Darkling beetles belong to the family Tenebrionidae and order Coleoptera. The Tenebrionidae is the most prominent beetle family with almost 20,000 species. These are also known as litter beetles because they feed on dead leaves, cloths, dry grains. Darkling beetle are considered a significant pest in the agriculture industry. They are the most aggressive pest of dry stored grains.
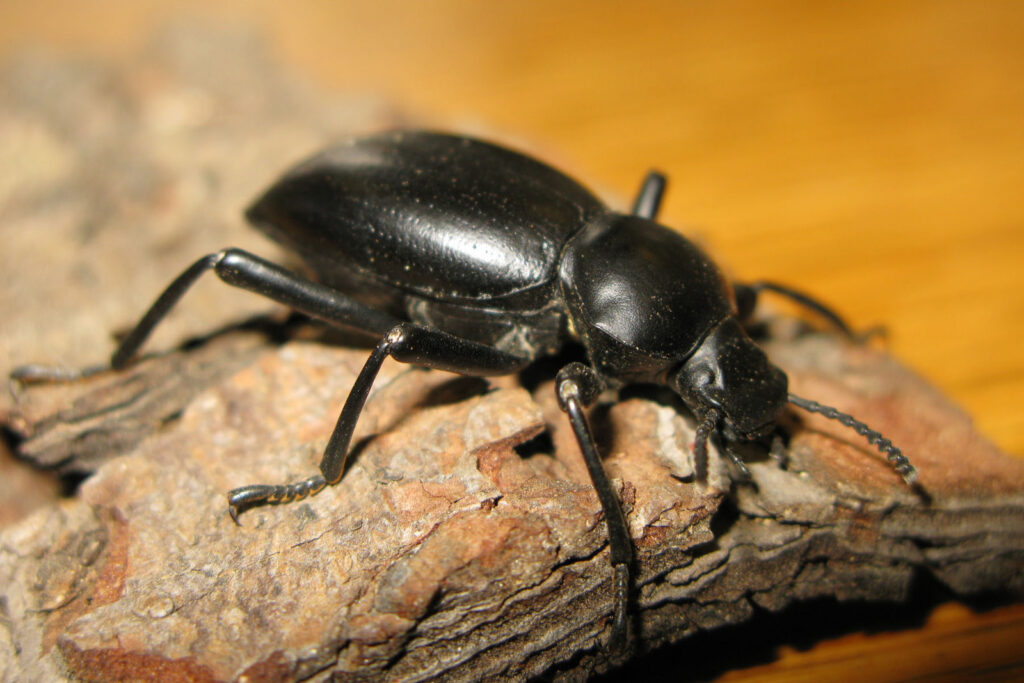

The name of darkling beetle comes from their habit of hiding during the day and emerging at night for feeding. They hide under fallen leaves, soil cracks, caves, and bins (grain storage bins).
Adult darkling beetles are small to medium-sized and of dark brown to reddish-brown. They have shiny markings on the entire body and have a body size of 2 to 19 mm. The darkling beetle is often confused with flour beetle due to its reddish-brown appearance.
