Flea beetles are the most common pests of the cole crop group and are active in late spring and early summer. These tiny jumping pests create serious trouble for vegetable growers.
Unlike sap-sucking plant pests (whiteflies, aphids, mealybugs, and scale insects), flea beetle feeding damage includes chewing foliage and making irregular holes in leaves. In other words, flea beetles impact the edible parts of plants.
It is challenging to manage flea beetles through chemical insecticides because they overwinter as adult flea beetles in leaf litter. So, combining cultural and chemical control methods is best to eliminate flea beetles.

Healthy vegetable garden—free from flea beetle and other garden insect pests
In this guide, we’ll discuss flea beetles in detail and how we can get rid of this vegetable pest effectively?
What are Flea Beetles?
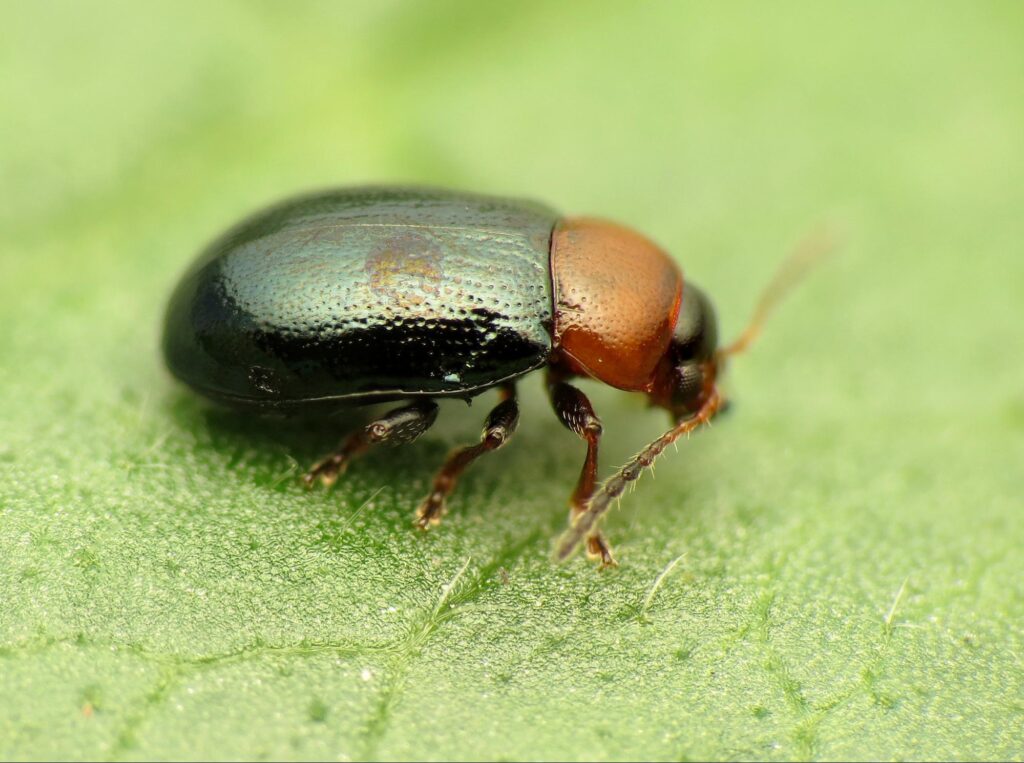

