There are few types of plants as recognizable as bamboo. This iconic plant is known for plenty of reasons, from its peculiar shape to its versatile uses – and of course, bamboo is famously the food of choice for pandas! There are over 300 species of bamboo worldwide. Mostly found in tropical regions, the bamboo plant is native to East Asian and South American countries, including Japan, Chile, Taiwan, and (most notably) China. For those interested in learning how to propagate bamboo, understanding its diverse species and natural habitats is essential.
Bamboo is a renewable resource that can be used for a variety of purposes. From building materials to furniture, from paper to food, bamboo is one of the most versatile and useful plants in the world.
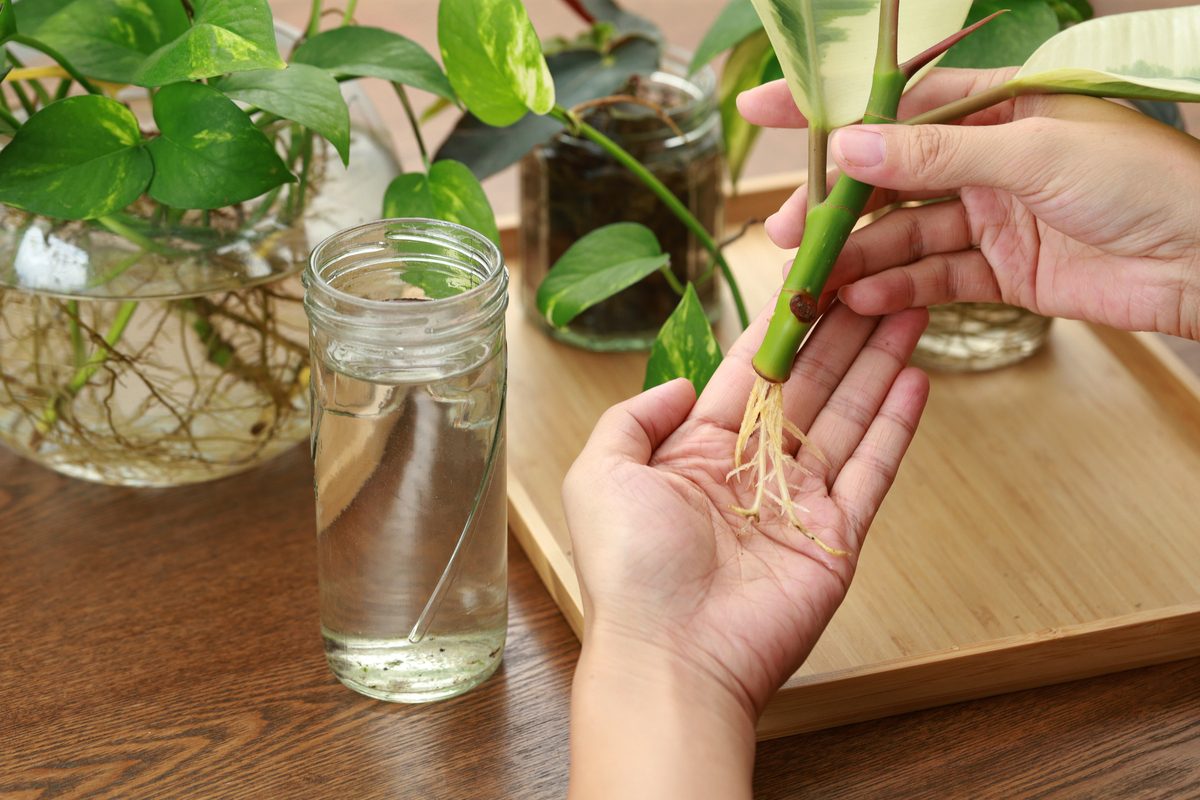

That’s not to say you need a tropical climate if you want to grow bamboo, however, and with a little effort you can propagate your own bamboo practically anywhere.
If you don’t know where to even start, then you’re in luck – this handy guide has everything you need to know about propagating and cultivating bamboo at home!
