Nutrients are a vital part of a plant’s life. These nutrients are grouped into macronutrients, micro, and trace nutrients based on their needs. They significantly speed up the process of growth and reproduction. In addition, these nutrients help plants to fight harmful pests—insects and microbes. In this article, I’ll tell you about the importance of calcium for houseplants.
Suppose a plant lacks any macro or micronutrients in its life cycle. As a result, they will not be able to germinate, grow, and reproduce correctly. The constant additions of these nutrients in liquid fertilizers ensure vegetative and reproductive growth.

Healthy tomato plants represent the balanced feeding of nutrients and water.
This write-up will explain the importance of calcium for houseplants and how we can feed calcium to our outdoor and indoor plants from different sources such as egg shells.
Calcium For Houseplants
Calcium is an essential nutrient like other secondary nutrients such as magnesium, nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, and oxygen. It is critical for the integrity of cell walls and helps plants grow. Calcium also acts as an internal messenger during stressful conditions such as attacks by insect pests and microbes.
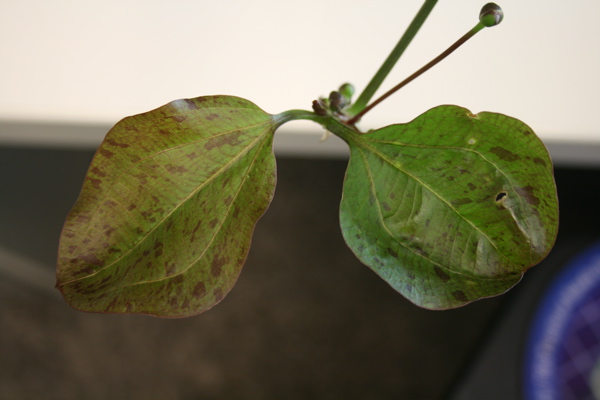

Calcium deficiency symptoms in the plant leaves
In indoor plants, calcium ensures the stability of cell membranes and promotes root growth. It also provides pollen tube growth in plants.
Calcium is a soil-derived secondary plant nutrient that travels up through the plant roots to cells and tissues where cells can use it. A plant becomes calcium deficient when there is insufficient nutrient availability in the soil. In addition, other factors impact the uptake of soil calcium. For example, plant roots cannot uptake calcium due to higher levels of magnesium and potassium in the soil.
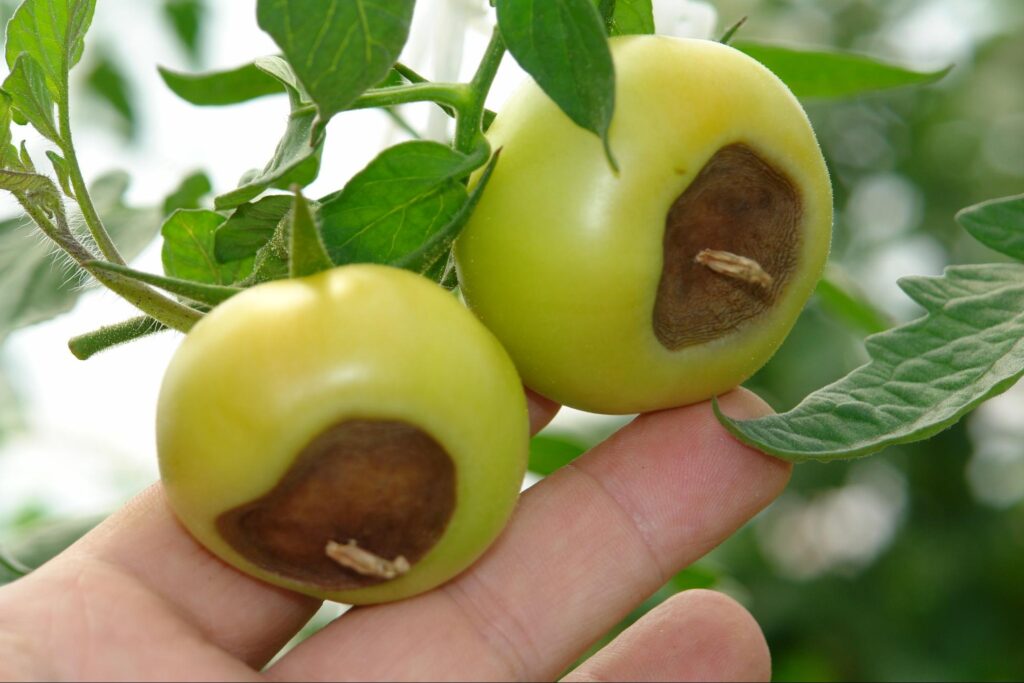

Blossom end rot in tomatoes—the most common disorder in vegetable plants due to calcium deficiency
RELATED: Cal-Mag for Your Plants: All The Necessary Information, Benefits, and Uses
Is Calcium Good For Houseplants?