A flea beetle on the host plant leaf
Flea beetles are tiny jumping insects (similar to fleas) from the order Coleoptera and the family Chrysomelidae. They are strong fliers and have long hind legs. Therefore, they can jump over long distances.
Flea beetles appear as dark and metallic shiny pests that attack the foliar crops of brassica and Solanaceae. Their favorite time of the season is late spring and early summer and are commonly found in home gardens. They are the voracious eaters of foliage, and under favorable circumstances (host plant abundance), the flea beetle can decimate the cole crops and lead to severe economic losses.
It is vital to devise appropriate control strategies before these aggressive vegetable crop pests cause damage to your favorite plants.
RELATED: Black Beetles 101: Types and A Comprehensive Identification Guide with Pictures
Most Common Flea Beetles
The flea beetles are a diverse group of the insect family Chrysomelidae. However, the following are the most flea beetles in the United States:
- Striped flea beetle (Phyllotreta striolata)
- Potato flea beetle (Epitrix cucumeris)
- Crucifer flea beetle (Phyllotreta cruciferae)
- Spinach flea beetles (Disonycha xanthomelas)
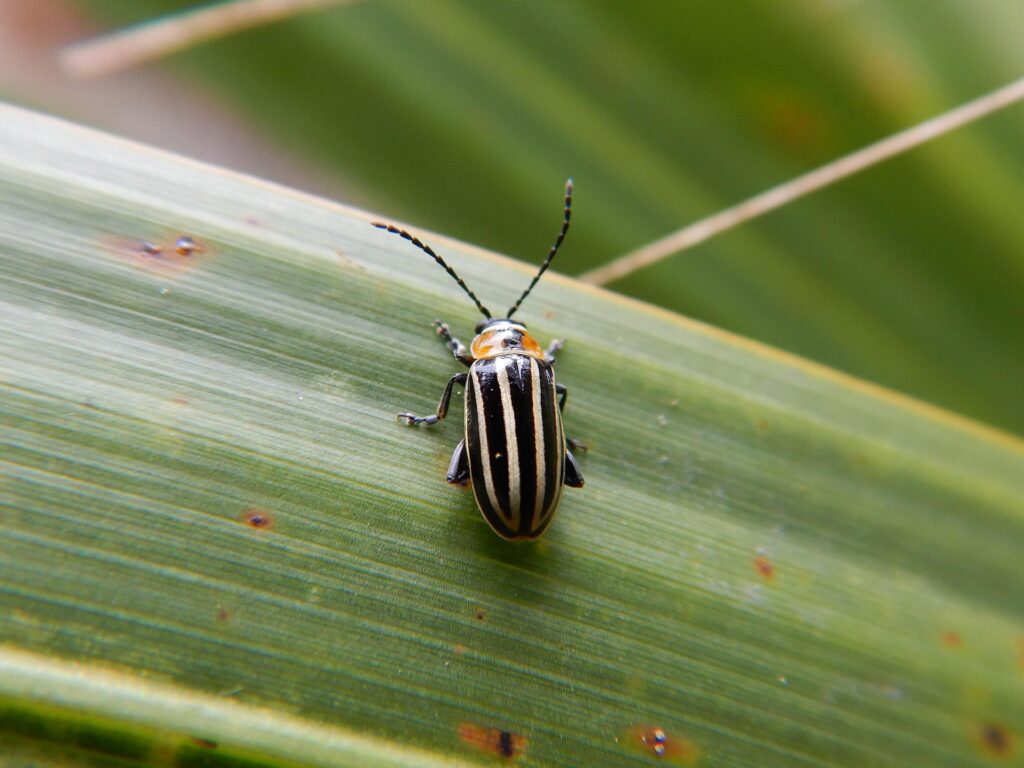

