Even though most lawn owners and gardeners despise weeds, some weeds can be pretty attractive. The beauty of these weeds comes from their flowers. Their flowers not only add to the aesthetics of a garden but can also attract beneficial pollinators to garden beds. Let’s take a look at weeds with pink flowers.
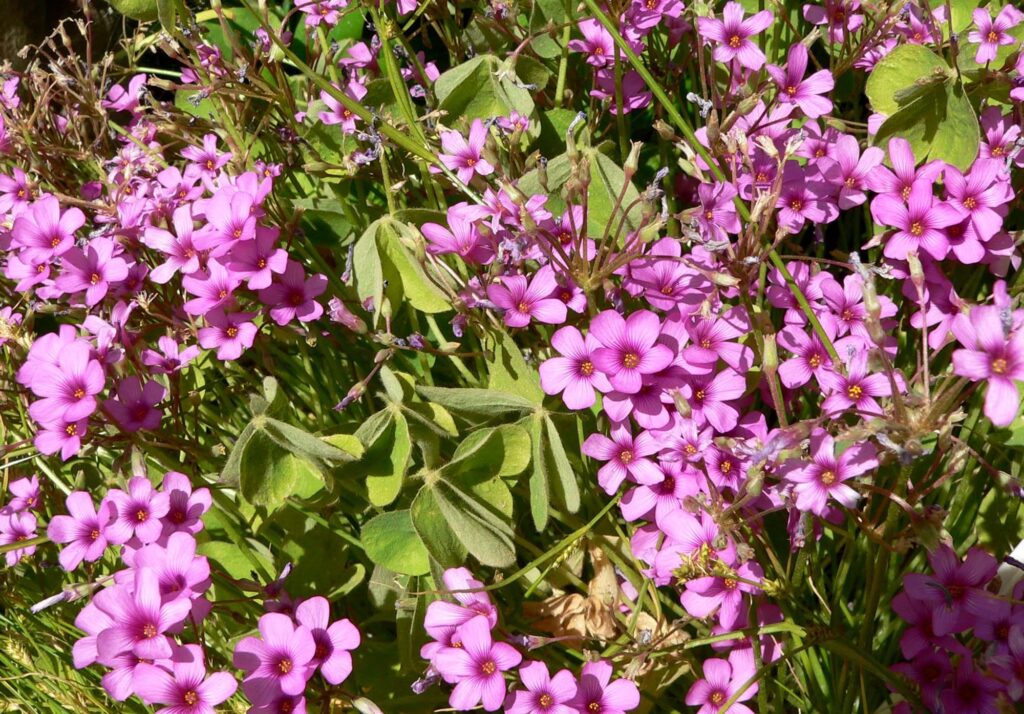

Pink-sorrel: These flowering weeds are an integral part of many flower beds that can become weedy if not kept in check.
Common garden weeds have all sorts of flowers. Some have purple flowers, others have yellow flowers, and then there are some that can have all yellow, white, and purple flowers.
If you want to learn about the weeds with purple, white, and yellow flowers, you should definitely check out the articles mentioned below:
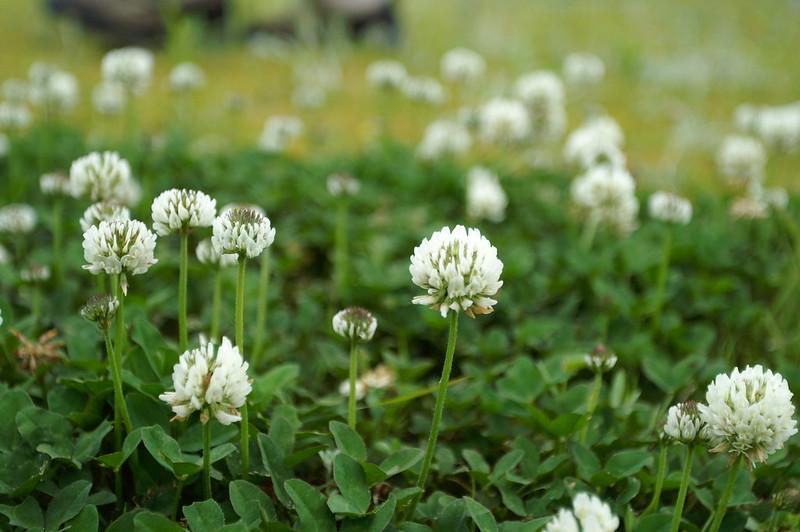

White clover: Perhaps, the most common lawn weed with showy white flowers in homes, gardens, and other turf areas.
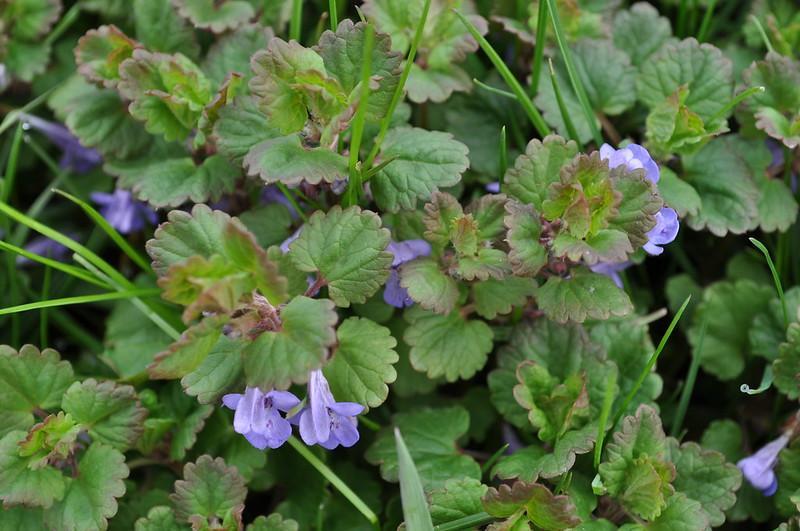

Ground ivy: A creeping weed with light purple flowers that spreads quickly via an extensive network of creeping stems.