Calcium is an essential nutrient for both leaf and root growth. The plant needs calcium in adequate concentrations to keep its older leaves healthy and new leaves to grow. Therefore, it is perfect for the health of house plants and outdoor gardens.
When a plant lacks calcium, it loses the integrity of cell walls and membranes and starts discoloration and rot both above and below ground. To prevent the bruises and deterioration of plant parts, indoor plant owners and gardeners should feed them balanced nutrients.
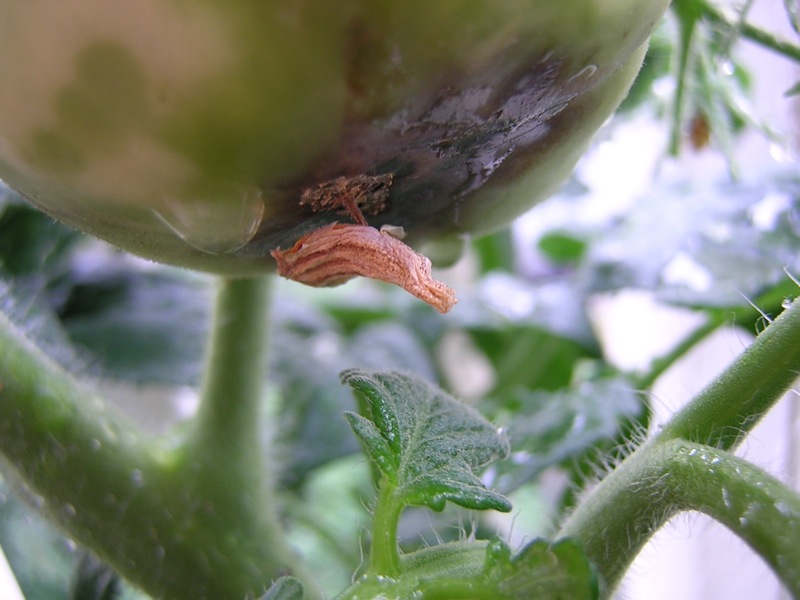

A calcium deficient plant with rotted tomato fruit—these symptoms occur when the tomato plant lacks calcium during the milking stage.
Causes Of Calcium Deficiency In Plants
There are many primary factors involved in the deficiency of calcium in plants. For example, it could be a nutrient imbalance, or your soil lacks the required amounts of calcium to nourish the plant.
The following are the reasons that cause calcium deficiency in plants;
Nutrient Imbalance
Calcium nutrient is a positively charged ion, and its positive charge binds with the negatively charged sites on clay and organic matter material. So, calcium binds to the negative areas.
Similarly, an overabundance of one nutrient can lead to nutrient saturation in soil. For example, applying the magnesium to the ground will bind to all negative sites. However, when you add calcium, it will not have anything to attach and may leach down to the soil or substrate.
Soil pH
Soil pH also plays an essential role in the availability and unavailability of calcium to plants. So, if your soil pH is below 6.0, the plants will have difficulty uptake the calcium nutrient.
Transpiration Rate
The low transpiration rate in plants also leads to calcium deficiency. A decrease in evaporation equals a reduction in water and calcium movement through the xylem. The low transpiration rate is inadequate for water applications during harsh climates and high humidity.
To prevent the calcium deficiencies in plants, ensure the adequate water applications below ground and optimum humidity levels above the ground.
What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Calcium Deficiency In Plants?