Pale striped flea beetle—a voracious eater of leaves with a broad host range
All flea beetle species are host-specific, which means they feed on particular host plants. At the same time, the palestriped flea beetle feeds on various plants like squash, beans, lettuce, potato, sunflowers, and maize.
Identification of Flea Beetles Feed Damage
Flea beetles have chewing mouthparts and prefer to gnaw on plant roots and leaves. In addition to that, they quickly go unnoticed due to their smaller size and can only be visible when they take long jumps when disturbed.
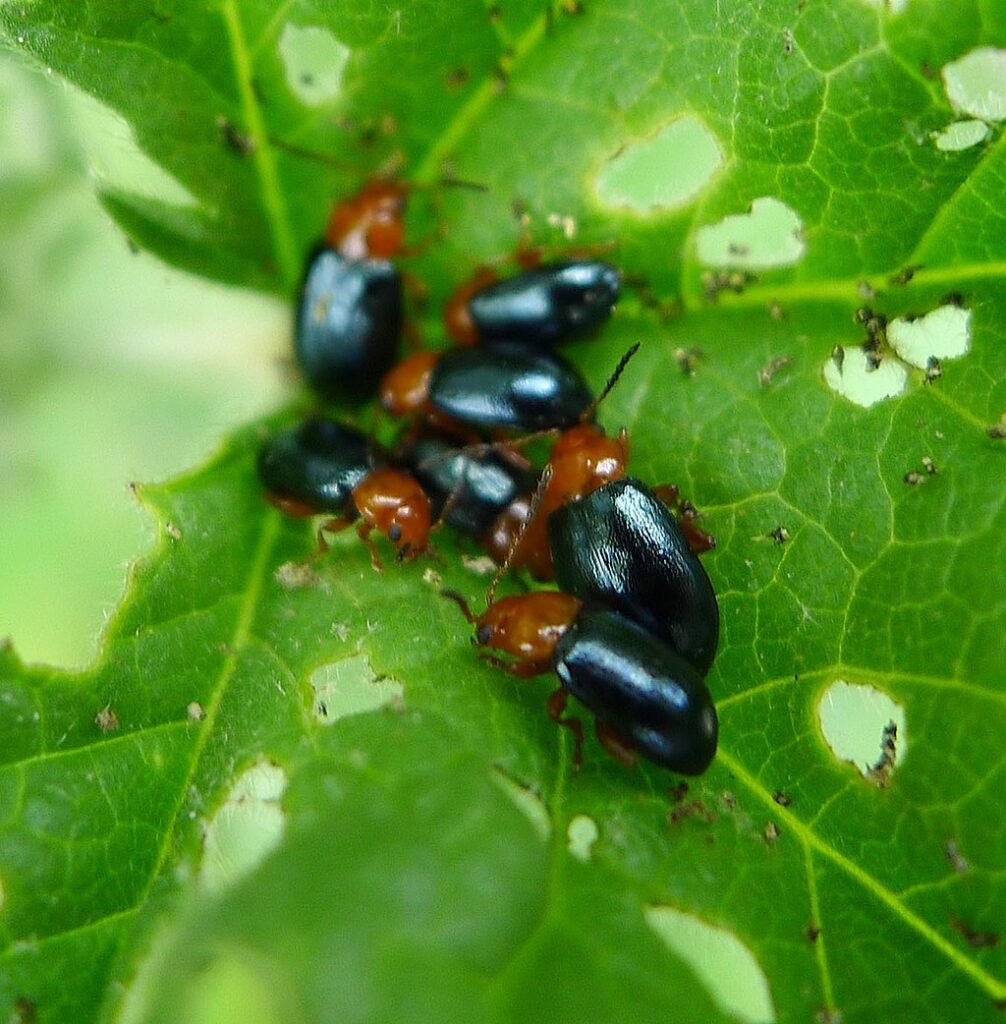

A group of mallow flea beetles busy munching on host plant leaf
The flea beetle adults eat plant leaves and cause small pit holes in them that resemble shothole wounds. While the larvae of flea beetles feed on plant roots and others adapt to chew on plant leaves.

Flea beetle injury on host plant leaf—the feeding damage resembles shothole
Young seedlings and plants are more susceptible to flea beetle feeding damage. It leads to growth reductions in leafy vegetables and ornamental plants. Under heavy infestations, the adult flea beetles feed, causing patchy growth (plants cannot sustain larva feeding damage and die) in a vegetable garden.
The flea beetle damage, particularly by the western black flea beetle, including
- They feed on host plant leaves and stems.
- The western black flea beetle damage produces shallow pits and irregular holes in leaves. These pit holes harm the plant’s food-making process.
- The plants started from seeds are more prone to feeding damage and succumb to flea beetle injury, while the transplants can sustain the injuries. However, severe infestations lead to the death of both seed-grown plants and transplants.
- The western black flea beetle larvae cause little to no damage to host plants except potato flea beetle larvae feed. The tuber flea beetle larvae feed leaves while the economic damage is mainly done to tubes because these larvae cause blemishes and produce holes in tubers.
RELATED: Identification and Control of Darkling Beetles by Natural and Chemical Ways

The western black beetle damaged leaves
Host Plants of Flea Beetle
The host plants for flea beetles include eggplants, squash, cabbage, potato, tomato, maize, turnip, radish, beans, and beets.
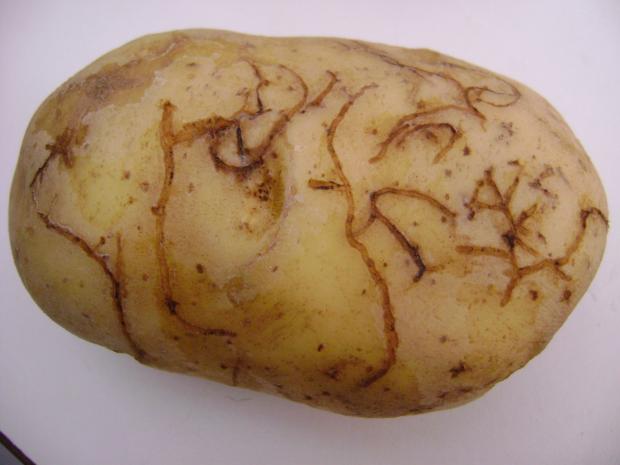

