seedlings need to be transplanted after three to four weeks.
Transplanting takes place at least two weeks before the last expected frost. Transplants should be placed at a depth of 8 inches and spaced 18 inches apart.
8. Okinawa Pine
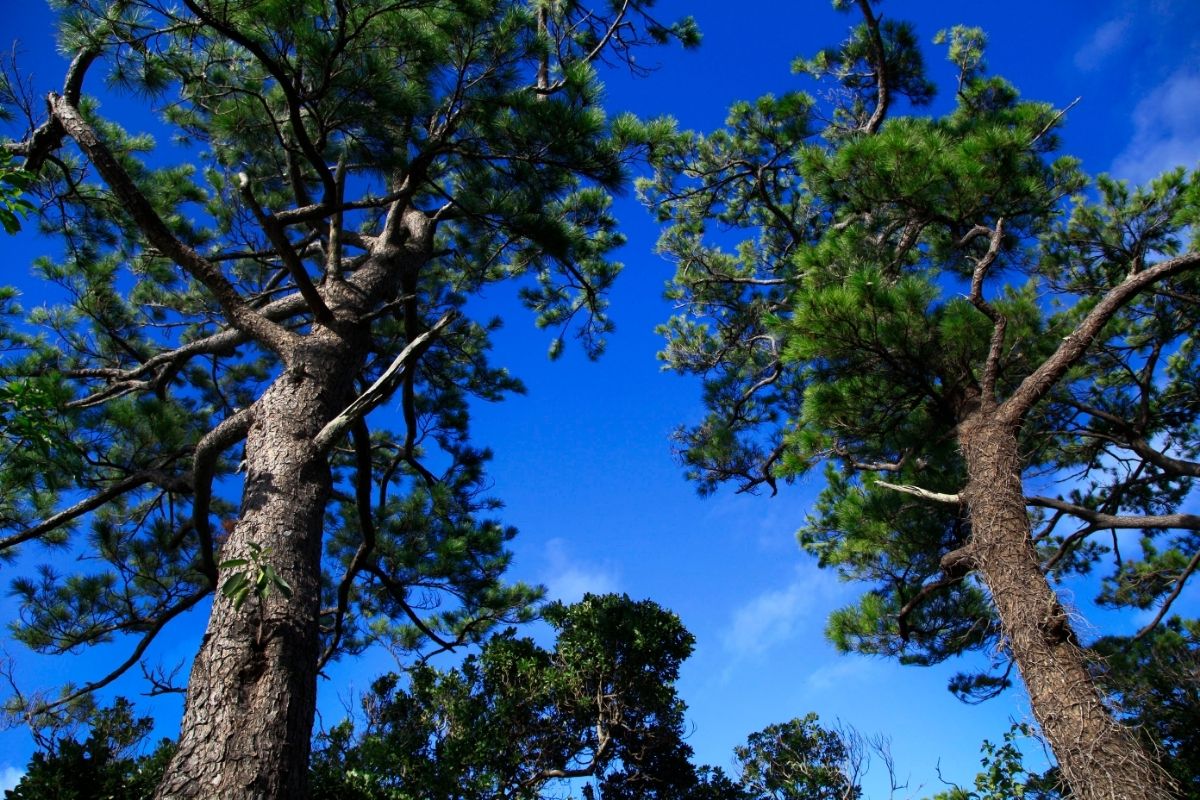

Okinawa pine trees grow in large forests in Japan and have done so since the Edo period. These trees look similar to Japanese spruce trees, but they are different.
The Okinawa pine has a higher temperature tolerance than the Japanese spruce tree, so they can live in areas where the temperature drops below -15°C.
In the past, Okinawan people used to use their trees as firewood. Their wood was very soft and highly flammable and could burn easily.
However, the Okinawan pine is still grown as a commercial forest plantation in Japan. It is mainly used for paper production and other uses.