The calcium deficiency symptoms in plants are easy to detect because they are similar to sulfur deficiency. So, keep an eye on your indoor plants and vegetables to detect and treat calcium deficiencies early.
The following are the most common signs and symptoms of calcium deficiency in plants;
Curling Of Leaves
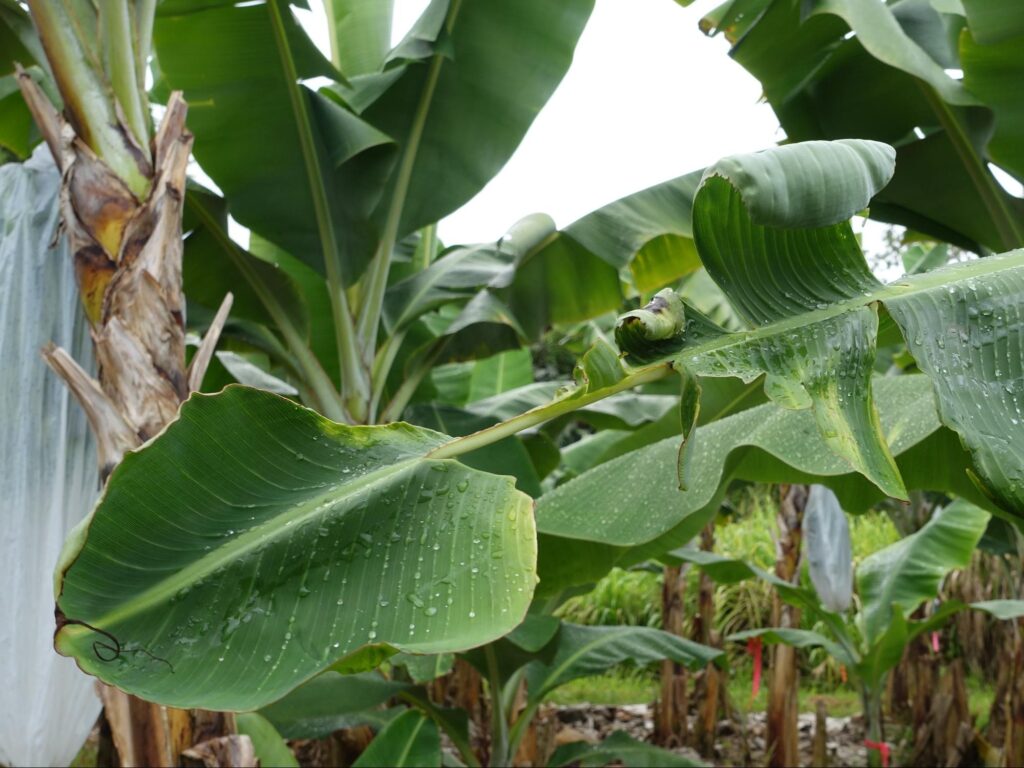

Banana leaf curling due to calcium deficiency
One of the common symptoms of calcium deficiency in outdoor and indoor plants is curling. This phenomenon is more severe in new growths or young leaves. Many termed this leaf appearance as parachute leaves.
Note: During routine monitoring, when you notice the curling of new leaves from the edges, the real cause is calcium deficiency.
Discolorations Of Leaves
Another most common symptom is the discoloration or spotting of leaves in calcium-deficient plants. It starts from the leaf tips and edges and continues to cover the whole leaf surface. This unusual spotting is due to the breakdown of chlorophyll, which interferes with the photosynthesis process.