Weeds with small yellow flowers
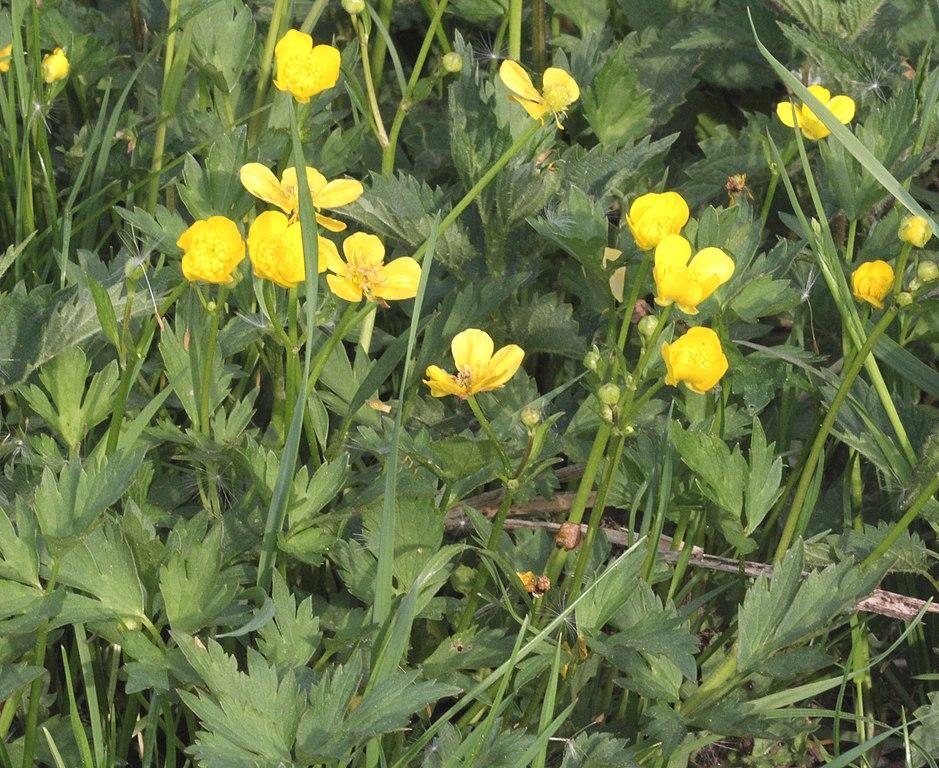

Creeping buttercup: A perennial broadleaf weed with bright yellow flowers that spreads via an extensive network of creeping roots.
The aim of this article is to give you a brief introduction of weeds with pink flowers. This guide will help you identify the most common weed plants with pink flowers.
We will also tell you about the different weed control methods and the time of the year when you are most likely to see weedy new plants in your lawns and garden beds. Happy reading!
Common Weeds With Pink Flowers
Red Clover
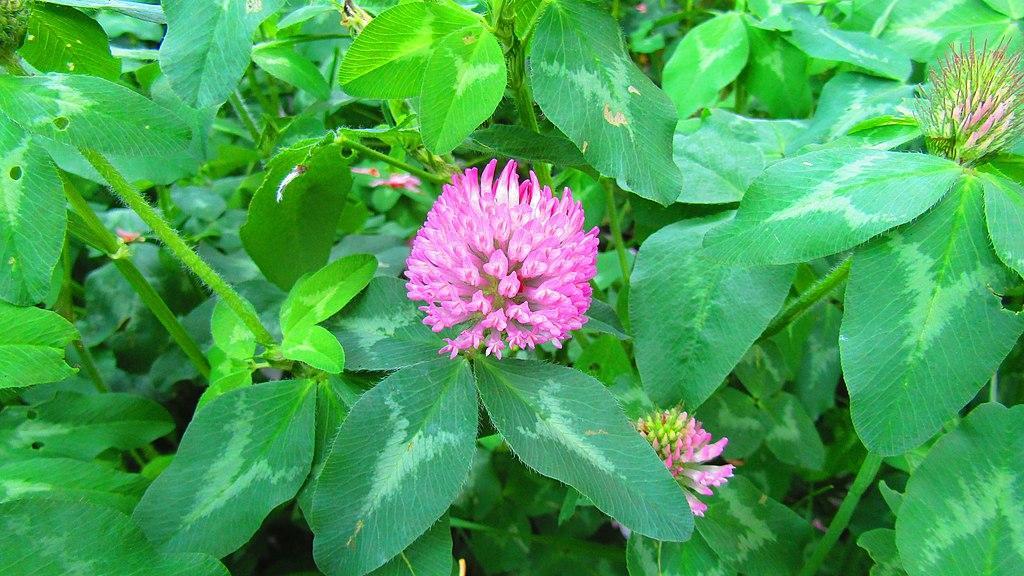

Red clover: The weed thrives in full sun and well-drained soil.