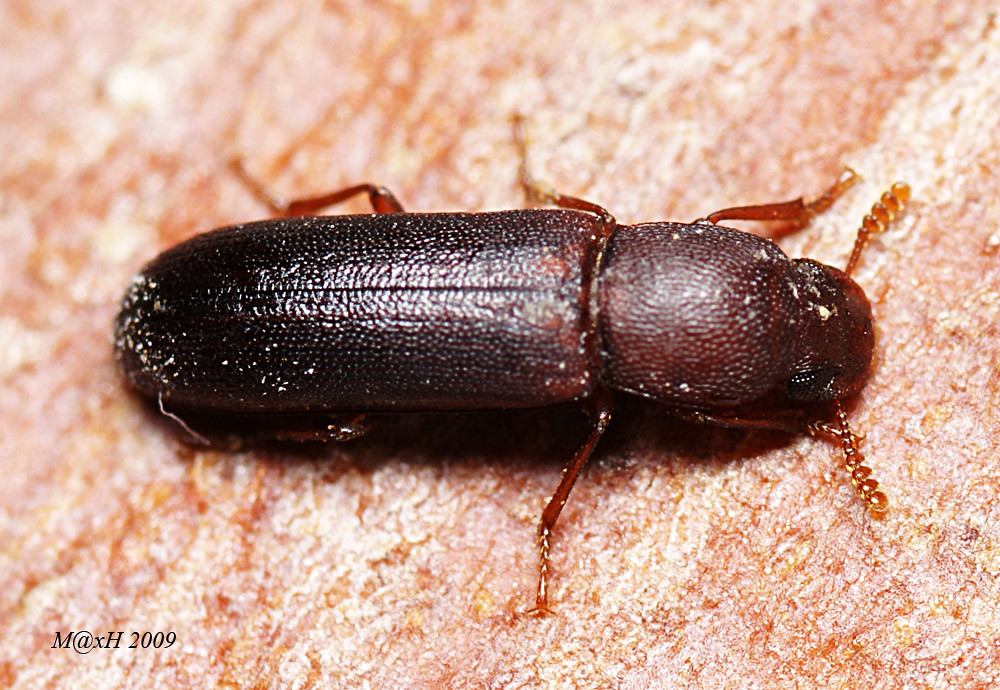

The elytra or forewings of darkling beetle are grooved and pitted that protect the flying wings. The adults of the family Tenebrionidae are active at night and avoid bright lights.
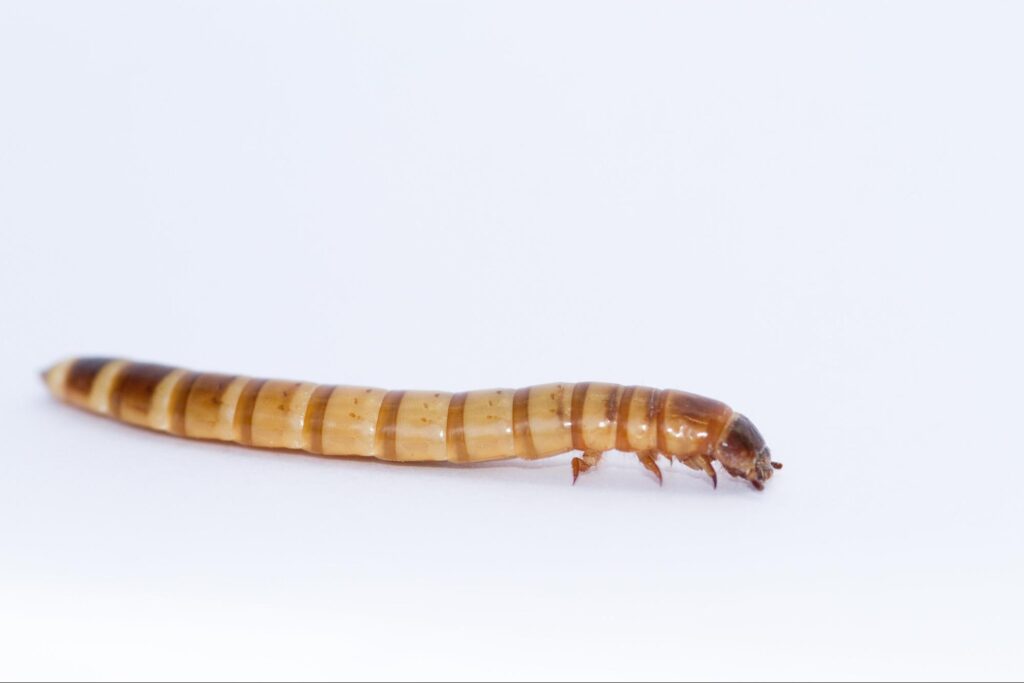

Darkling beetle larvae are called mealworms, or false wireworms are long and cylindrical. Their body is covered with a hard protective covering. These larvae are active crawlers and feed off dead insects, dry stored grains, and leaves of vegetables, trees, etc.
The larvae of darkling beetles have shiny yellow body color, while many species may have reddish to dark brown color larvae. Also, they are the active crawlers and the worst enemies of stored grains. The mealworms or false wireworms raises in many parts of the world as a food source for birds, reptiles, and fish.
