In this article, I will discuss the primary distinguishing features between palm and coconut trees, which will help you tell them apart. Maybe it’s not as hard as you’re making it out to be. Let’s talk about coconut tree vs palm tree.

Photo Credit While all palm trees share many characteristics with coconut trees, only some palm trees actually bear coconuts.
Are you familiar with the differences between a palm tree and a coconut tree? They are frequently confused with one another, and for a good reason! There is a widespread misunderstanding that palm trees always produce coconuts as their fruit. Unfortunately, that’s not the case. So, you must be wondering how different or alike these two trees are.
A few telltale signs can be used to differentiate a coconut palm from a non-coconut palm. The leaves are the key differentiating factor. The leaves of a palm tree are shaped like a fan, whereas those of a coconut tree are broad. The coconut tree only yields coconuts, while palm trees produce a variety of fruits and palm oil.
In short, all coconut trees are palm trees, but not every palm tree is a coconut tree!
Still confused? Keep calm and read on.
Palm Trees
The palm tree is, without a doubt, one of the most well-known types of trees found all over the world. This tree has been featured in many of our favorite media works.
For instance, you can bet your bottom dollar that there will be palm trees present if a scene involves a beach. The term “palm tree” can actually refer to any tree categorized under the Arecaceae family of plants. There are about 230 different families within it, and it has more than 3,000 different species that can be found all over the world.
And even though palm trees can be found throughout the world, they thrive best in tropical regions. In the US, they are commonly found in Florida and California. The palm family contains only one Cocos nucifera species capable of producing coconuts.
However, this does not necessarily imply that none of the other palm trees produce any fruit at all. The palm trees described below are examples of palm trees that produce fruit.
Fruit-Bearing Palm Trees
Coconut palms are just one example of a palm tree that produces food. These fruits are abundant in tropical areas, giving them great agricultural value. So, let’s take a look at some other common palm trees that also produce fruit.
The Coconut Tree (Cocos nucifera)

Photo Credit Cocos nucifera, also called coconut or coconut palm, is native to the western Pacific islands.
The coconut is arguably the most recognizable palm fruit. Various individuals categorize coconut as a fruit, nut, and seed. However, in terms of its botanical categorization, it is a fruit. The flesh of the coconut has three distinct layers.
The layer at the very top is smooth, the layer in the middle is fibrous, and the layer in the very center of the coconut, known as the endocarp, is typically eaten together with the white pulp.
To prepare coconuts for retail sale, the fibrous layer in the middle and the smooth layer on top are cut away. What is left is the endocarp layer, which is a circular layer that is dark brown in color and contains the meat of the coconut.
Related: Coconut Vs. Palm Trees: Top Similarities and Differences You Need To Know
The Date Palm (Phoenix dactylifera)
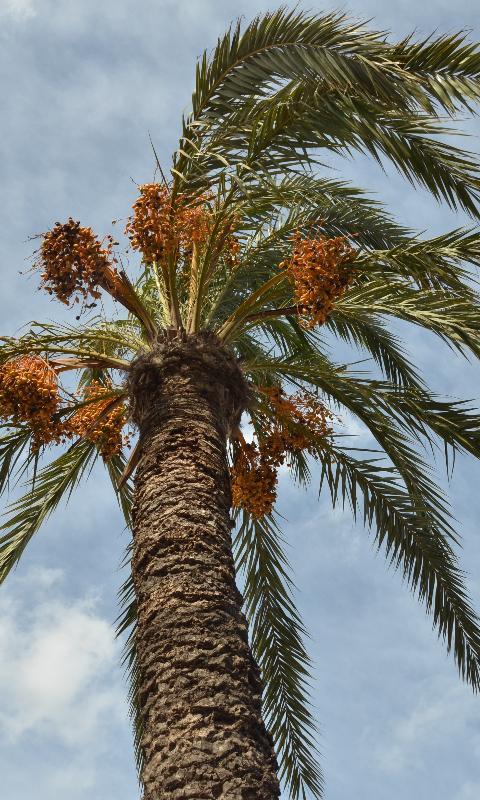

Photo Credit The date palm, Phoenix dactylifera L., is a dioecious perennial native to North Africa and the Middle East.
The date palm (Phoenix dactylifera) is a prolific tree that bears tasty dates like the Medjool. However, some date palms are kept solely for their aesthetic value as ornamental plants.
However, even ornamental date palms, such as the Zahidi, which are primarily grown for their stunning look, yield date fruits that can be eaten. Moreover, these delicious dates don’t have any seeds inside them.
When these dates have reached their peak maturity, they turn a golden yellow color and become exceptionally tasty. Unfortunately, due to the lengthy storage period, they are dry and dark brown by the time they reach the market.
The Palm Acai (Euterpe oleracea)

