Grasshoppers are voracious feeders, particularly of outdoor plants. Interestingly, they are not picky about their favorite plants and can destroy any garden plants when hungry. In this articles, I’ll share with you effective organic grasshopper control.
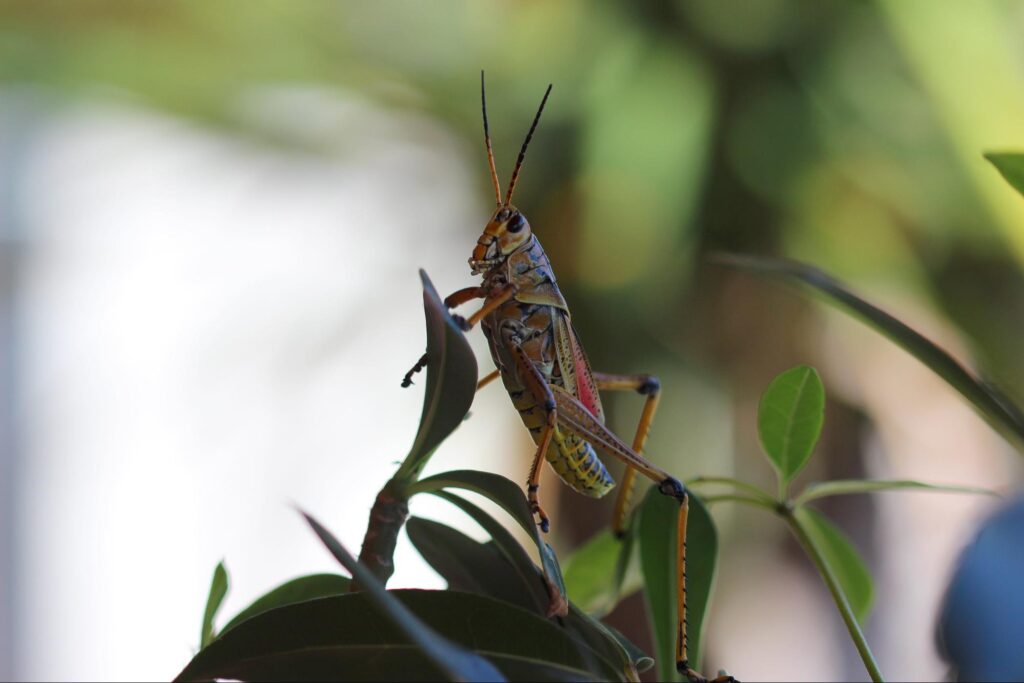

Grasshopper resting on his host plant
Under certain circumstances, grasshoppers cause severe damage to essential crops and pastures, just like locusts.
They chew on the leaves and stems of plants. During higher grasshopper populations, they entirely defoliate the crops and negatively influence the crop produce.
Let’s learn about various methods for organic grasshopper control and how to protect plants from their harmful infestations.
What are Grasshoppers?
Grasshoppers are members of insect order Orthoptera and suborder Caelifera. They eat one-half of their body weight (up to 50% per day) and can quickly decimate your crops. No matter where they are in their life stage, grasshoppers will chew every part of your garden plants, leaving them unable to grow.