Blemishes on potato tuber—economic damage and trouble for growers
Note: Flea beetles are also responsible for transmitting bacterial pathogens such as bacterial wilt in corn.
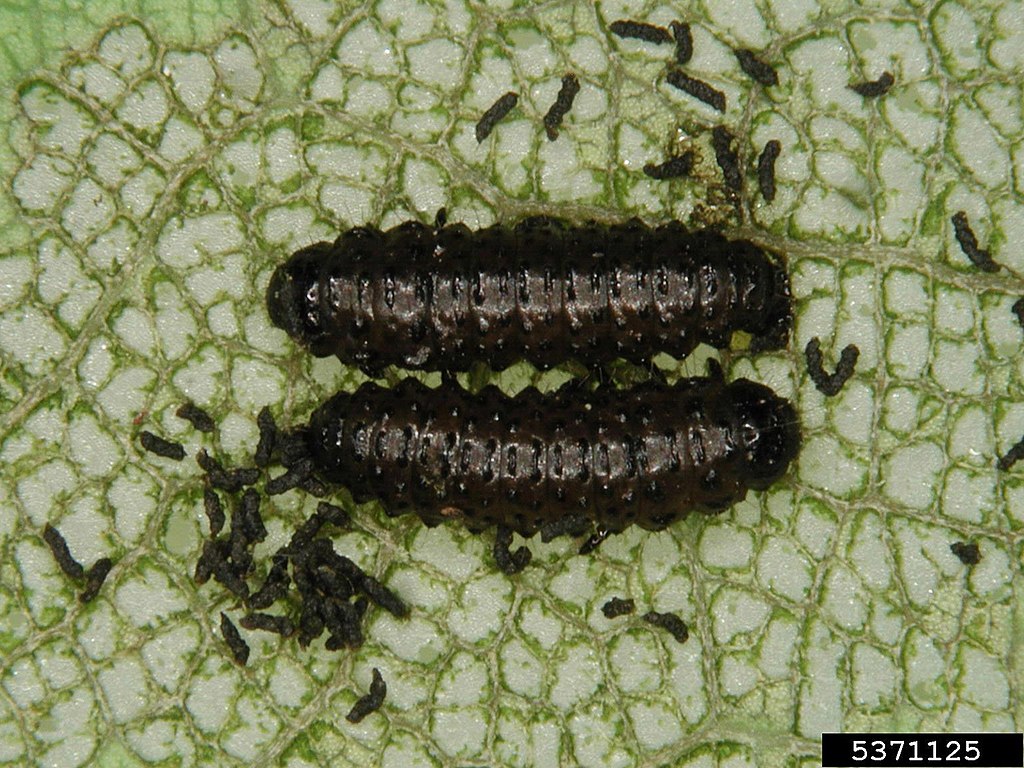