This article will take you through some simple and easy methods for propagating bamboo, as well as cover what conditions and nourishment your bamboo plants will need.
Not only that, but we’ve also included an FAQ section to answer any questions you might have.
What Is Bamboo?
As mentioned above, bamboo has all sorts of uses. But what exactly is bamboo?
Bamboo is actually a grass-like plant, belonging to the Poaceae family. In Chinese culture, bamboo symbolizes strength and stability.
In fact, bamboo is so flexible that it can withstand extreme weather and pressure without breaking.
One of the most notable things about bamboo is its shape. Bamboo plants grow in tall, thin stalks, with some varieties reaching heights of over 100ft while measuring less than a foot in diameter.
Bamboo stalks are also hollow, which improves the plant’s stability and strength while reducing its weight dramatically.
Bamboo grows in dense pockets in forests known as groves, with the long stalks hiding under a thick canopy of leaves above.
Bamboo’s purposes are almost endless. The plant is used as a construction material (it is 2-3 times stronger than regular timber), its shoots can be cooked and eaten, and it can be converted into all sorts of useful materials including paper, fabrics, and renewable biofuel.
Not only that, but this beautiful plant makes the perfect addition to any garden or home.
How To Grow Bamboo?
With your bamboo trivia up to snuff, now it’s time to grow it! There are three main methods used to propagate bamboo: using cuttings from the roots, using cuttings from young plants, and growing them from seeds.
Here we’ll cover each method with some simple step-by-step guides.
Propagating Bamboo Using Root Cuttings

Selecting Your Cuttings
Before you can plant your bamboo roots, you first need to pick out the ones you want to use.
The roots of bamboo come in two forms; running bamboo has long and stringy roots that grow outward from the plants, while clumping bamboo has more compact roots that stay close to the plant and form ‘clumps’ (hence the name).
Running bamboo is easier to gather and propagate trimmings from, as their roots (otherwise known as rhizomes) can be collected, cleaned, and separated more easily.
The long, thin strands spread out separately from each other, and you can gather and trim them without any hassle.
Clumping bamboo, on the other hand, is much trickier to gather trimmings from. The dense clusters of rhizomes are hard to separate and you need to put in more work to get your trimmings.
While running bamboo is easier to get root cuttings from, you can use rhizomes from either type of bamboo to propagate your own.
RELATED: What Are the Best Practices to Get Rid of Destructive Leaf Miners?
Prepare For The Transplant
Don’t be alarmed – transplanting might sound intimidating, but it just refers to the process of removing the root cuttings from the ‘mother’ plant and replanting them in their new pots.
All you need to do to prepare is get your pots ready and make sure the mother bamboo is in good condition.
You’ll need some new pots to plant your cuttings in. Aim for a one-gallon pot for each rhizome you’re propagating.
Depending on the size of the root you’re planning on removing and the species of bamboo, you may need a bigger pot like a 5-gallon.
Each piece of root you’re propagating will need its own pot so it will have enough room to grow.
Preparing the right soil beforehand is also a good idea. Most bamboo likes light and rich soil that drains well. You want something that will retain moisture but also has good drainage.
Soils with lots of clay or moisture are poor choices for bamboo, as it is easy for them to get waterlogged.
Along with the soil, get some high-nutrient compost to help your bamboo grow to its full potential.
The day before you harvest the rhizomes, water the mother bamboo. This will leave it well-watered without the soil being wet and soggy, and will make it much easier to gather healthy root cuttings.
Gathering The Root Cuttings
With everything prepared, now you harvest your root trimmings. First things first, gather your tools.
You’ll need a small trowel to dig up the rhizomes, and some garden clippers to cut the sample. You should also wear a pair of gardening gloves for some basic protection.
Look for a rhizome that is far away from the main bamboo plant. Running bamboo can have roots stretching for several feet, while clumping bamboo will have roots much closer.
If the mother bamboo is already in a pot then it will be much easier to find the roots.
Dig up a root and follow it towards the plants, keeping it as isolated as possible. Look for healthy sections along the root – you’ll want strong, white rhizomes with small tendrils and buds growing off them.