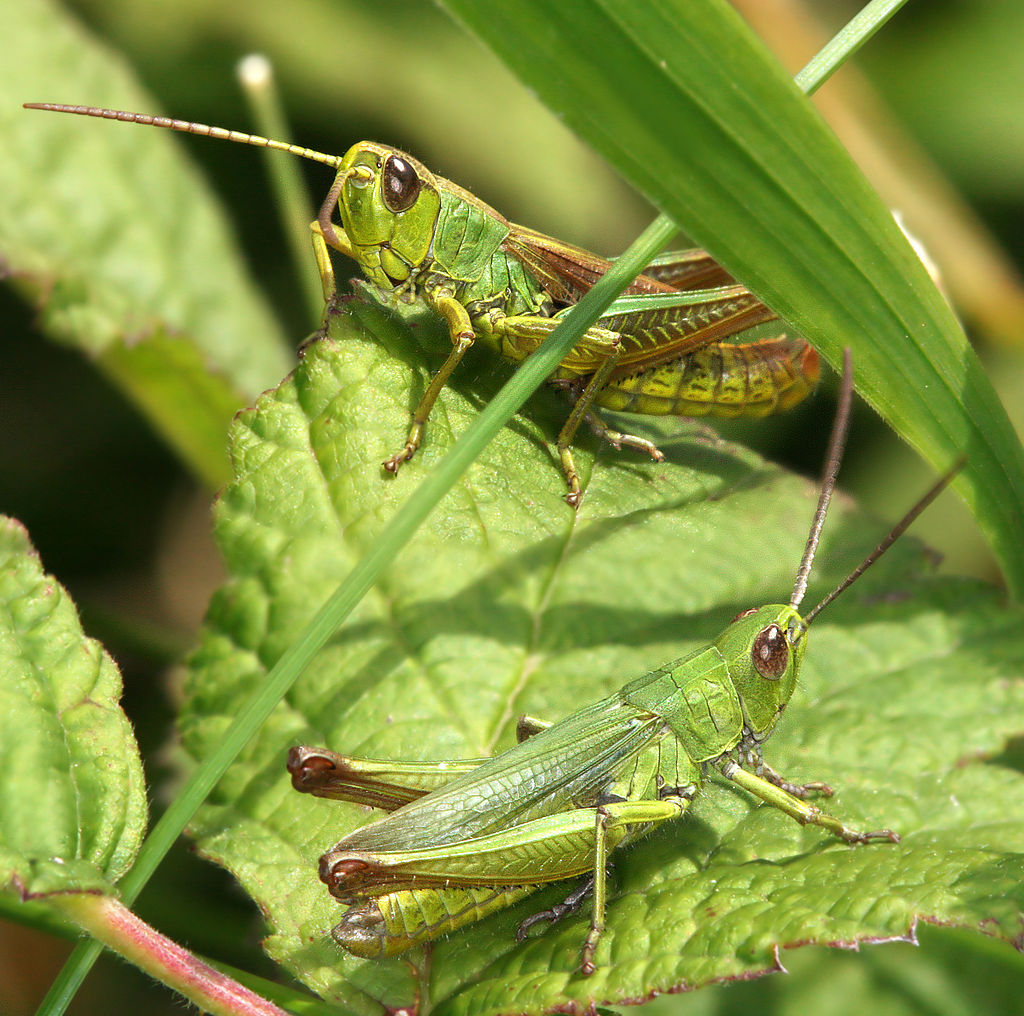

Grasshoppers are herbivorous pests and sometimes known as robber flies
Important Facts About Grasshoppers
- The summer song produced by grasshoppers is used to attract females for mating.
- Grasshopper species are more noticeable pests of crops with strong chewing mouthparts.
- They have solid and enlarged hind legs used for jumping.
- Grasshoppers are most challenging to control because of their high mobility.
- There are 20,000 species of grasshoppers worldwide, and over 1,000 exist in the United States.
- Grasshoppers lay eggs in the soil and remain active from spring to fall, with more significant activity in warm, dry summer.
Identification Of Grasshoppers
Adult grasshoppers are 1 to 2 inches long with fully developed wings and enlarged hind legs—that help them take a long jump during defense and preying. They appear brown to reddish yellow or green in color and distinguished body parts (head, thorax, and abdomen) and smaller antennas than the head.