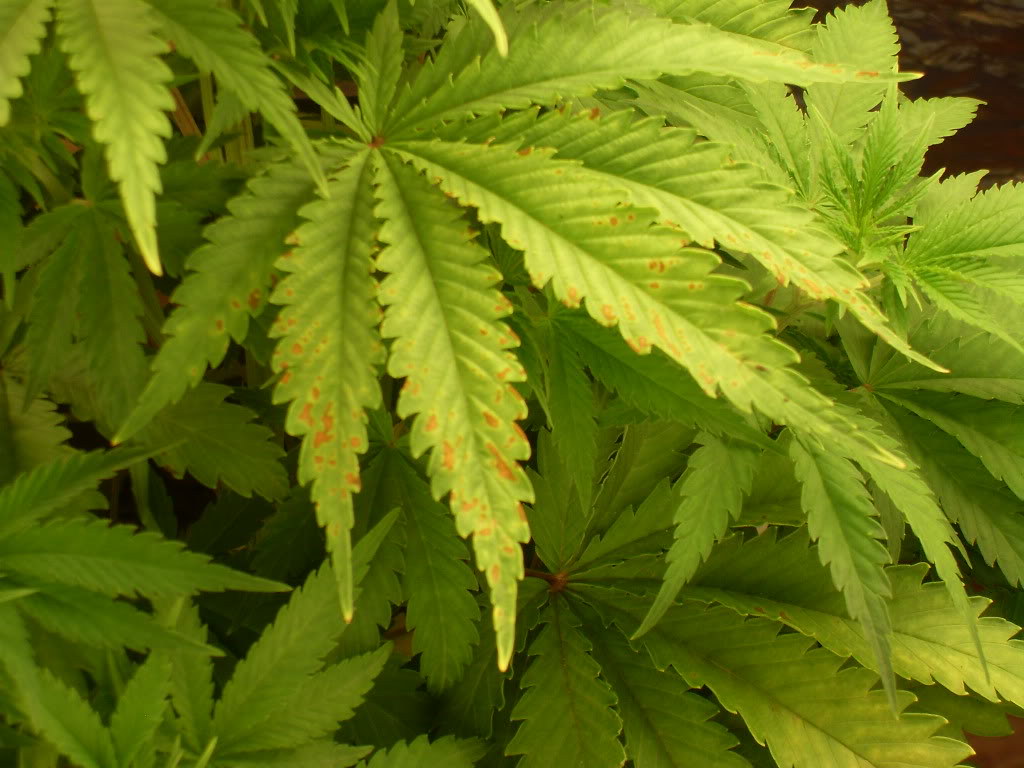

Yellowing of leaves from the edges due to calcium deficiency
Rot
Calcium deficiency leads to the rotting of new leaves, fruits, and vegetables. However, the main factor of aboveground damage is root rotting. For example, tomato blossom end rot is due to the below-ground root rot.
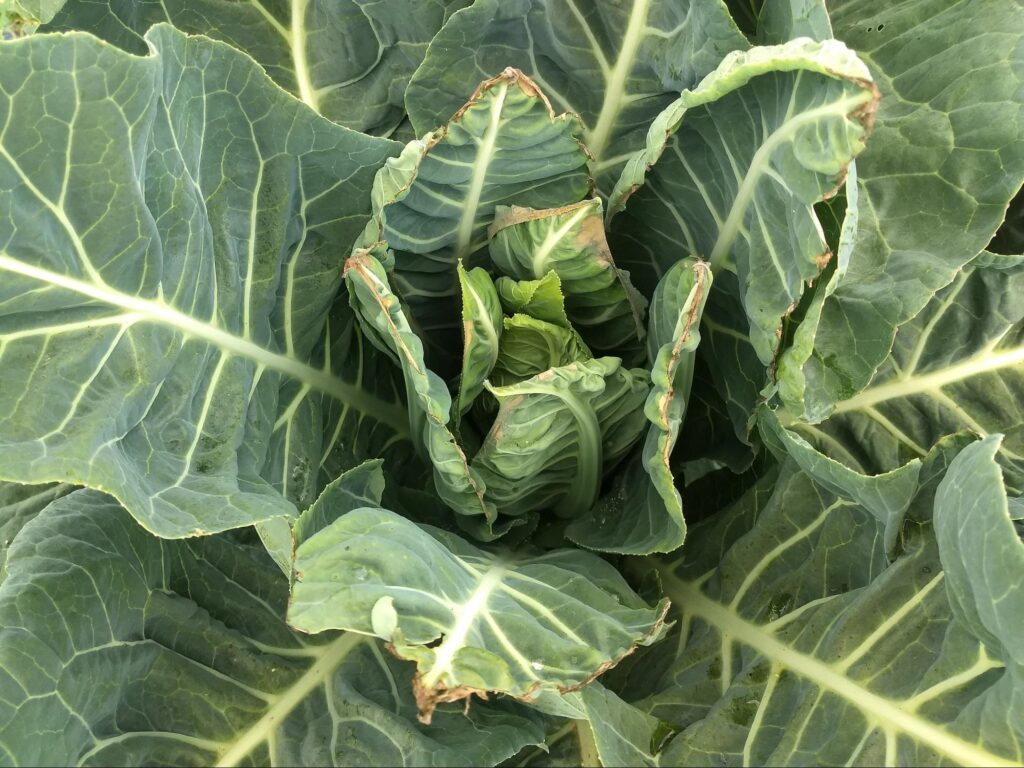

Tips burning in cabbage foliage due to calcium deficiency will lead to the rotting of the head with severe necrosis of edible parts.