These perennial weeds are a common sight in lawns, gardens, roadsides, parks, and meadows. They are also used as fodder for livestock animals. Red clover grows well in areas with bright sun and under-fertilized soil. It is also used as a medicinal plant in alternative systems of medicine.
Its taproots allow it to survive during drought stress. The root system also allows it to spread, making patches and clumps in new lawns that are not sufficiently fertilized.
The weed is best controlled by selective herbicide containing dicamba and quinclorac. For best results, you should use the herbicides during the fall months.
Red Clover Quick Facts
| Scientific name | Trifolium pratense |
| Other names | Wild clover, meadow trefoil, three-leafed grass, bee bread, trefoil, cow grass |
| Weed type | Short-lived perennial |
| Height | 20 to 80 cm |
| Flowering & Leaves | – Inflorescence consists of bright pink flowers on top of hairy stems – Flowers bloom from late spring to early summer – Foliage is comprised of light green leaves that are palmately trifoliolate |
| Distribution & Habitat | – Native to Western Asia, northwest Africa, and Europe – Planted and naturalized worldwide – Red clover grows best in well-drained soil, open forests, and forest margins |
Pink Wood Sorrel
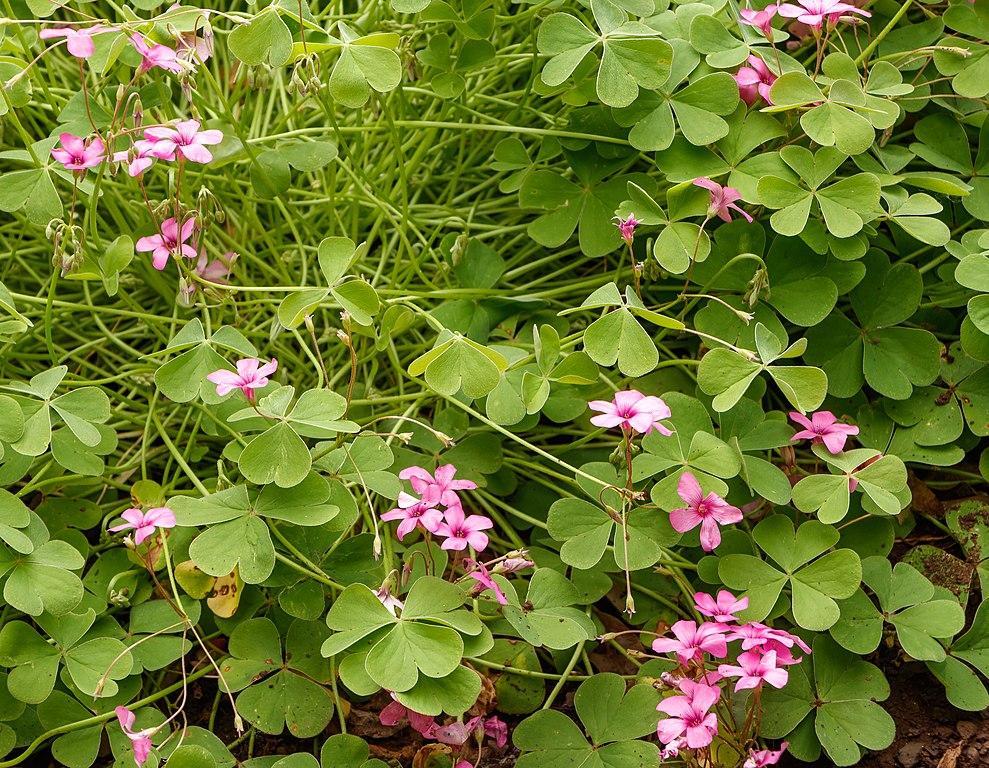

Wood sorrel: Common lawn weeds in Australia, Victoria, and New South Wales.
Wood sorrel is a common perennial weed of lawns and gardens. The plant prefers moist soil, and even though it can survive dry soil, it may enter dormancy in dry, hot summers or if not watered enough. Wood sorrel is used as an ornamental plant in China and Turkey.
However, the plant is also regarded as a weed in many regions of the world, including South Australia, New South Wales, and Victoria.
To control wood sorrel in your lawn, you should uproot plants before they start producing seeds. If there are too many wood sorrels in your yard or garden, you can use a selective herbicide.