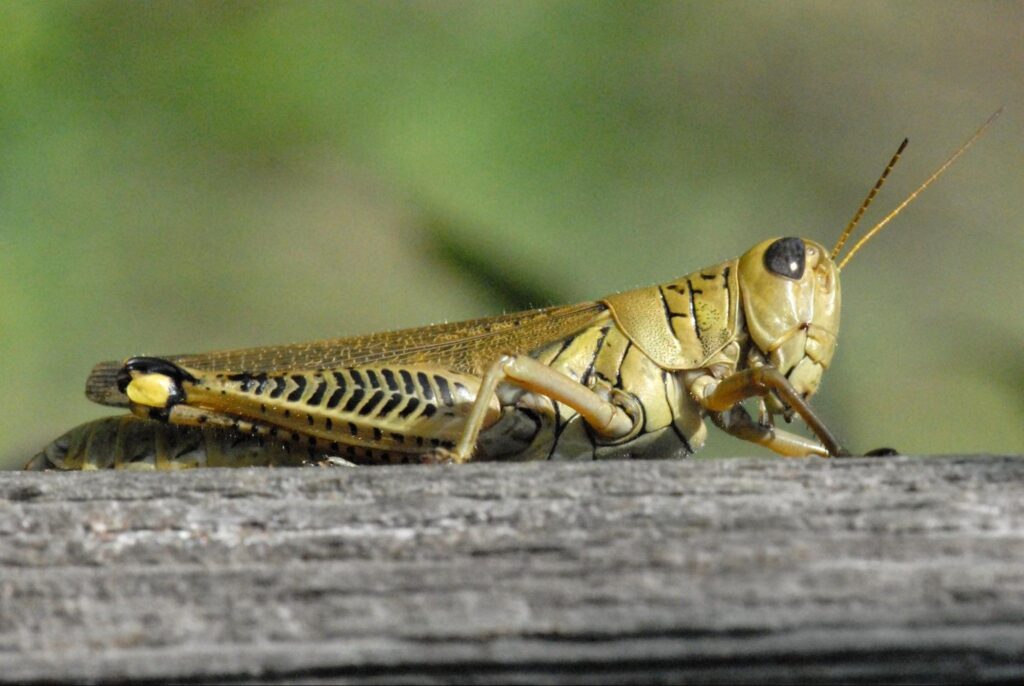

A short-horned grasshopper
Grasshoppers are divided into short-horned and long-horned (the horn refers to antennas). The long-horned grasshoppers have larger antennas than their bodies and are plant eaters, only active at night.
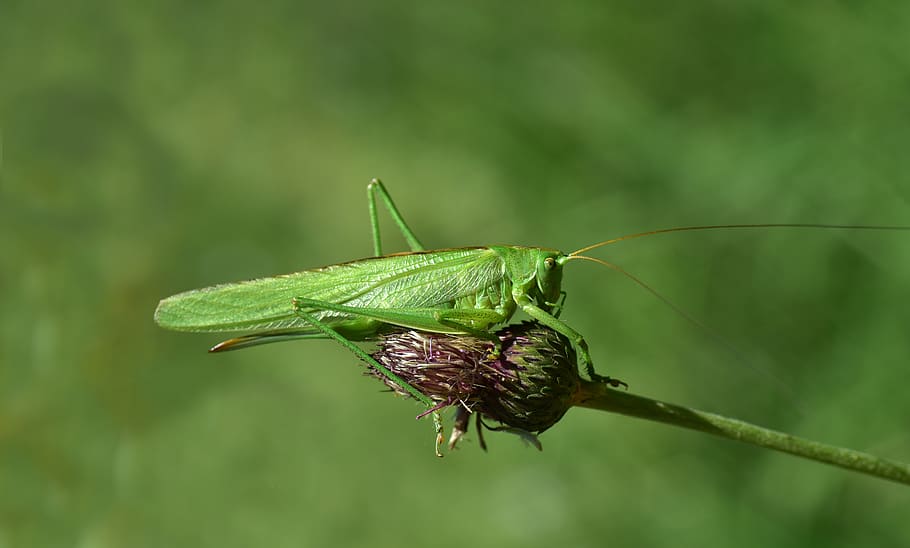

Long-horned grasshopper actively feeding on a flower
On the other hand, the short-horned grasshoppers have smaller antennas than the body and are active during the day.
The young grasshoppers are similar to adults in appearance but are smaller in size. In addition, instead of fully developed wings, grasshopper nymphs have wing buds.
See also: Best Worms For Composting: Its Basics and Guide for Beginners!