Use your clippers to cut off a section of root around 4-6 inches long. You might need to settle for smaller cuttings if the mother plant is in its own pot as the length of the roots will be reduced.
Planting And Propagating
Transfer the cuttings to their new containers as soon as possible after trimming them. Cover the roots completely in around 2-3 inches of soil.
The root itself should be parallel to the ground, and the shoots and buds need to point upwards.
Water the roots straight away, keeping the dirt moist but not wet. Use a spray bottle to keep the soil at the perfect saturation.
Keep watering and nurturing the cuttings, and you’ll soon see them start to grow into new bamboo!
Propagating Bamboo Using Cuttings From Bamboo Plants
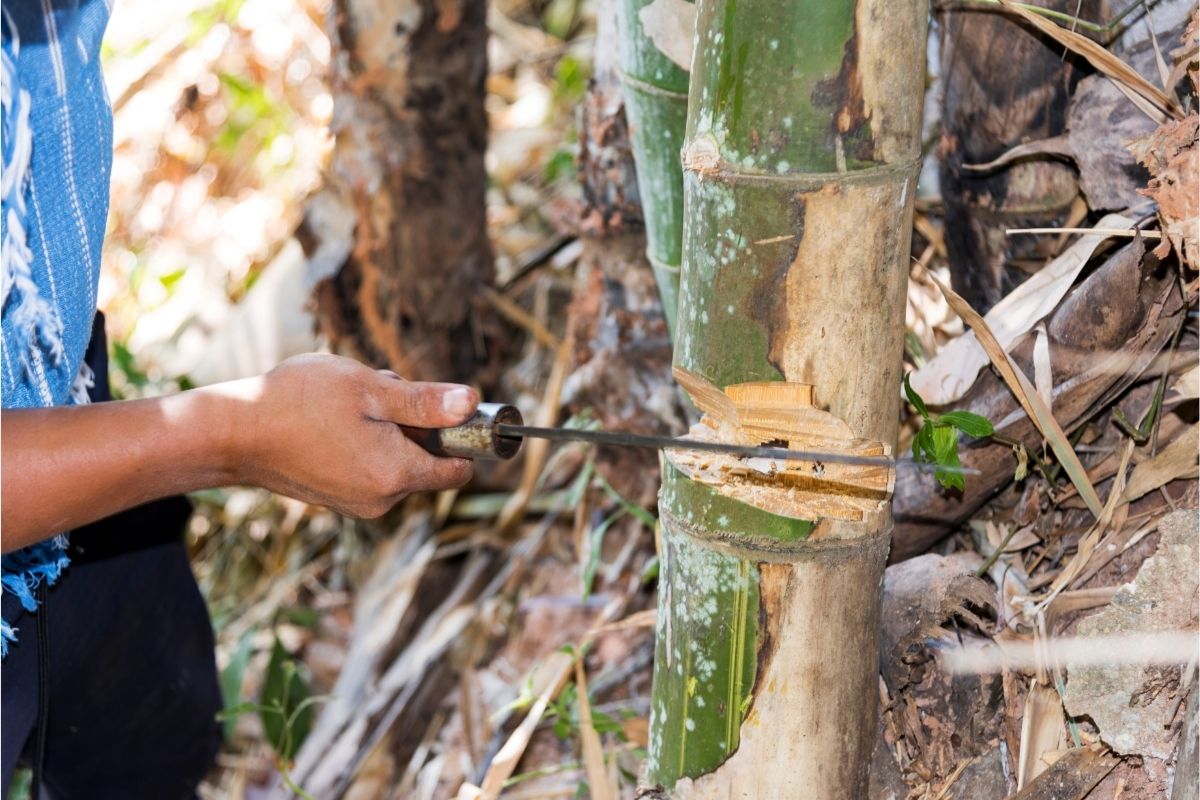

Gather Your Cuttings
This is a much easier method of propagation than using root cuttings, but you’ll need more material to grow each new plant.
You’ll need to get samples from younger bamboo, around 1-2 years old; at this age, the bamboo will be healthy and ready to grow, and the parent plant will heal easily.