Act quickly to prevent the loss of your favorite indoor and outdoor garden. Consider amending soils with soluble calcium chloride or crushed eggshells as fertilizer.
RELATED: Giving Your Plants a New Home: How to Repot Your Plants
Slow Growth
Slow growth is also another sign and symptom of calcium deficiency. So lack of calcium in plants leads to growth inhibition of apical tips, root tips, and tissues. Thus, causing the death of plants. If you notice the browning of leaf tips and the plant cannot complete its vegetative growth, it surely wants calcium. So, act immediately and treat your plants with calcium-based fertilizer to speed up the growth process.
How Do I Add Calcium To My House Plants?
The answer is to add crushed eggshell tea to the potting soil of your houseplants. Eggshells will do wonders for houseplants because they are rich in calcium carbonate and other nutrients.
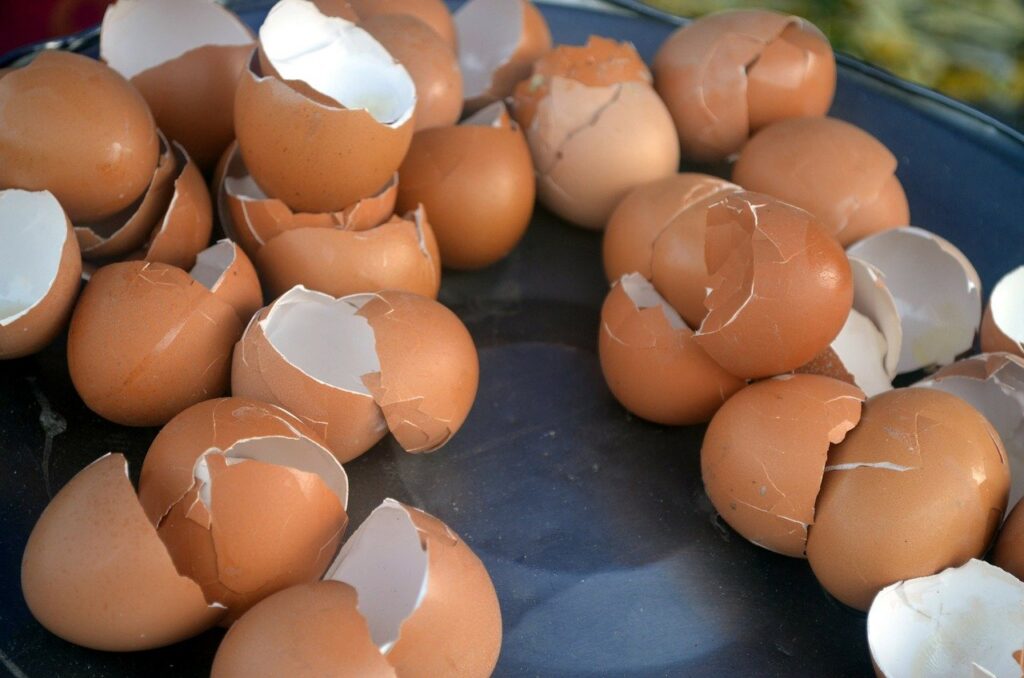

Eggshell fertilizer for healthy plant growth
For years, eggshells have been used to amend soil conditions such as soil pH and calcium levels because they contain higher calcium contents. Any gardener in the world swears by the eggshell’s benefits to potting soil. They believe that adding six to eight eggshells in the plant hole will eliminate the deficiency problems of calcium and blossom end rot.
How To Use Eggshells For Houseplants?