Life Cycle Of Grasshoppers
All grasshopper species undergo similar developments in their life cycle. First, egg pods are deposited in large masses in the soil in late summer. Then, these egg masses overwinter in the ground and start hatching in late May and early July. Finally, the baby grasshoppers search for food in their immediate places.
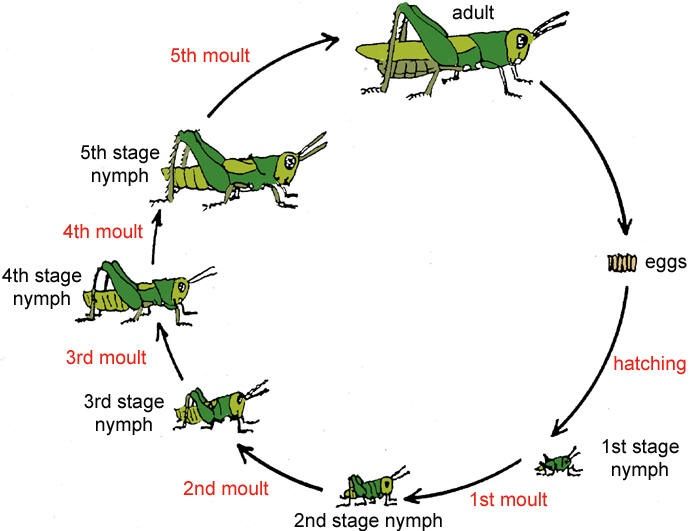
The complete life cycle of grasshoppers
These pest species go through an incomplete metamorphosis as the young grasshoppers are similar to their adults in appearance but smaller in size. These young grasshoppers undergo 4 to 5 molts resembling adults, slightly smaller and wingless.
The young nymphs voraciously feed on vegetable crops as they mature.
The feeding continues into adulthood, and food sources become scarce, then migration for other food sources occurs. During this time, mating also occurs, and female grasshoppers lay eggs in large masses. Each mass contains 100 eggs, and egg-laying completes in August, September, and October.
The infestations of grasshoppers occur after every 3 to 7 years and remain for five years, depending upon the weather conditions and food sources.
See also: What Do Caterpillars Eat? Top 3 Host Plants You Must Know!
What Are the Best Organic Grasshopper Control Products?
The following are the best organic grasshopper control products,
- Garlic Spray
- Hot Pepper Wax
- Neem Oil
- Nolo Bait
- Kaolin Clay
- Diatomaceous Spray
- Pesticidal Soaps
Note: Grasshoppers eat as many croplands and vegetables as the cow and pose a severe threat to growers. Such as, ten adults per square yard are damaging vegetables and gardens. Therefore, growers’ first and foremost priority should be to control grasshoppers.
Organic Grasshopper Control
Garlic Spray
Garlic spray applications are an effective organic treatment to control grasshoppers. The garlic odor works as a repellent to deter the hungry grasshoppers. So the coating of your garden plants with garlic will prevent them from grasshopper damage.