Pink Wood Sorrel Quick Facts
| Scientific name | Oxalis articulata |
| Other names | Pink sorrel, pink-wood sorrel, sour grass, netho saag, window box wood-sorrel |
| Weed type | Deciduous rhizomatous perennial |
| Height | Up to 6 inches |
| Flowering & Leaves | – Inflorescence consists of bright or dark pink flowers – Flowers bloom in early spring and then again in fall – Young leaves are light green, while mature leaves are dark green |
| Distribution & Habitat | – Native to temperate South America – Introduced and naturalized in Europe, Asia, and Australia – Habitats include woodlands, riverbanks, lawns, and other moist, usually shaded areas |
Shining Geranium
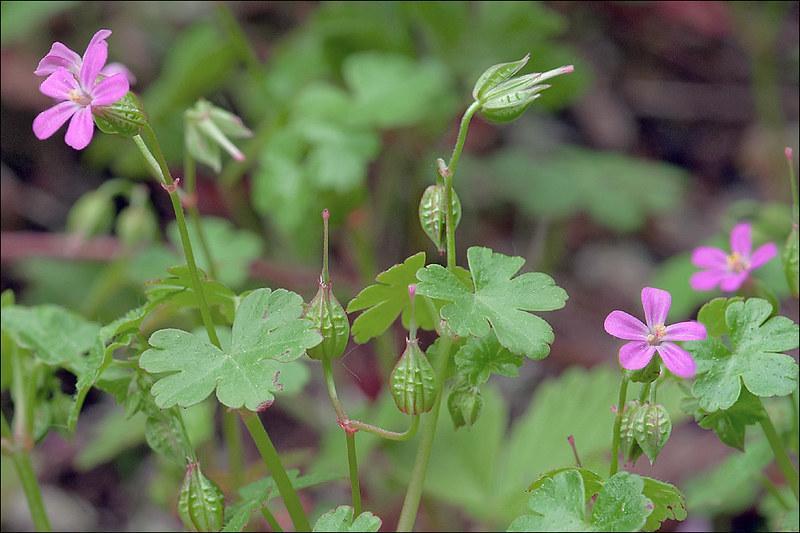

Shining Geranium: Invasive and common weeds in many regions of the US.
Shining geranium is considered a noxious and invasive plant in many regions of the United States. It has escaped from gardens into wildlands and is regarded as a serious contaminant of nursery stocks, lawns, and gardens. It grows mixed with grasses, forbs, and moss in shady areas. These weeds have branching stems that are reddish in appearance.
The weed spreads by seeds that are forcefully ejected by seed pods or seed heads. To control the spreading of shiny geranium, you can uproot new plants.
However, try removing their extensive root system as much as possible. Larger patches can be controlled by mulching or using chemical control methods.
Shining Geranium Quick Facts
| Scientific name | Geranium lucidum |
| Other names | Shining cranesbill, shiny geranium |
| Weed type | Annual weeds |
| Height | Around 18 inches |
| Flowering & Leaves | – Inflorescence consists of pink flowers with rounded petals and sharp sepals – Weed blooms from May to August – Foliage consists of dark green leaves that are kidney-shaped |
| Distribution & Habitat | – Native to western Asia, North Africa, and Europe – Introduced and an invasive weed in North America |
Related: A Lovely Shade Of Pink: The Ultimate Guide To Oleanders
Field Bindweed
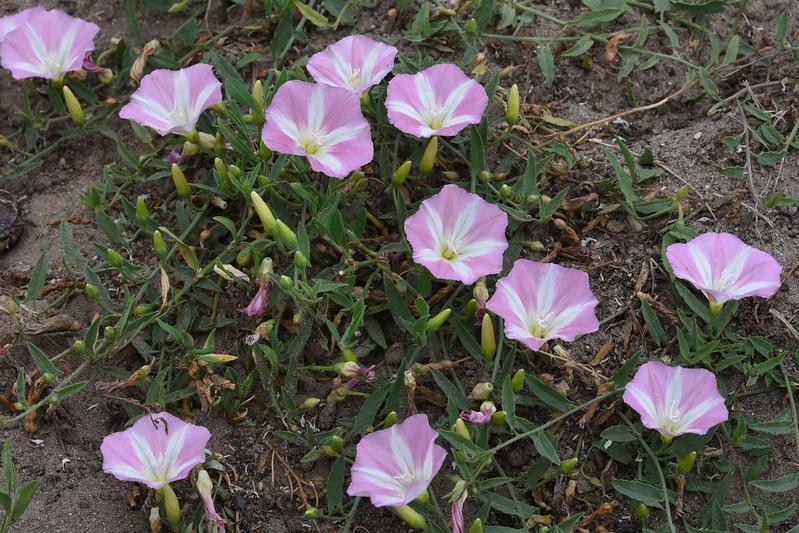

Field Bindweed: A perennial weed that can survive prolonged periods of drought.
Field bindweed is a long-lived perennial weed that forms a dense mat and has an extensive root system. The root system can reach depths of 20 to 30 feet and can give rise to new other plants. Weeds growing in optimal conditions can compete with the desirable plants and eventually compete them out.
Weed control in the case of field bindweed is not easy. The weed shows vigorous growth in fertile, rich soil, and its seed heads can stay dormant in the soil for up to 60 years. That is why weed control involves regular and constant vigilance.
