Mustard plants are several species of plants belonging to the family Brassicaceae and are in the genus Brassica Sinapis.

The name ‘mustard’ derives from the Latin word ‘mustum’, meaning ‘sour’, and anyone who has tasted the fiery, yellow condiment will understand why.
The seeds of mustard plants have long been ground and crushed into a powerful spice and added to cookery, dips, sauces and dressings. Indeed, during the Roman Empire, mustard was considered a delicacy, and was served at banquets held in honor of foreign ambassadors.
It is said that the Romans introduced this plant to Britain during their invasion of 43 AD. The first record of the cultivation of mustard in England dates back to 1292 when it was grown in the garden of St John’s College, Cambridge.
It was also cultivated in France and Germany. Today, mustard is widely grown throughout the world. It is one of the most important crops worldwide.
Species Of Mustard Plant
1. Field Mustard

Field Mustard (Sinapis alba) is a biennial plant that produces large yellow flowers. It is a member of the mustard family Brassicaceae. It is native to Eurasia and North Africa. It is one of the oldest crops known to man. It is believed to have been domesticated around 8,000 years ago. It is still widely grown today.
2. Wildflower Mustard

Wildflower Mustard (Sinapissylvestris) is a perennial herbaceous plant that grows in moist areas such as meadows and riverbanks. It is native to Europe and western Asia. It is one of two species of Sinapis Sylvestris. The other species is S. arvensis. The leaves of this plant are used to make mustard oil.
3. Garden Mustard

Garden Mustard (Sinapism Gorilla) is an annual herbaceous plant that grows well in warm climates. It is native to eastern North America. It is one of six species of Sinapism Gorilla.
The others are S. alba, S. arvensis, S. schoenoprasum, S. turanica, and S. viminea. Garden Mustard is widely cultivated throughout the world. It is used for both culinary and medicinal purposes.
4. Mild White Mustard (Sinapis Alba)

The mild white variety of mustard is used as a salad green or cooked vegetable. Its leaves can be eaten raw or cooked, although they do not retain much flavour after cooking.
Mild white mustards are suitable for children because they contain no sulfur which makes them unsuitable for those with an allergy to sulfites. They are available in supermarkets and health food shops.
5. White French Mustard (Sinapiz Alba)

This is the most common type of mustard sold today. It is made by drying the seed until it becomes hard and brittle, then grinding it before adding vinegar and salt.
The resulting paste is left to ferment and mature for about two weeks. After this time, the mixture is poured into jars where it is allowed to settle. When ready, the mustard is strained through muslin cloths into sterilized bottles.
6. Amara Mustard Plant

Ethiopian kale is an African plant that grows well in warm weather. It is easy to grow and needs very little water. It is a must-have vegetable in any garden.
Baby leaves start growing in 3 weeks, and are ready to be harvested when they are 45 days old. A very popular species of mustard. Amara contains only 1% sulfur making it safe for people with allergies to sulfur.
7. Colonel Mustard

The Colonel is an American mustard that was developed at the beginning of the 20th century. It is named after its creator, Joseph J. Daniels. This mustard is made from yellow mustard seed, which is ground into a paste.
It is mixed with vinegar and sugar, and then bottled. It is available in both mild and hot versions. The mild version is less spicy than other mustards, while the hot version is much spicier.
8. Florida Broadleaf

A member of the genus Brassica, the broadleaved mustard plant is native to North America. There are four varieties of broadleaf mustard: Alabama, Florida, Georgia and Louisiana.
All these varieties produce small round mustard greens with dark green stems and pale green leaves. The flowers are tiny and yellowish-white.
Broadleaf mustard is usually planted in springtime. In summer, the plants flower and set fruit. This is followed by harvest of the young leaves, which are tender and delicious.
These leaves are best enjoyed fresh but can be stored for up to three days if kept cool.
9. Kodiak

Kodiak is a species of wild mustard plant that hails from Alaska. It is found on rocky slopes and cliffs along the coast.
It is often seen growing near beaches and is known for its bright red flowers. This cultivar of Brassica juncea is sold as a green manure cover crop.
It grows really fast, providing a biomass that will keep weeds from establishing a foothold in any season. The deep roots also prevent soil nutrients from eroding in heavy rain or strong winds.
And when it’s done covering the soil to benefit the next crop, you can chop the leaves finely with a hoe or clippers, and then turn the whole plant under the soil for added aeration and to encourage earthworms.
10. Green Wave Mustard