RELATED: Black Beetles 101: Types and A Comprehensive Identification Guide with Pictures
Habitat Of Darkling Beetles
Darkling beetles are the most common residents of tropical and temperate regions of the world. And their familiar living places are forests, caves, leaf litter, deserts, and soil cracks.
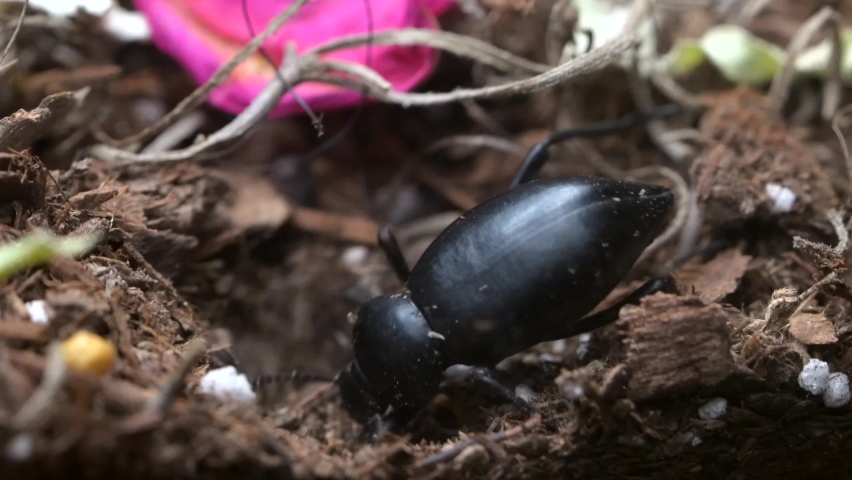

Life Cycle Of Darkling Beetles
The darkling beetles have complete metamorphosis because their life cycle consists of egg, larvae, pupae, and adult stages.
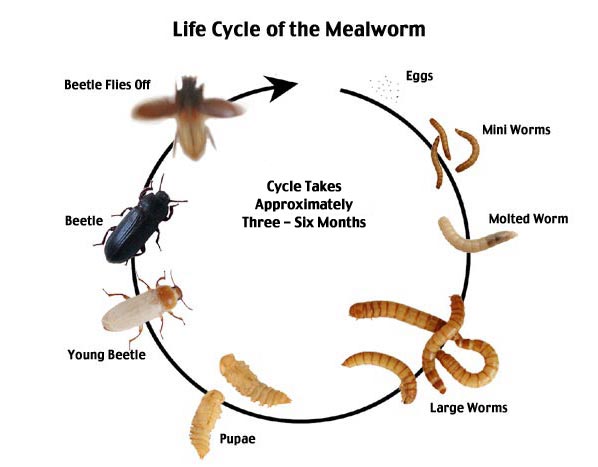
The life cycle of the darkling beetle completes within three to six months due to a slow growth rate. First, the adults lay their eggs in the soil. Then, after 10 to 20 days, the egg hatch into mealworms. These larvae are active crawlers and feed on leaves, fungi, pests, stored grains, and other animals.
They live 3 to 4 months in larval stages and then fall to the ground for pupation. After 12 to 20 days, the adults (darkling beetle) emerge. The darkling beetle undergoes many molting during these stages, living up to one year.
Exciting Facts About Darkling Beetles
Following are some fantastic facts about darkling beetles:
- The darkling beetle family Tenebrionidae is the most prominent Arthropoda class in Animalia phylum. And they love darkness as their name suggests
- Darkling beetles have chemical defenses. They secrete foul-smelling molecules to protect themselves from predators. Because of these molecules, the darkling beetle is also known as the “stink beetle.”
- They have unique defensive behavior, such as when the darkling beetle is disturbed, they stand on their head and run randomly.
- In North America, there are 1,300 darkling beetles species, which is just a fraction of them from almost 30 000 species.