Field Bindweed Quick Facts
| Scientific name | Convolvulus arvensis |
| Other names | Creeping Jenny, perennial morning glory, bellbine, sheepbine, cornbind |
| Weed type | Perennial vine |
| Height | Tall weed, reaching up to lengths of 2 meters or more |
| Flowering & Leaves | – Inflorescence consists of bell-shaped flowers that grow in dense clusters- Flowering occurs between June and September – Foliage consists of dark green leaves |
| Distribution & Habitat | – The flowering weed is native to Europe and Asia – Habitats include cultivated fields, gardens, lawns, pastures, roadsides, and waste places |
Common Stork’s Bill
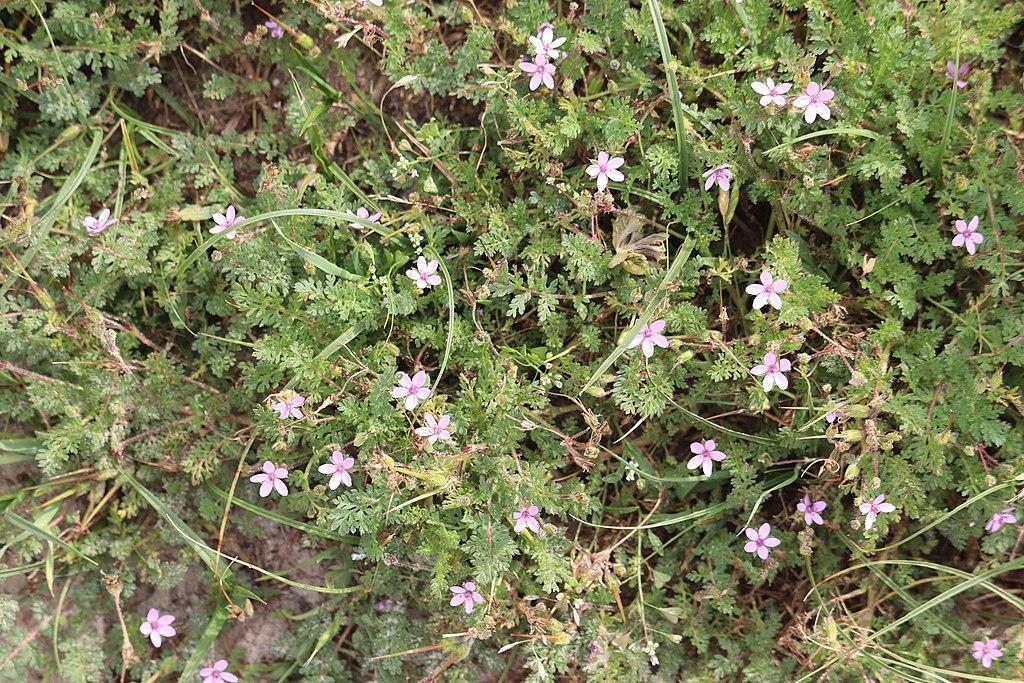

Common stork’s-bill: A weed of sandy and dry grassy areas.
The weed is named so because of the presence of seed pods that are shaped like Stork’s Bill. On maturation, the seed pods explode, sending the seed heads flying. These seed heads are feathery like dandelion seeds which helps them spread to great distances. Common stork’s bill is among the first plants germinating in late fall or spring.
If you see the above-ground growth of common stork’s bill, you should treat it with herbicides as soon as possible. The weed quickly advances through various growth stages and often escapes the herbicide application window. Also, only a few herbicides are usually effective against these lawn weeds.
Common Stork’s Bill Quick Facts
| Scientific name | Erodium cicutarium |
| Other names | Redstem filaree, pinweed, redstem stork’s bill |
| Weed type | Biennial weed |
| Height | 5 to 50 cm |
| Flowering & Leaves | – Inflorescence consists of pink flowers with dark spots on the basis – The weed blooms from May until August – Leaves are pinnate with hairy stems |
| Distribution & Habitat | – Native to temperate Eurasia, North Africa, and Macaronesia – Introduced and naturalized in North America – Habitats include deserts and arid grasslands |
Milk Thistle
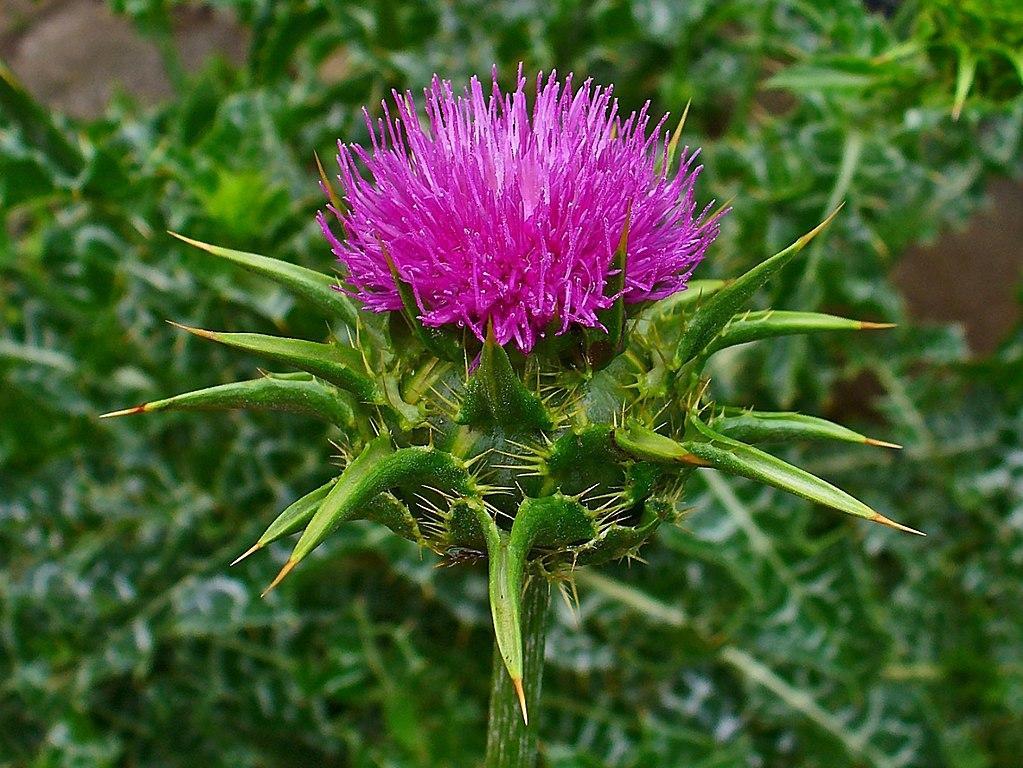

Milk thistle: An annual winter weed of wasteland areas.