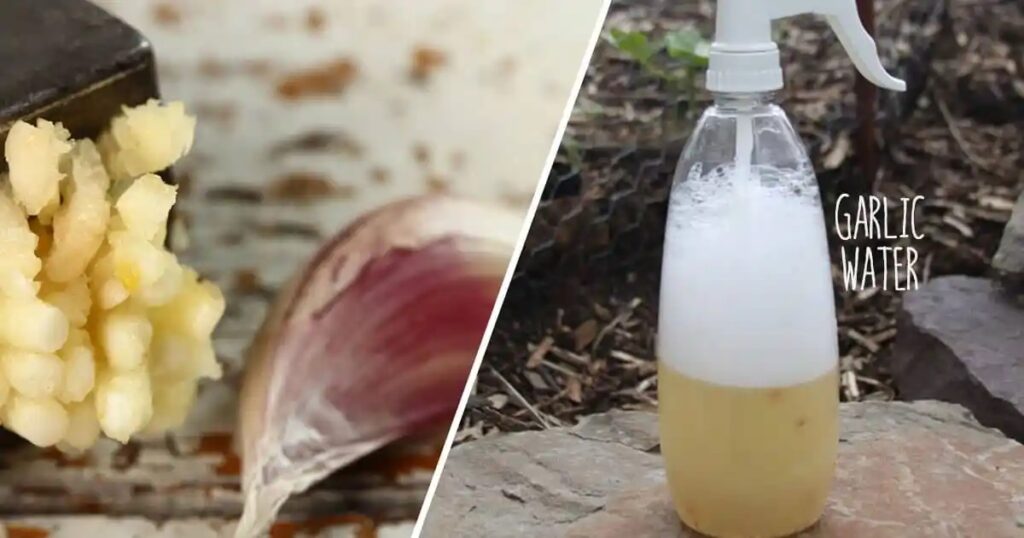

Garlic spray is organic prevention from grasshoppers
To prepare a garlic spray,
- Blend two bulbs of garlic with ten cups of water
- Heat the garlic water mixture until it starts boiling
- Then let it sit overnight
- To use it as a spray, take one part of the garlic concentrate with three pieces of water, pour it into a spray bottle, and apply it for two days to repel the grasshoppers and locusts.
Note: The garlic spray is the fastest and most organic solution to repel and kill grasshoppers.
Nolo Baits or Semaspore Baits
Semspore baits contain Nosema locustae —a naturally occurring single-celled protozoan that infects and kills grasshoppers.

Semaspore bait—a rapid action agent against grasshoppers
After feeding on semaspore, the grasshoppers eat less and die due to starvation. So it is because these pathogenic spores spread throughout the grasshopper’s body and impact their physiology.
Apply 1 pound of Semaspore bait manually per acre for young nymphs.
Also, treat the hatching beds of your lawns (the young grasshoppers start feeding on grasses right after hatching). Do not apply Semaspore baits when the rain is expected within eight hours.
Note: The shelf life of Semaspore bait (nosema locustae baits) is eight weeks when refrigerated. Always follow the product label instructions before applications. Also, the heavy infestations of grasshoppers require multiple applications.
Encourage Beneficial Insects
The most notable natural predators of grasshoppers are insect-eating birds. Such as swallows and ibis. The presence of these two birds in your garden can prevent damage to broadleaf plants and tall grass. Therefore to attract the natural enemies of grasshoppers, provide them a source of water and free nesting sites.
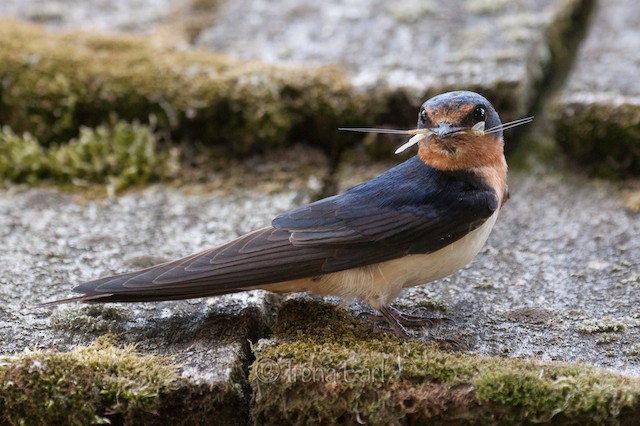

The voracious eater of grasshoppers at all stages of their life cycle
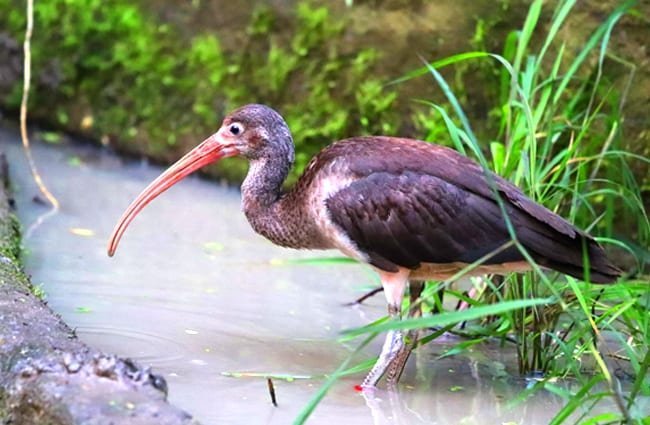

Actively feed on grasshoppers and help gardeners in protecting their plants
Tiny toads and snakes feed on adults and young grasshoppers despite these two birds.