Oak flea beetle larvae
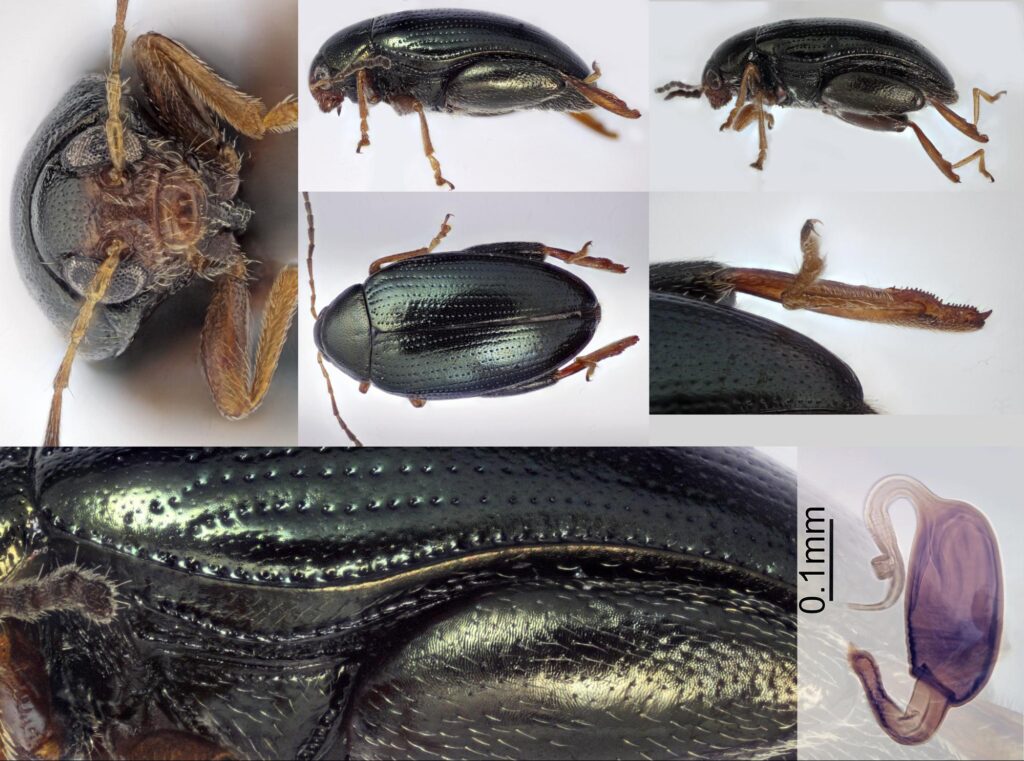

Cabbage flea beetles
Life Cycle of Flea Beetle
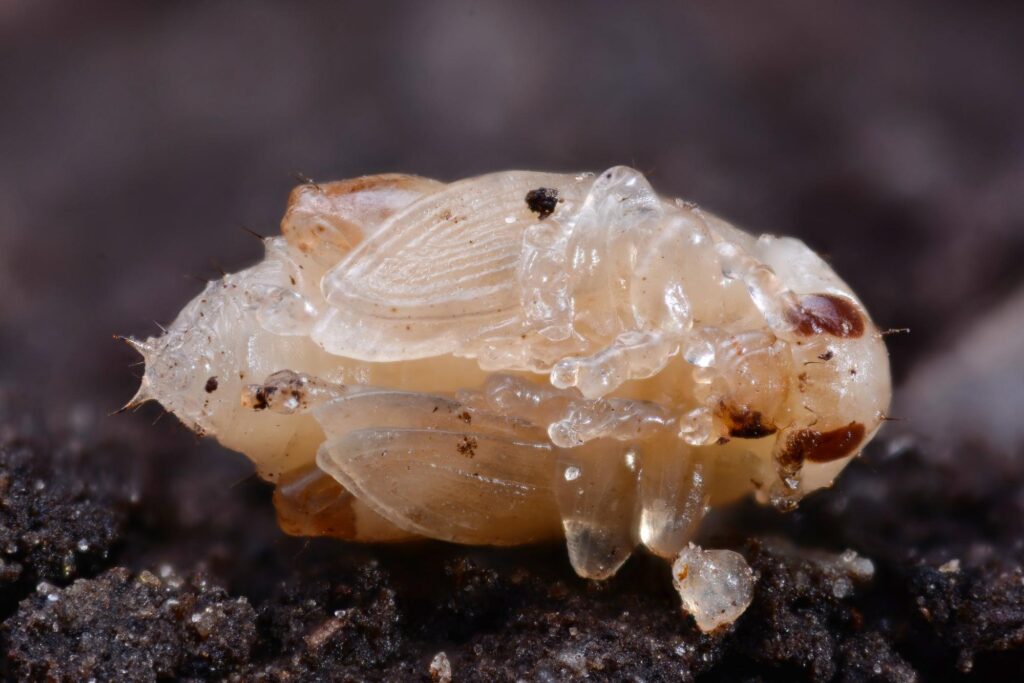