9. Japanese Beech
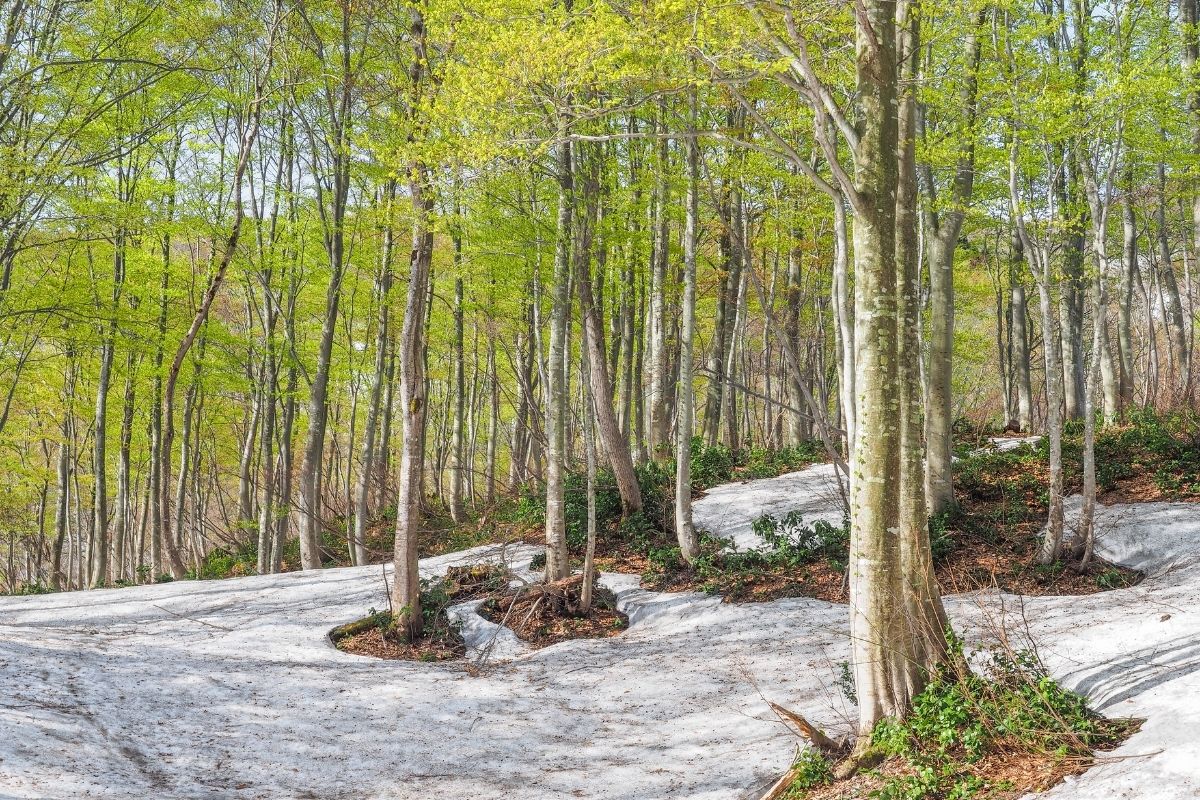

The Japanese beech tree shares many similarities with other beech trees that can be found across the world.
A native of the Japanese islands, this tree can grow up to 35 meters (or 115 feet) tall in the largest examples.
Many people think that the Japanese Beech originated in Europe. However, this is false. As we already established, whilst related to other beeches, this tree is endemic to this part of the world.
Today, the Japanese Beech is widely spread throughout Japan. People use them to decorate gardens and parks.
The Japanese Beech is a deciduous tree. It has thick branches. Its trunk is usually round. The bark is smooth. The leaves are oval-shaped. They come out between March and May. They are dark green.
In June, the leaves begin turning yellow. Then, they change into bright orange-yellow colors. Finally, they turn red in October. The leaves die in November.
When the Japanese Beech is fully matured, it has a spreading crown. It has many branches.
Conclusion
As you can see, many trees call the islands of Japan their home. With such a reputation for beautiful plant life, it’s no wonder that so many people view Japan as a place of natural beauty.
Editor’s Recommendations
17 Stunning Yellow Orange Flowers (With Pictures)
Here Is Why Your Peace Lily Flowers Are Turning Brown & How To Fix It Fast!