Beneficial insects—praying mantis eating the grasshopper.
The praying mantis insects are also a great addition to the biological control of grasshoppers. It aggressively feeds on them and eliminates their infestations in Gardners.
Hot Pepper Wax Spray
Hot pepper wax spray is another organic grasshopper control approach that best protects plants and grasses from feeding damage; otherwise, the grasshoppers wreak havoc on important crops. The active ingredient in the hot pepper wax spray is cayenne pepper which a few species of grasshoppers can not stand.
So applications of hot pepper spray on the leaves of plants that are more prone to damage will repel and deter this damaging pest.
Use Neem Oil to Control Grasshoppers
Neem oil applications on plants have numerous benefits, such as its spraying controls insects, fungal pathogens, and mites. Moreover, it is also used to bring shine to leaf surfaces. In addition, it contains azadirachtin—the critical ingredient which kills insect pests.

Neem oil—triple-action agent to kill insect pests of essential crops
The biweekly spray of neem oil successfully controls the grasshopper populations and makes it impossible for this pest to develop resistance against it.
Using neem oil is beneficial because it is non-toxic to beneficial insects such as bees, green lacewings, and lady beetles. It also effectively controls the all adult and immature stages of grasshoppers.
Till the Ground
Remove the remains of vegetables and plants from your garden in late summer and early fall, and then till the ground to expose the eggs hidden in the soil, plant debris, and leaf litter to natural enemies. Because the female grasshoppers lay their eggs in the earth, and the eggs hatch in the ground.
The tilling of the ground will also improve the soil texture and nutrition. In addition, it will improve the soil aeration and water holding capacity. So, this is the best and most effective solution for the organic management of grasshoppers.
Eliminate Alternate Hosts of Grasshoppers
The weeds in your garden will provide shelter and food to the baby grasshoppers who hatch from eggs without their host plants. To avoid the heavy populations of grasshoppers, employ good weeding practices in your gardens. It would help in long-term protection against grasshoppers.

Removal of alternate hosts of grasshoppers such as weeds will provide long-lasting protection.
Dust Flour to Plants
Dusting flour on your garden plants will impact the feeding behavior of grasshoppers because it will gum up their mouthparts. As a result, they will not be able to eat leaves and cause any injury in the future. Reapply the flour after rain to keep the grasshoppers away.
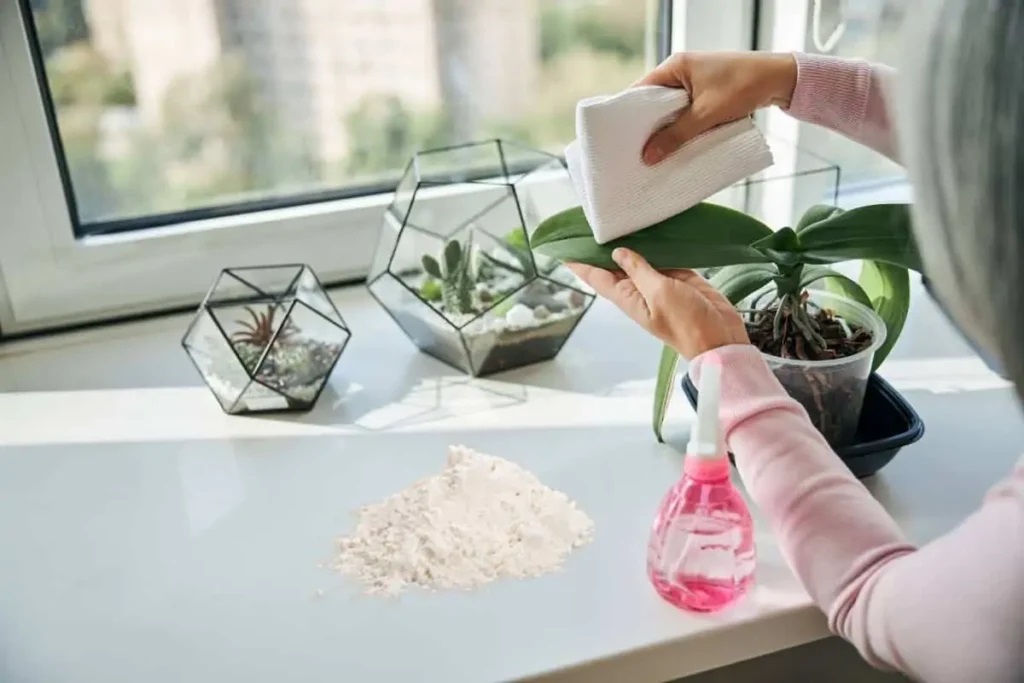

Dusting flour on garden plants will gum up their mouthparts and stop their feeding damage.