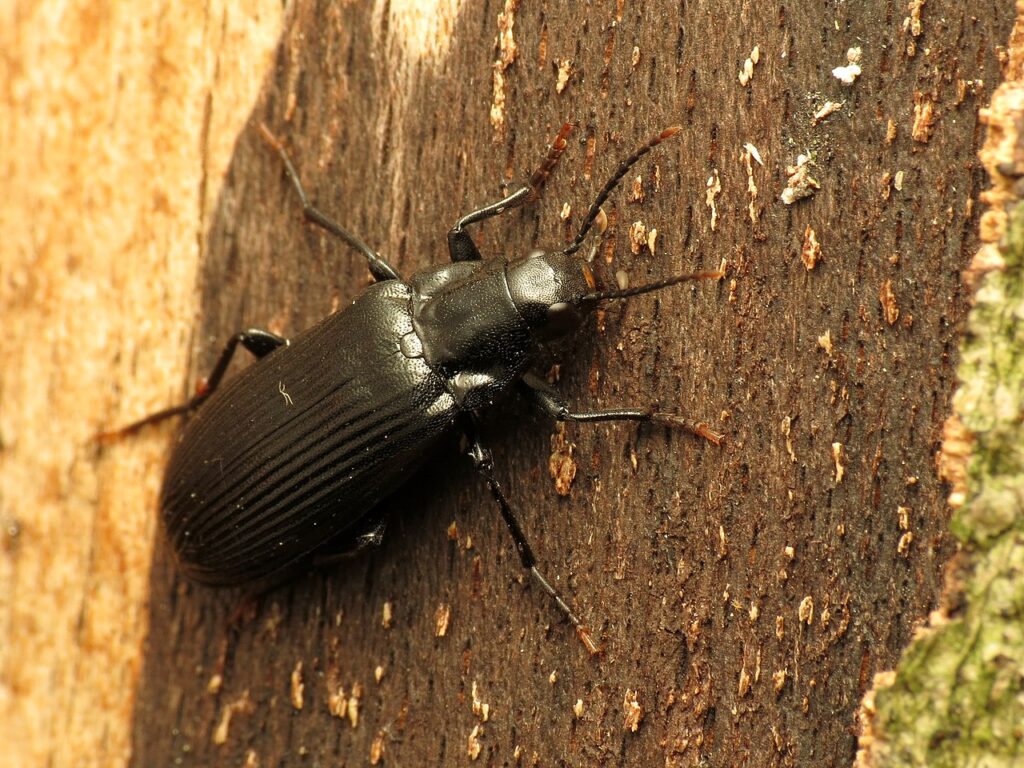

Damage Due To Darkling Beetles
Darkling beetles are considered a serious pest of the agriculture and poultry industry. In agriculture commodities, they are the invasive pests of stored grains. Darkling beetle is commonly found in dry food and improperly stored grains. These pests also reduce the grain quality and are moldy with a foul smell and taste.
The darkling beetle is responsible for microbial diseases such as Salmonella and Newcastle disease in the poultry industry.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How to Get Rid of Darkling Beetles?
Darkling beetles are difficult to control with chemical insecticides because these chemicals may contaminate indoor spaces and cause harm to humans and pets.
So the best way to get rid of these stored grain pests is to remove the dead leaves and decomposing matter. In addition, the removal of decomposing material will help in darkling beetle control, which they use as hiding places.
The second approach to get rid of the darkling beetle is the removal of food sources such as stored grains and dry food items.
Sources For Further Reading
- Dellinger, T. A. (n.d.). Darkling Beetles and Mealworms. Department of Entomology, Virginia Tech. Retrieved March 5, 2022, from https://www.pubs.ext.vt.edu/content/dam/pubs_ext_vt_edu/ENTO/ento-283/ENTO-283.pdf
- Introduction to the Darkling beetles of the Eastern United States and Florida. (n.d.). University of Florida Entomology and Entomology Dept. Retrieved March 5, 2022, from https://entnemdept.ufl.edu/teneb/intro.htm
- Care Guide: Darkling Beetle. (n.d.). Carolina.Com. Retrieved March 5, 2022, from https://www.carolina.com/resources/detail.jsp?trId=tr10493
Now that you know about darkling beetles, read our other articles to discover more plant bugs:
An All-In-One Guide to Small Brown Bugs | Fun Facts, Pictures and Identification Guide
Furry Caterpillar Types with An Identification Guide, Fun Facts, and Pictures
Types of White Spiders – A Complete Identification Guide, Fun Facts and more