There are three ways to use eggshells as a natural fertilizer for plants;
Eggshell Tea Water
Eggshell tea water is the best organic calcium water for houseplants. It nourishes the plant and does not harm the environment simultaneously. To prepare the eggshell tea;
- Crush the dried and clean eggshells in a food processor
- Add the eggshell powder into the boiling water for five minutes and let it cool
- Add one teaspoon of apple cider vinegar for better uptake of calcium
- In the morning, add the eggshell tea to the soil to give extra nutrition to houseplants.
- You can mix this tea with the potting soil mix and then plant succulent babies for healthy growth.
Ground Eggshells Into Fine Powder For Plant Use
The second method is to use eggshells as a fine powder to fulfill the calcium requirements of houseplants. First, take eggshells in a food processor or a coffee grounder to obtain a fine powder to prepare the powder. Then, spread the eggshell powder over the soil of the houseplants. You can also mix it with the ground for better root growth.
Use Eggshells To Start Seeds
The other practical use of eggshells is to start seeds. For this purpose, take empty eggshells and fill them with soil and organic matter. Then, place your seed in it. Keep in the egg carton as long as the seed germinates. Once the seedling emerges, make a little crack in the shell and plant the seedling into the soil directly with eggshells.
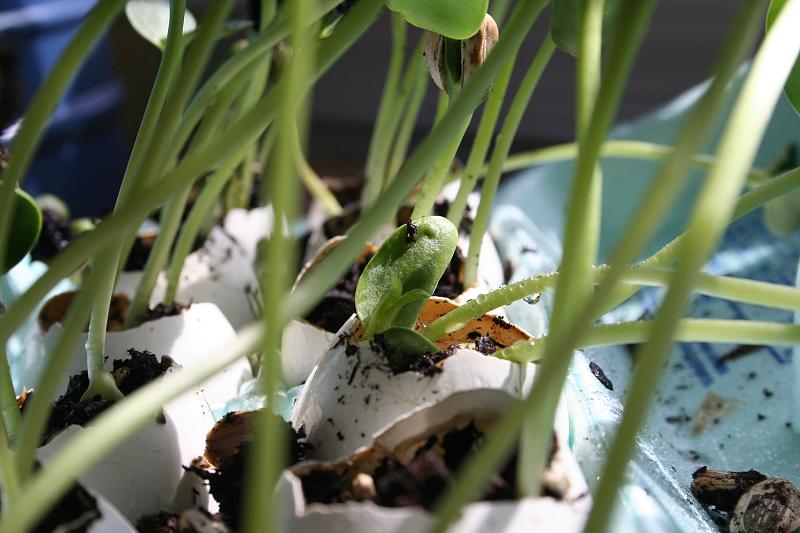

Eggshell seedlings of lettuce—organic fertilizers
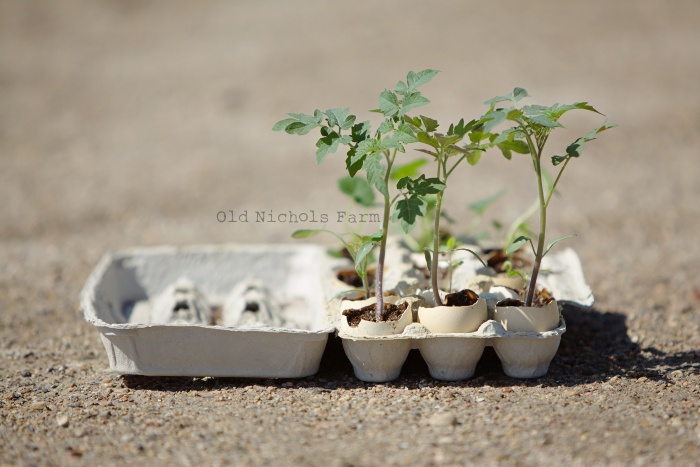

The seedlings are ready to go to the garden p
Other Natural Fertilizers
Despite the fantastic benefits of eggshells for plant health, many gardeners use other organic fertilizers to speed up growth. These are;
Coffee Grounds
Coffee grounds help plant nourishment and kill pests and weeds. In addition, it provides plants with magnesium and potassium, which are excellent for plant growth. Mix equal parts of brewed coffee with water and apply to the soil as you usually water your plants.