Pupa of spinach flea beetle
The life cycle of flea beetles comprises four stages, from eggs to adults. The adult flea beetles overwinter in garden debris and the soil and become active in late spring and early summer. Because at this time of the season, the host plants are abundant.
The potato flea beetle lays eggs at the base of the plant on or in the soil. The eggs are small and hatch within seven to fourteen days. After hatching, larvae feed on various plant parts, especially the leaves and roots.
Within two weeks of feeding (11 to 13 days), the larvae pupate in the soil near the plant base before emerging as adults. The adult flea beetles are shiny black with yellow color stripes on the body (palestriped flea beetle) and are active throughout the summer.
Note: The flea beetles can have three to four generations per year, depending on the availability of host plants and weather conditions.
How to Get Rid of Flea Beetles on Vegetable Crops?
The significant flea beetle damage is on foliage and plant roots. Thus, making it difficult for growers to get the rewards of their struggle. Because flea beetle damage
- Stunted plant growth
- Wilting and withering of host plants
- Shotholes in foliage destroy the photosynthesis
So, the early detection and employment of integrated pest management approaches are vital to preventing these harmful beetle’ cole crops.
Flea Beetle Management by Monitoring
Flea beetles are more damaging in spring. So, timely damage detection is critical, and monitoring of vegetable crops for flea beetles plays a crucial role in their effective management.

Beetle traps to determine the populations of flea beetles
- Use yellow sticky traps to capture the adult jumping flea beetles. Place them throughout the garden, rows 15 to 30 feet apart. These traps will provide information about infestations and help in reducing flea beetle populations.
- Regularly check your crops mainly for crucifer flea beetle damage and pale striped flea beetle.
- Take rapid action when you notice five flea beetles per plant and treat your seedlings right away for flea beetle control.
- If more than 10 to 30% of the foliage of your vegetable crops has dropped off, then pull out damaged plants and discard them.
- Use floating row covers to prevent the seedlings from feeding damaged flea beetles. These row covers are incredibly beneficial during spring and summer and prevent huge losses.
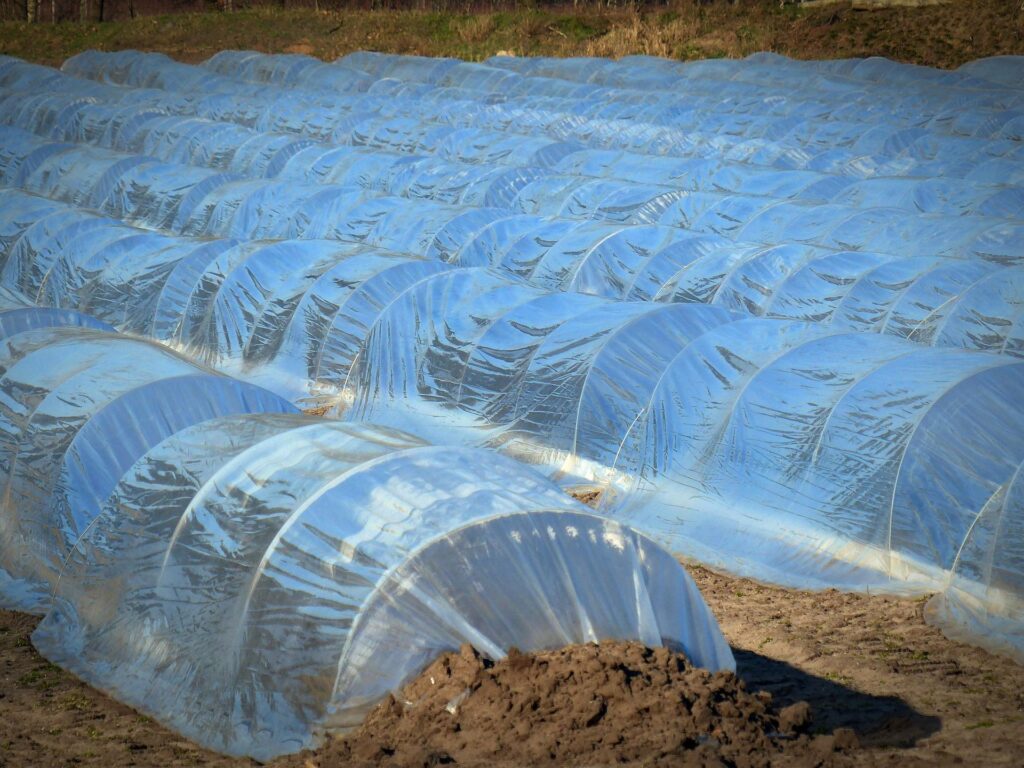