Milk thistle is a prominent weed in disturbed areas such as roadsides, ditches, and fencerows. It can cause nitrate poisoning in cattle and other livestock animals. If not controlled, it can spread quickly, pushing out other plants in the area. It can form dense mats in heavily infested areas and produces 4 tons of weight per acre.
To control milk thistle plants in your lawn or garden, you can try uprooting them before the seed heads form. For heavily infested areas, foliar, broadleaf herbicides have proven the most effective. However, do not use non-selective herbicides as they can harm other plants in the area as well.
Milk Thistle Quick Facts
| Scientific name | Silybum marianum |
| Other names | Blessed milk thistle, Marian thistle, Mary thistle, variegated thistle, and Scotch thistle |
| Weed type | Winter annual |
| Height | 30 to 200 cm |
| Flowering & Leaves | – Inflorescence consists of pink flowers with a globose spiky appearance – Weed blooms from April and October – Foliage consists of shiny pale or dark green leaves |
| Distribution & Habitat | – Native of Southern Europe and Asia – Introduced and distributed throughout the world |
Field Madder
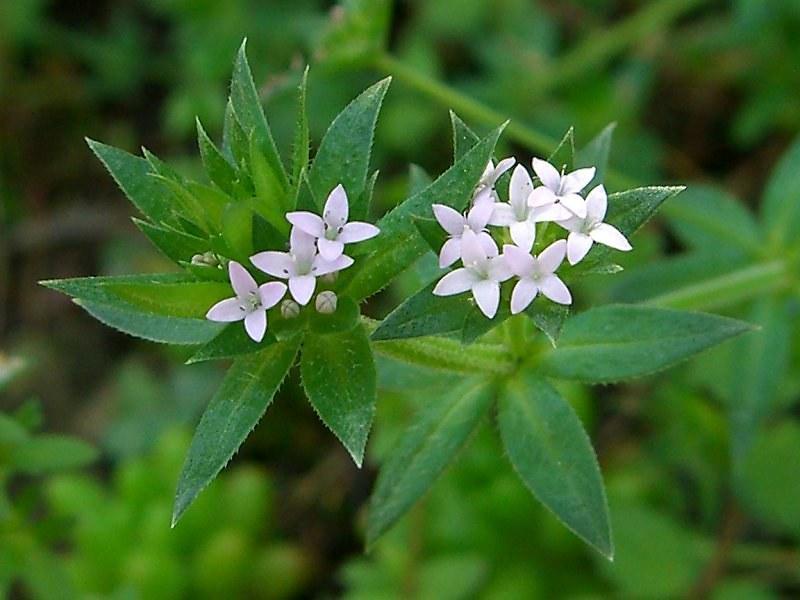

Field Madder: A widely distributed weed in many parts of the world.
Field madder is a weedy plant of lawns, gardens, parks, and other turf areas. The plant is also occasionally a weed of small grains. Field madder plants sprawl on the ground and makes dense mats. These thick growths can compete with other plants of the area, eventually driving them out.
To control the weed from spreading, you can try surface cultivation. However, if the infestation is present on a large scale, you might need to use herbicides.