Use of Less Toxic Chemicals for Organic Grasshopper Control
Canola oil can be an excellent attractant in baits to attract and trap grasshoppers. It can also be combined with neem and vegetable oil spray to effectively kill immature and adult grasshoppers.
Spray plants with potassium-based insecticidal soaps to control grasshoppers before damaging cropland, trees, and vegetation. Use Natrasoap to kill young grasshoppers.
Use BotaniGuard ES to control the grasshopper. It effectively kills them because it contains the natural enemy of this pest—Beauveria bassiana. This fungus penetrates the grasshopper body and multiplies in it, thus causing the death of grasshoppers. It is commercially available in spore forms.
BotaniGuard ES is effective against all stages of this pest and causes killing within 3 to 5 days of application. It is also effective against bugs such as aphids, whiteflies, mealybugs, thrips, and spider mites.
Spray plants with pyrethrin-based insecticides to kill this pest. Do not apply these chemicals during high temperatures because these chemicals will kill the beneficial insects and burn the leaves at that time of the day.
Cover Crops to Protect the Vulnerable Plants
Cover your crops with cheesecloth to protect them from feeding damage of the grasshopper. This method will prevent the produce from arriving insects but is ineffective if your garden has had grasshopper infestations in the last year. The overwintering eggs will hatch in spring and cause damage below the covers.
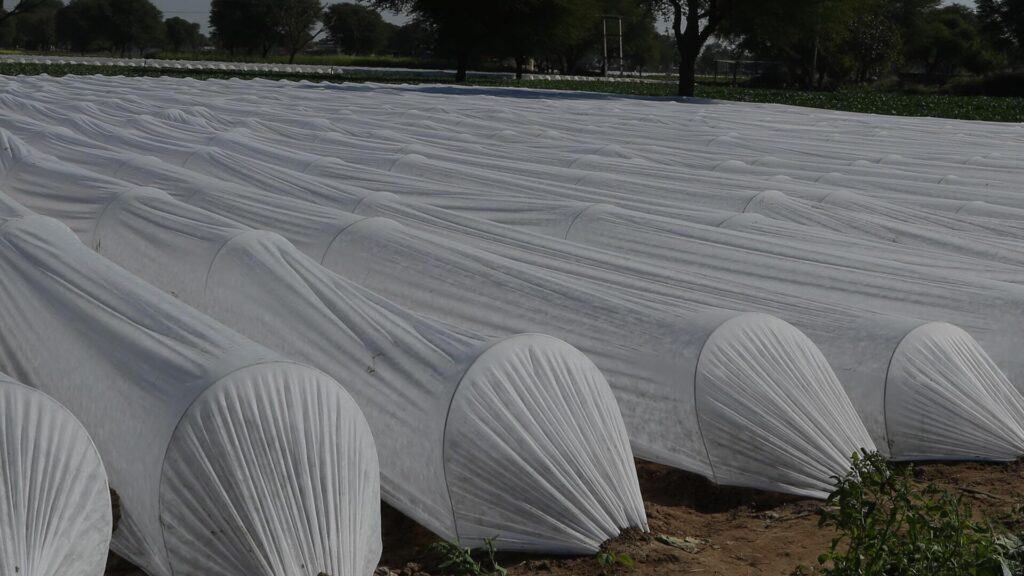

Crop covers to protect plants from the feeding damage of grasshoppers
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Effective Against Grasshoppers?