Photo Credit The aça palm (Euterpe oleracea Mart.) is native to South America and produces edible black-purple fruit.
Acai berries are the fruit of the acai plant. These berries are considered to be superfruits due to the high levels of antioxidants and other healthy ingredients that they contain. In many subtropical climates, you can find these berries growing wild.
Euterpe oleracea grows rather large after a few years and starts to produce acai berries. When fully mature, acai berries take on a deep purple color and the look of blueberries.
The Wine, Jelly, Or Pindo Palm (Butia capitata)

Photo Credit Native to the Brazilian states of Minas Gerais and Goiás is the jelly palm, or Butia capitata.
The wine palm, also known as Butia capitata, produces fruit that is not only palatable but also sour and sweet, and it is commonly utilized in making jellies and wines. In addition to its natural habitat in Brazil and other arid parts of South America, the tree is also cultivated in certain parts of California as an ornamental plant for the state’s landscapes.
The clusters of yellow fruit are reminiscent of enormous bunches of grapes. Some people chew it for the nectar and discard the fibrous parts because the fruit is fibrous when eaten raw.
The Peach Palm (Bactris gasipaes)

Photo Credit The palm species Bactris gasipaes is endemic to the humid forests of Central and South America.
The peach-palm fruit, which is high in carbs, dietary fiber, and vitamins A, B, C, and E, is a valuable source of food in various parts of Central and South America.
The fruit of the peach palm is not a true peach. It doesn’t taste very pleasant when ripe and is therefore cooked before eating. The fruit is about the size of a date and, depending on the type, appears yellow or red once ripe.
Related: Madagascar Palm Tree: The #1 Care, Propagation, and Watering Guide
The Palmetto Or Saw Palm (Serenoa serrulata, Serenoa repens)

Photo Credit The palm species Bactris gasipaes is endemic to the humid forests of Central and South America.
Saw palmetto is a dietary supplement that is derived from the fruit of the saw palm tree, often known as the palmetto tree. Saw palms are most commonly located in Florida due to the state’s warm temperature, which is suitable for the growth of these trees.
Native Americans used the berries as a source of food and medicine, and early immigrants used them as a way to stave off starvation. When they have reached their full maturity, the berries have a sweet aroma, and their color ranges from blue to virtually black.
African Palm (Elaeis guineensis)

Photo Credit A palm species that is commonly known as oil palm but is also known as African oil palm or macaw-fat.
Palm oil is obtained by pressing the fruit of the Elaeis guineensis palm tree, which is native to Africa. Palm oil can be found in a wide variety of products, including packaged bread and biodiesel fuel.
Palm oil accounts for more than one-third of all vegetable-based oils consumed on a global scale, making it one of the components found in packaged goods that are utilized the most frequently. Palm oil can be broken down into two distinct categories or varieties.
The pit of the fruit is where palm kernel oil, which is of a superior and more pricey quality, is produced. In contrast, the fruit is the source of low-quality crude palm oil.
Coconut Palm Trees
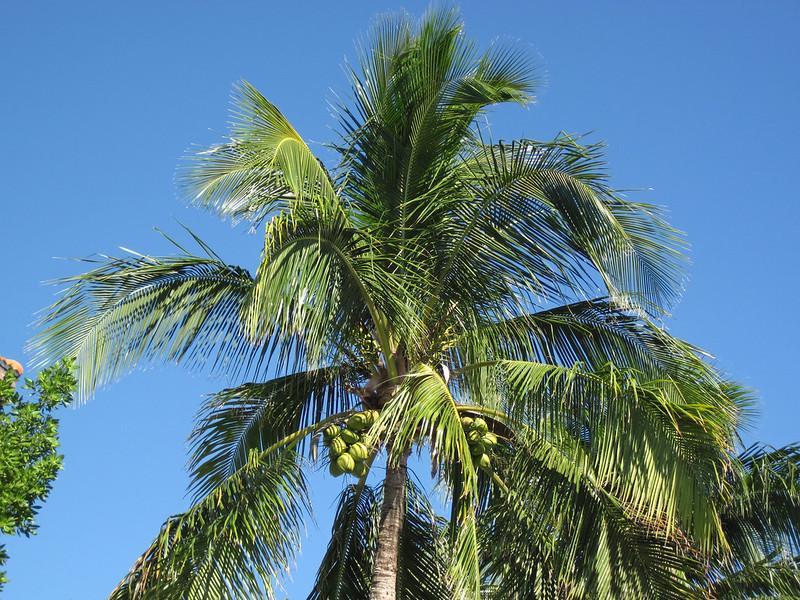