Field Madder Quick Facts
| Scientific name | Sherardia arvensis |
| Other names | Sherardia, blue field madder |
| Weed type | Summer annual |
| Height | 5 to 30 cm |
| Flowering & Leaves | – Flowers bloom in spring – Inflorescence consists of light pink flowers with four petals – Leaves are bristly and present in whorls |
| Distribution & Habitat | – Distributed widely throughout the world – Common weed of turf areas |
Himalayan Balsam
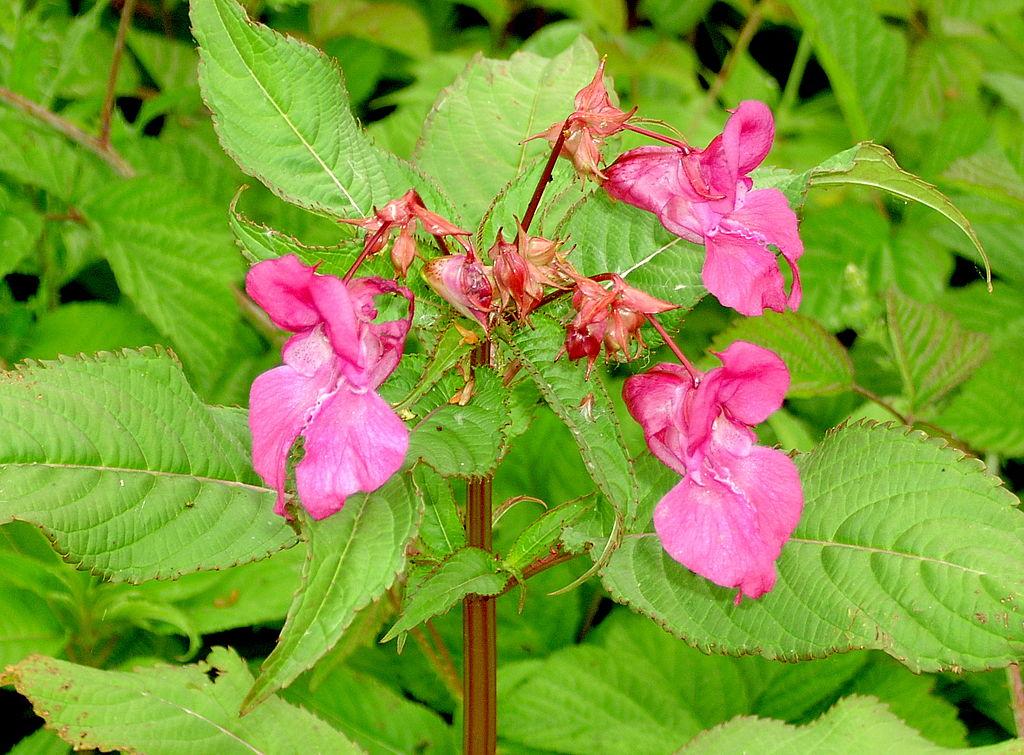

Himalayan Balsam: A weed that can also spread by water.
Himalayan balsam is a significant weed problem of riverbanks and wastelands. However, due to its invasive nature, the weed can also invade lawns and gardens, taking out other vegetation. Moreover, it is an explosive weed and can also be spread by water.
The primary method to control these explosive weeds is by uprooting them before they floor and setting seeds. However, for large infestations, you can also use chemical control options.
Himalayan Balsam Quick Facts
| Scientific name | Impatiens glandulifera |
| Other names | Kiss-me-on-the-mountain |
| Weed type | Annual |
| Height | 2 to 3 meter |
| Flowering & Leaves | – The weed flowers from June to October – Flowers are pink and have a hooded-shape – Laves are lanceolate and soft green in color |
| Distribution & Habitat | – Native to the Himalayas – Introduced and spread across much of the northern hemisphere now – Habitats include riverbanks, ponds, streams, etc. |
Spotted Knapweed
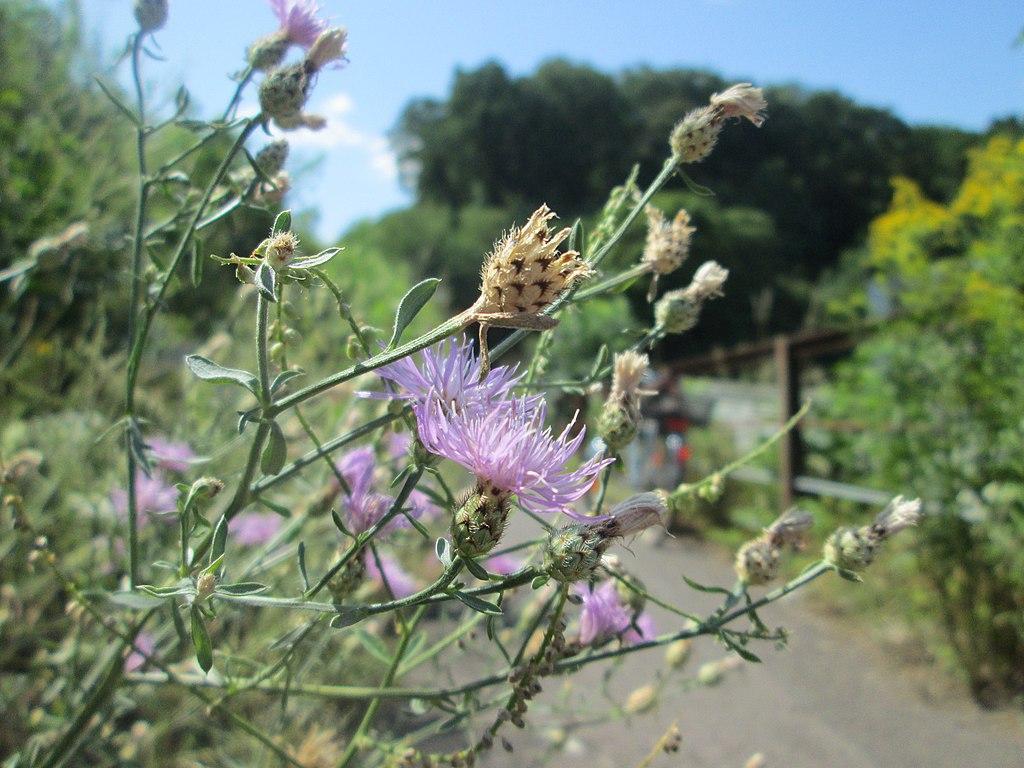

Spotted Knapweed: A prolific seed producer and contaminant of agricultural seed.
Spotted knapweed is listed as a noxious prohibited weed by the Agriculture Department of Michigan, USA. It is a prolific seed producer and can cause skin rash in some individuals as well.