Several insecticides are effective against grasshoppers and are successful in long-term protection against these mobile pests. Such as carbaryl, malathion, permethrin, and bifenthrin. In addition to that, an insect growth regulator such as Dimilin is also available for commercial applications to get rid of these nasty pests.
These insecticides can be applied as dust, sprays, and baits. Their applications are more effective in late summer and early spring when the females lay eggs in pods in the soil in open fields, croplands, and garden soil.
Are Grasshoppers Harmful To Man?
Grasshoppers are considered harmful to trees, vegetation, and croplands depending upon their species. Still, they are non-toxic to humans indirectly because they voraciously feed on crops and are not host-specific.
What Animal Eats a Grasshopper?
Grasshoppers have many natural animals, such as foxes, bats, raccoons, red foxes, hawks, hedgehogs, dragonflies, ibis, sparrows, bluebirds, robins, and blue jays, owls.
Do Birds Eat Grasshoppers?
Birds serve a significant role in biocontrol methods in the management of grasshoppers. Wide bird species feed on grasshoppers, such as blackbirds, flycatchers, chickens, wild turkeys, jays, European starlings, bluebirds, nuthatches, etc.
It is because the grasshopper provides excellent nutrition to them. They contain Vitamin A, Vitamin B, and Vitamin E, and they are also enriched with many proteins.
So the presence of birds in your garden is a win-win situation for both growers and birds. Because the birds get proteins while eating the grasshopper, the growers get environment-friendly management of this pest.
To attract birds to your gardens, set accessible nests, food, and water sources.
How Do You Keep Grasshoppers Away?
To keep grasshoppers away from your gardens, spray your plants with homemade chili spray, garlic, and onion spray. This mixture is known as organic grasshopper repellent spray.
How to Prepare it?
To prepare the organic grasshopper repellent spray, we need:
- One clove of garlic, two onions, and two tablespoons of cayenne pepper.
- Add all the ingredients to a blender with three glasses of water.
- Blend the ingredients thoroughly, strain the mixture and store the concentrate in a jar.
- Before spraying on plants, dilute the concentrate with water and uniformly coat the plants to repel and deter grasshoppers and the young.
A helpful guide to getting rid of grasshoppers
Sources for Further Reading
- Planet Natural. (2018, March 22). How to Get Rid of Grasshoppers. Retrieved April 14, 2022, from https://www.planetnatural.com/pest-problem-solver/lawn-pests/grasshopper-control/
- Colorado State University Extension. (2016, April 15). Grasshopper Control in Gardens and Small Acreages – 5.536. Extension. Retrieved April 16, 2022, from https://extension.colostate.edu/topic-areas/insects/grasshopper-control-in-gardens-small-acreages-5-536/
- Grasshoppers Management Guidelines–UC IPM. (2013). UC-IPM. Retrieved April 14, 2022, from http://ipm.ucanr.edu/PMG/PESTNOTES/pn74103.html
- Organic Grasshopper Control | Chemical-Free Solutions. (n.d.). Arbico Organics. Retrieved April 14, 2022, from https://www.arbico-organics.com/category/pest-solver-guide-grasshoppers-crickets
Do you know other methods for organic grasshopper control? Share it with us below. Also, check out our other articles:
How to Get Rid of Earwigs (Pincher Bugs) Naturally in Homes and Gardens?
How to Get Rid of Bugs in Plants? Plus Their Identification & Effective Management!
Are Japanese Beetle Traps Helpful for Organic Pest Management?