Cabbage cultivation and protection from garden pests (adult beetles) through row covers
Cultural Control of Flea Beetles
- Remove plant litter, dead fallen leaves, and infested plant parts from your garden; otherwise, these decaying plant materials will provide flea beetles a haven for winter survival.
- Control weeds from your garden to protect plants because they can serve as alternate hosts and hiding places for adult flea beetles and larvae.
- Use row crops to keep the beetles out from your vegetables.
- Plant trap crops before the main crops to avoid damage. So, first plant radish crops then turnips. Because the flea beetles attack the earliest and tallest crop available, spray them with a mild toxic pesticide. Make sure the beneficial insects and birds are not there.
Biological Control of Flea Beetles
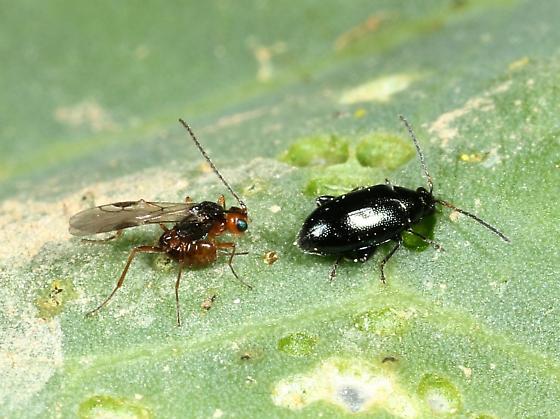

A parasitic wasp is ready to munch on a flea beetle
The beneficial insects are also a practical approach to getting rid of flea beetles. For example, Microctonus vittatae is a hymenopterous wasp that lays eggs on or in flea beetles and kills them. These parasitic wasps actively parasitize on crucifer flea beetles and pale striped flea beetles.
Apply Diatomaceous Earth to Reduce Flea Beetle Damage
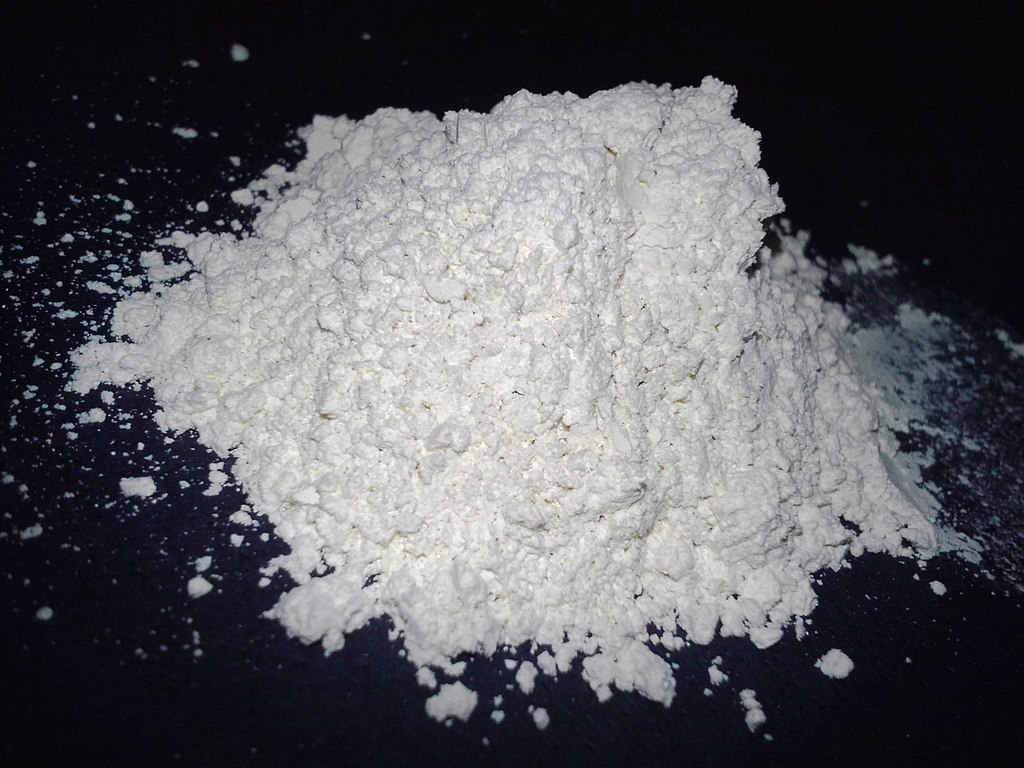