The weed is also a contaminant of agricultural seeds. As a result, it has become a severe problem for pastures and rangeland in the western United States.
Because of its invasive nature, knapweed is extremely difficult to control. It can take years to achieve satisfactory results.
Spotted Knapweed Quick Facts
| Scientific name | Centaurea stoebe |
| Other names | Panicled knapweed |
| Weed type | biennial or short-lived perennial |
| Height | 8 to 40 inches |
| Flowering & Leaves | – Plant blooms from June to November – Flowers are vibrant pink with black-tipped sepals that look like spots – Leaves are hairy and deeply lobed |
| Distribution & Habitat | – Native to eastern Europe – Invasive in Canada, northwestern Mexico, and United States |
Sweet Joe-Pye-weed
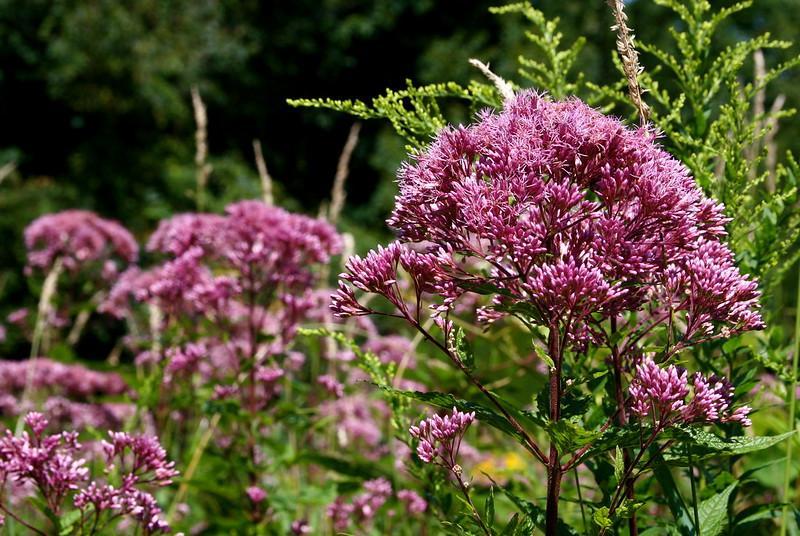

Sweet Joe-Pye-weed: An aesthetic plant native to North America.
It is an early fall blooming wildflower that is often present on the roadside ditches in sunny and moist areas. The weed is named after a man from New England that used this weed to treat people with typhus fever.
In addition to its medicinal properties, the weed has also been used to produce red and pink dyes for the textile industry.
The flowers of these plants produce very high numbers of seeds. So, getting rid of their flowers or preventing the weeds from spreading seed is the most effective way to control Joe-Pye weed. However, in large-scale infestation, chemical control options might become necessary.
Sweet Joe-Pye-weed Quick Facts
| Scientific name | Eutrochium purpureum |
| Other names | Sweet-scented Joe Pye weed |
| Weed type | Perennial |
| Height | Up to 8 feet |
| Flowering & Leaves | – Flowers bloom from mid to late summer – Flowers are purplish-pink and are produced in clusters – Foliage consists of whorled leaves |
| Distribution & Habitat | – Native to North America – Habitats include wet meadows, moist thickets, wooded slopes, and roadsides |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are the little pink flowers in my lawn?
If it is not a flower of a plant that you have planted yourself, chances are, it is a weed with pink flowers. Depending on the type of weed, these pink-flowering plants can ruin your beloved lawns and gardens. Therefore, it is better to get rid of them as soon as possible.
However, some of the pink-flowering weeds might also attract pollinators to the law and might be worth keeping around. Please read our guide above to find out about different pink-flowering weeds and whether or not they are worth keeping around.
What’s the difference between wildflowers and weeds?
From a bee’s perspective, they both are the same. However, as far as the human perspective is concerned, a wildflower grows in the wild, away from human settlements in its natural habitat, on its own. In contrast, a weed is a plant that is growing in the wrong place or where it is not supposed to grow.
However, these definitions are often relative, and one person’s wildflower can be another person’s weed.
How do you get rid of weeds with pink flowers?
It will all depend on the type of weed you are dealing with, the life stage at which you found the weed, and the severity of weed infestation. Sometimes, simple hand pulling might suffice, and other times, you might have to use chemical control methods to prevent weeds from taking over.
Sources For Further Reading
- Pink flowers – Cooperative Extension: Maine Wild Blueberries – University of Maine Cooperative Extension. (2022). Retrieved 11 April 2022, from https://extension.umaine.edu/blueberries/weed-images/herbaceous-broadleaf-weeds/pink-flowers/
- Gardens: weeds to love and loathe. (2020). Retrieved 11 April 2022, from https://www.theguardian.com/lifeandstyle/2020/jan/11/good-cop-bad-cop-weeds-to-love-and-loathe
- Pink Purslane. (2022). Pink Purslane | NC State Extension Publications. Retrieved 11 April 2022, from https://content.ces.ncsu.edu/pink-purslane
Now that you know about weeds with pink flowers, make sure to also read our other articles:
Is Sand Good For Lawns? (and What Type of Sand for Lawns Is Best)
Spiky Weeds That Can Ruin Garden Beds (And How To Get Rid Of Them?)