Photo Credit This remarkable palm tree stands tall and alone; its broad, glossy pleated leaves stand out.
As was just stated, there is only one palm tree capable of producing coconuts, and that is the Cocos nucifera. However, there is a wide range of coconut palms available.
Some of the coconut trees are relatively tall, reaching heights of between 60 and 100 feet, while others are pretty small or dwarf in size (between 20 and 60 feet high). The following is a list of several kinds of coconut trees that can be found all over the world.
West Coast Tall Coconut
This variety of coconut is often referred to as the Common Tall Variety or the Ordinary Variety. These trees can thrive in any soil and produce between 80 and 100 coconuts annually.
East Coast Tall Coconut
Yet another towering coconut palm! It produces between fifty and seventy coconuts in a single year and thrives on the sand. They begin bearing fruit after approximately seven years of growth.
Macapuno Coconut
The Macapuno tree bears coconuts that are exceptionally good for one’s health. And these trees are most commonly found in arid and desert regions.
Maypan Coconut
The size of a Maypan coconut is what sets it apart from other types of coconuts. These coconuts are among the largest in size compared to other coconuts. In addition, the Maypan coconut is well-known for its delicious flesh and capacity to withstand chilly climates.
King coconut
These coconut trees grow in clusters of 30 and are native to Sri Lanka. The flesh of the coconuts that are produced by the king coconut tree has an orange color (not white). They are not very sweet, and in comparison to regular coconuts, they have significantly less sugar.
Malayan Dwarf Coconut
Malayan dwarf palm trees are relatively short, reaching a maximum height of about five feet. However, this specific kind of coconut palm holds the record for the most coconuts produced by a single palm in a calendar year (about 100 to 120 ).
Coconut Vs. Palm Tree
Once more, the coconut palm is merely one species of the larger genus of palm trees. Therefore, it might be challenging to distinguish between the two. Nevertheless, there are a few distinguishing features that you should keep an eye out for.
Leaf Shape
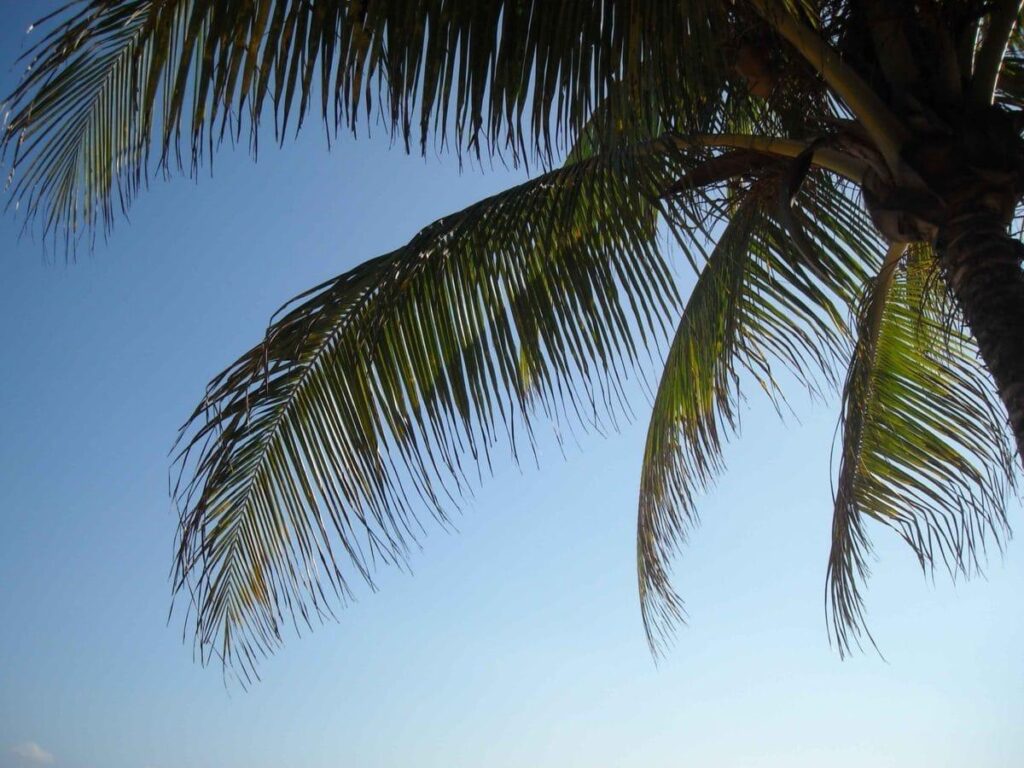