Be careful with the plants that do not grow in acidic soil. Apply only to the plants that can bear coffee’s acidic nature, such as ferns, roses, and aloe.
Epsom Salt
Epsom salts are rich in two essential minerals—magnesium and sulfate. Together, these two nutrients provide great nourishment to plants, allowing them to grow taller and fuller. Epsom salt can be used as a foliar spray and soil drench. Mix one tablespoon of high-quality Epsom salt per gallon of water and mist on plant foliage. On the other hand, add Epsom salt granules directly to the soil during repotting.
RELATED: Epsom Salt for Plants: Is it Good for Your Garden & How to Use it?
Green Tea
Green tea also works as natural fertilizer because it increases the nutrient levels in soil and improves the soil oxygen level for plant roots to thrive. You can add tea leaves directly to the ground or tea water (equal parts of brewed tea with water) to enhance the soil and plant nutrition. Be sure to use it for plants that thrive best in acidic soil.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What Does Calcium Deficiency Look like in Plants?
The calcium deficiency in plants appears as follows;
- Curling of leaves from the edges or “parachute leaves.”
- Discoloration of leaves (yellowing or browning)
- Slow growth or plant takes months to reach reproductive growth
- Root rot leads to the abnormal development of fruit in plants that unable to absorb calcium
How Do You Fix Calcium Deficiency in Soil?
The eggshell powder is the best organic food for plants and soil to fix calcium deficiency. This is because they contain more than 90% of calcium contents.
There are many ways to add eggshells to the earth to cure the soil’s calcium deficiency. For example, you can add eggshell tea water to the ground or fine powder.
Can Expired Calcium Tablets be Used for Plants?
Yes. The expired calcium tablets can be used for your garden plants. Apply them to the soil in powder form or mix it with water and mist on leaves and dirt to speed up the growth of your favorite garden plants.
Can You Add Too Much Calcium to Soil?
Calcium regulates the soil pH. Therefore, too much feeding of calcium nutrients to your plants means more pH towards alkalinity. The more alkaline the soil is, the less will be the absorption of macronutrients and abnormal growth of plants.
Which Plants Like Eggshells?
The calcium content in eggshells benefits the tomato, bell pepper, and eggplants. It (eggshells) will the plant in root growth and prevent root rot and blossom end rot. Moreover, the other calcium-loving plants are orchids, African violet, kalanchoe, hoyas, spider, and ivy plants.
What Is the Best Source of Calcium for Plants?
The best organic calcium sources are calcite, dolomite lime, ground oyster shell, and crushed eggshell. All these sources are cheap and readily work in acidic soils to provide magnesium and calcium.
Do Succulents Need Calcium?
All succulents need these five essential nutrients for their adequate growth;
- Nitrogen
- Magnesium
- Iron
- Calcium
- Phosphorus
Can I Use Milk to Water my Plants?
Yes, it is best to add milk to your plants. However, the best way is to dilute the water in equal ratios, such as half liter milk and half liter water.
Where Does Calcium in Soil Come From?
The calcium comes from animals, plants, and microorganisms. For example, when their bodies decompose, the calcium is released and mineralized in the soil. Similarly, plant roots also exude sugars, minerals, liquids, and calcium.
Sources For Further Reading
- Coffee grounds, eggshells and Epsom salts in the home garden. (2020). UMN Extension. Retrieved May 15, 2022, from https://extension.umn.edu/manage-soil-nutrients/coffee-grounds-eggshells-epsom-salts
- Enroth, C. (2018, March 28). Using Eggshells in the Garden and Compost. University of Illinois Extension. Retrieved May 15, 2022, from https://extension.illinois.edu/blogs/good-growing/2018-03-28-using-eggshells-garden-and-compost
- Oldham, L. (n.d.). Calcium and Magnesium in Mississippi Crop Production. Mississippi State University Extension Service. Retrieved May 15, 2022, from http://extension.msstate.edu/publications/calcium-and-magnesium-mississippi-crop-production
Editor’s Recommendations
What are the Effective Ways to Fix Nitrogen Toxicity in Houseplants?
Importance of Soil pH and Nutrient Availability for Plant Health