Diatomaceous earth to kill flea beetle larvae and eggs
Diatomaceous earth provides long-lasting protection against all species of flea beetles. It comprises fossilized ocean animals and can be used as a soil drench to kill the overwintering adults of flea beetles, their eggs, larvae, and pupae.
Diatomaceous earth kills the flea beetle generations by puncturing their outer body covering when insects crawl over it. However, make sure to reapply after rain to ensure its proper functioning.
Use 70% Neem Oil to Kill Flea Beetles
Neem oil spray comes in the least toxic chemicals with excellent benefits. It is because,
- Neem oil spray can kill insect pests at all stages of their life cycle
- Effective throughout the growing season
- It kills insects, fungi, and mites
Mix one tablespoon of 70% neem oil per gallon of water and mild dish soap. Pour the solution into a spray bottle and spray on your garden vegetables, fruit trees, and houseplants.
Note: Ensure to thoroughly saturate the leaf surfaces and apply in the early morning and evening to protect beneficial insects.
Use Surround WP Crop Protectant

Effective against a variety of pests
Surround WP crop protectant is effective against various pests such as powdery mildew, downy mildew, aphids, whiteflies, spider mites, mealybugs, flea beetles, and psyllid. It is made up of modified kaolin clay and sprayed as a liquid on leaves, stems, and near the plant base.
The water evaporates, leaving behind a thin powdery layer of WP crop protectant which works best as
- Small kaolin clay particles attach to the insect body and play a vital role in repelling them.
- The flea beetles find powdery films on leaf surfaces unsuitable for feeding and egg-laying. In this way, insects do not rest on leaves.
- The white powdery covering protects plants from sunlight and improves their health, ultimately resisting the tuber flea beetle.
Chemical Control to Prevent the Economic Loss
When high populations of flea beetles threaten the vegetable and fruit crop’s survival, it is crucial to apply chemicals to control them within hours.
Spray plants with pyrethrin, cypermethrin, and cyhalothrin. These chemicals at the seedling stage control the flea beetle invasion throughout plant growth.
Frequently Asked Questions
Do Flea Beetles Go Away?
The management of flea beetles involves the combination of different practices such as cultural, chemical, and biological control. By employing these control methods in your garden, you can easily control the flea beetle. These practices comprise,
- Identify flea beetles by monitoring (use yellow sticky traps)
- Introduce beneficial insects such as parasitic wasps (these wasps chase and locate the flea beetles to lay eggs on or in them)
- Remove garden debris and crop leftovers to discourage hiding places for flea beetles
- Spray plants with neem oil
- Surround plants with WP crop protectant near the base to discourage egg-laying sites for flea beetles
- Apply diatomaceous earth on soil and leaves to kill flea beetles instantly
What Do Flea Beetles Look like?
Flea beetles look like tiny beetles which appear shiny black, brown, and blue. At the same time, some species of flea beetles have pale stripes and spots. On host plants, they look like tiny black spots. They are active during summer and late spring and feed on the leafy parts of spinach, cabbage, radish, carrots, eggplants, potatoes, squash, beans, beets, and tomatoes.
Do Coffee Grounds Deter Flea Beetles?
Coffee grounds are effective in repelling flea beetles and other indoor and garden pests, but for the long term, the control uses diatomaceous earth and WP crop protectant.
While WP crop protectant works by repelling the flea beetles, it creates a white powdery covering on the leaf surface, which blocks the foliage eating of host plants. The WP crop protectant also protects plants from sunlight and improves plant health.
What are the Little Black Bugs in my Garden?
These minor black bugs are flea beetles that appear in late spring and early summer and create trouble for vegetable gardeners. Because these black jumping beetles feed on various host plants and damage young seedlings, their roots, and first true leaves, they create small irregular holes in the leaves of infested crops and cause economic losses.
Sources for Further Reading
- Flea beetles in home gardens. (2022). UMN Extension. Retrieved April 28, 2022, from https://extension.umn.edu/yard-and-garden-insects/flea-beetles
- Flea beetle. (n.d.). Missouri Botanical Garden. Retrieved April 28, 2022, from https://www.missouribotanicalgarden.org/gardens-gardening/your-garden/help-for-the-home-gardener/advice-tips-resources/pests-and-problems/insects/beetles/flea-beetle.aspx
- Colorado State University Extension. (2019, January 14). Flea Beetles – 5.592. Retrieved April 28, 2022, from https://extension.colostate.edu/topic-areas/insects/flea-beetles-5-592/
Hope you like our tips on how to control flea beetle. Also, check out our other articles:
What are the Best Practices to Get Rid of Thrips on Houseplants?