Bamboo plants aren’t perfectly smooth, and they will have smaller branches coming off from the sides.
You’ll typically find these branches growing from ‘nodes’, with several young branches stemming from each node. To gather your cuttings, these are what you need to trim.
Using a sharp knife or small saw, cut the branches away from the main plant. Only cut around 75% of the branch away, leaving a little remaining on the node.
This will let the parent plant continue growing branches uninhibited.
Transplant The Cuttings
For this step, you’ll need to follow pretty much the same process as with root cuttings. Keep the cuttings wet, and plant them in pre-prepared pots one-apiece.
To help them grow, score a shallow cut along the bottom of the branch where it goes into the soil.
The bamboo should be facing upward, and needs to be buried with between 1/2 to 3/4 of its length submerged in the soil.
Keep the bamboo well-watered, and you can see much faster results than with fresh roots. This is a less reliable method, however, and not every branch will grow into a new plant.
Related: How To Get Rid Of Spider Mites For Good? A Comprehensive Guide
Propagating Bamboo Using Seeds

Get Your Seeds
This is the slowest method of growing bamboo, and you may struggle to even find bamboo seeds to begin with.
Bamboo seeds are very small and most species of bamboo take many years before they flower, meaning that the seeds can be hard to get your hands on.
Your best bet is to visit a garden supply store or try to order the seeds online. Alternatively, if you know a cultivar who grows bamboo they might be able to supply you with seeds.
Prepare The Soil
Bamboo seeds need slightly different soil to other propagation methods.
While you still want a high-nutrient and aerated soil, you should also add some other form of substrate to help keep the seeds in the best condition.
Coconut fiber, sphagnum moss, and other loamy substrates are a great choice for your seeds.
Plant And Propagate
Sprinkle some seeds into each pot. Start out with small planting trays with individual sections, as you can transfer the seedlings into their own pots when they grow a bit.
Keep the soil moist, taking extra care not to soak the seeds; this is even more important than with other propagation methods as it’s easy to drown sprouting seeds.
As the seeds sprout and the seedlings start to grow, transfer them into their own pots. Continue to keep them watered, and avoid keeping your seedlings in direct sunlight.
While this method takes longer, you’ll have a more consistent success rate and a whole batch of unique bamboo plants!
Frequently Asked Questions

How Long Does It Take Bamboo To Grow?
This depends on the variety of bamboo you’re growing, but bamboo generally has a much faster grow-time than other plants. In fact, bamboo holds the title of fastest-growing plant in the world.
Some species of bamboo can grow several inches per day after they germinate, and the fastest-growing bamboo has been recorded as growing over 30 inches per day!
Don’t worry about dealing with massive bamboo plants, however, as home-grown bamboo in pots typically doesn’t reach these insane speeds. That said, you’ll still be able to notice your bamboo growing on a day-to-day basis if you measure it.
How Often Should I Water My Bamboo?
Bamboo needs aerated soil that holds moisture but doesn’t get too wet. As mentioned before, a misting bottle is the best way to keep your bamboo hydrated without saturating the soil.
You should give your bamboo around 1-2 inches of water per day. If you notice the soil is too dry and the plant is wilting, give it some more water.
Contrastingly, if the soil is getting waterlogged you should give it less water or water it less frequently.
Do I Need To Prune Bamboo?
Pruning bamboo isn’t necessary, but you might want to tidy up loose branches and leaves to help maintain the appearance of your plant.
If you’re growing multiple bamboo plants nearby, pruning will also help you control and keep track of each plant’s growth.
Don’t overdo it with the pruning, as your bamboo will need leaves to absorb sunlight and stay healthy. Trimming too many branches also risks harming your bamboo, especially as it grows older.
You should also avoid cutting the tops off your bamboo plant, as this will stop the plant from growing vertically ever again.
Final Thoughts
Growing bamboo indoors at home is an incredibly rewarding experience, and with so many different methods you’re sure to find something that works for you.
As long as you follow these simple steps and give your bamboo the care and nurture it needs, then you’ll be able to start growing your own miniature grove in no time. Good luck!