Photo Credit The leaves of palm trees are fan-shaped, whereas the leaves of coconut trees are more broad.
The leaves of any palm tree, including those of the coconut tree, are referred to as fronds, which is a generic name for palm tree leaves. The fronds have a central stem that branches out into a fan-like arrangement of leaves. In a broad sense, every palm tree’s fronds, also known as the leaves, can be classified into one of the following three subgroups.
- Pinnate Leaves
The structure of these leaves is similar to that of compound leaves, consisting of a stalk in the middle and smaller leaves on either side. These leaves are most frequently discovered on palms of the date, queen, and coconut varieties.
- Palmate Leaves
These leaves have lobes that radiate outward from a central point, creating the appearance of an open hand. Windmill palms, Mexican fan palms, and sugar palms are the kind of palms that are most likely to have these leaves.
- Costapalmate Leaves
These are fan-shaped leaves with a midrib (costa) continuing into the blade. Sometimes the midrib extends far enough into the blade to cause it to curve. These are a hybrid of pinnate and palmate leaves. You’ll find these leaves on sabal species.
Trunk Size And Shape

Photo Credit The trunks of coconut trees are often a shade or two lighter in color than the trunks of most palm trees.
There are many different varieties of palm trees, and their heights can range anywhere from a few inches to more than 200 feet. The Rhapis super dwarf palm tree only grows between one and two inches tall, but its leaves can reach lengths of several inches.
In contrast, the Quindo wax palm, which is native to the highland forests of the Andes and has the potential to reach a height of 60 meters (200 feet), is the tallest palm in the world.
Coconut trees, on the other hand, have the potential to grow to heights of up to 100 feet and widths of up to 20 to 30 feet at their widest points. In addition, in comparison to the trunks of other types of palm trees, the trunks of coconut trees are noticeably lighter in color.
They also have a less scaly appearance and a smoother overall texture.
The palm tree’s trunk might be straight, slightly bent, or very thin; however, the base of the trunk is always wider than the top, and a dense network of roots surrounds it.
Distribution

Photo Credit While palm trees are generally endemic to the tropics, the distribution of coconut palms is more limited.
Because of the high levels of humidity and warm temperatures, tropical climates are perfect for the growth of palm trees.
For optimal growth, palm trees require temperatures over 20 degrees Fahrenheit. However, palm trees need temperatures slightly higher than average (about 35 degrees Celsius) to produce fruit successfully. Furthermore, pollinated fruits thrive in dry, hot temperatures, especially when paired with warm summer nights.
The climate along the coast is particularly favorable for the growth of coconut palms. This is due to the fact that coconut trees are resistant to both wind and the salt that naturally occurs in the soil. Therefore, any tropical region that receives at least 25 to 157 inches of precipitation on an annual basis is ideal for the growth of coconut palms.
Palm Tree Vs. Coconut Tree Summary
| Characteristics | Palm Tree | Coconut Tree |
| Water Requirement | Rainfall of 90 to 100 inches annually. But, some can tolerate even drought. | Rainfall of 30 to 50 inches annually. |
| Sunlight Requirement | Prefers shade and indirect sunlight. | It needs 2,000 hours of sunlight per year |
| Primary Benefits | 1. Cosmetic soaps, waxes, inks, and toothpaste.2. Palm oil and palm sugar | 1. The husk is used to make compost, bags, and ropes.2. Coconut water |
| Life Span | More than 100 years | 60 to 80 years |
| Growth speed | Can grow more than 6 feet every year | Can grow 2 to 5 feet in one year |
| Leaf shape | Fan-shaped fronds | Wide-shaped pinnate Fronds |
| Trunk | has scales and texture. It can have a spiral or twisted shape | It has a smooth texture and is comparatively lighter in color. |
Conclusion
Everyone, regardless of where they’ve been or how often they’ve traveled, has seen a palm tree in some form or another in popular culture. However, there are occasions when it might be challenging to tell the difference between palm trees and coconut trees.
We hope that this article has been able to answer any and all questions you may have had regarding palm trees and coconut trees, including whether these two types of trees are linked to one another.
Editor’s Recommendations
15 Best Low Light Indoor Trees For Your Homes
Top 10 Types of Elm Trees| Elm Tree Uses, Pictures and Identification Guide