Green Wave Mustard is a hybrid between Brassica juncea and Brassica rapa. It has been bred specifically for use as a winter annual crop.
It produces large quantities of leaves during the first year of growth, but loses vigor quickly after that.
It is therefore useful as a cover crop, providing a dense canopy over the soil surface. It grows rapidly and can be cut down at ground level once established.
Leaves are used fresh, dried, or frozen. They are rich in vitamin C, calcium, potassium, iron, phosphorus, and magnesium.
11. Red Russian Mustard
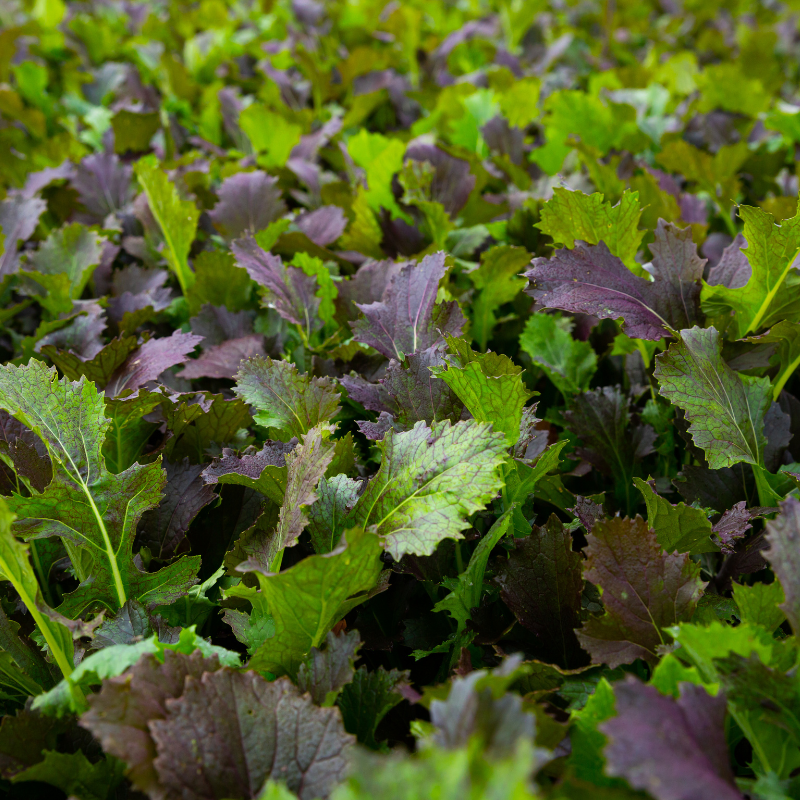

The Red Russian Mustard is a variety of Brassica nigra. It is grown primarily for its seeds, which are used to make oil.
It is not eaten directly, although the leaves may be used in salads. It is a biennial plant, producing two sets of leaves each year.
One set is produced before the second flowering, and the other set is produced after the second flowering. The first set of leaves is smaller than the second set, and the second set is more bitter. The seed pods are long and slender, and contain many black seeds.
12. White Russian Mustard

The White Russian Mustard (Brassica alba) is an edible vegetable grown mainly in Eastern Europe.
It was originally cultivated in Russia, Ukraine, Belarus, Poland, Germany, and Hungary. It is closely related to the cabbage family Brassicaceae.
White Russian mustards are similar to regular white cabbages except they have a milder flavor. They are considered a delicacy in eastern European cuisine.
13. Purple Wave Mustard

Purple wave mustard is another variety of Brassica nigrescens. It is a bi-annual plant that bears small purple flowers. It is widely grown in Asia, especially Japan.
It is very popular in China where it is called “Jiucai ” or ”Chuzao “. In Vietnam, it is called “Tôm chua”, and in Korea, it is called “Bokbunja”.
It is also grown in India, Pakistan and Nepal. Its seeds taste very hot, and not in a quiet way! Your tongue will feel purple after tasting its spice.
14. Osaka Purple Mustard
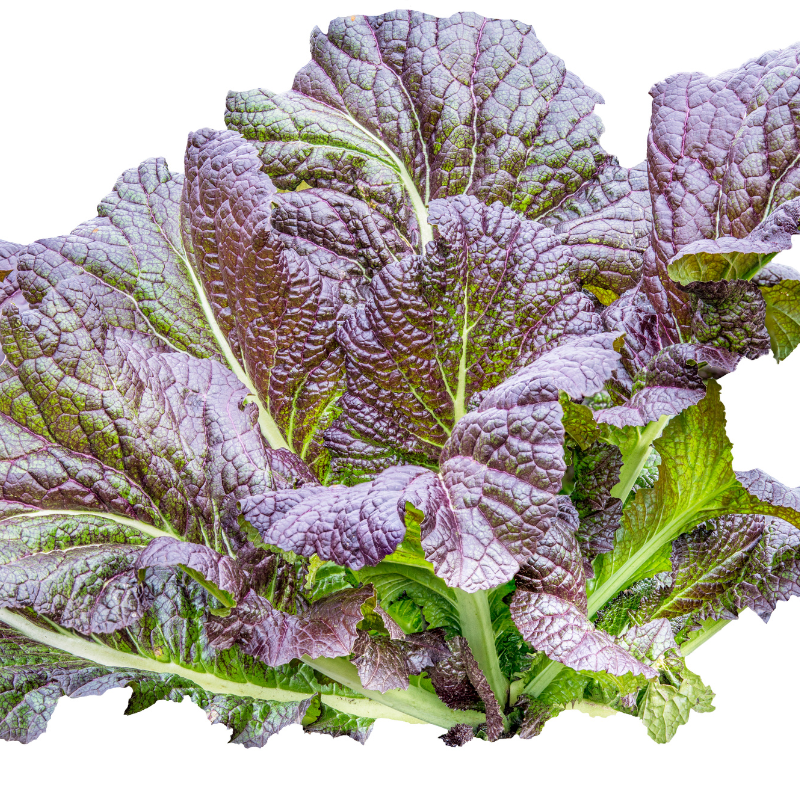

This is a Japanese variety of Brassica nigrascens var. japonica. It is a biennial plant that bears tiny purple flowers. It is highly regarded for its spicy flavor. It is used in pickles, soups, and sauces.
It is also used in traditional medicine. It will grow up to 6 inches in height within a few weeks, and can be harvested for salads after that.
15. Siberian Mustard
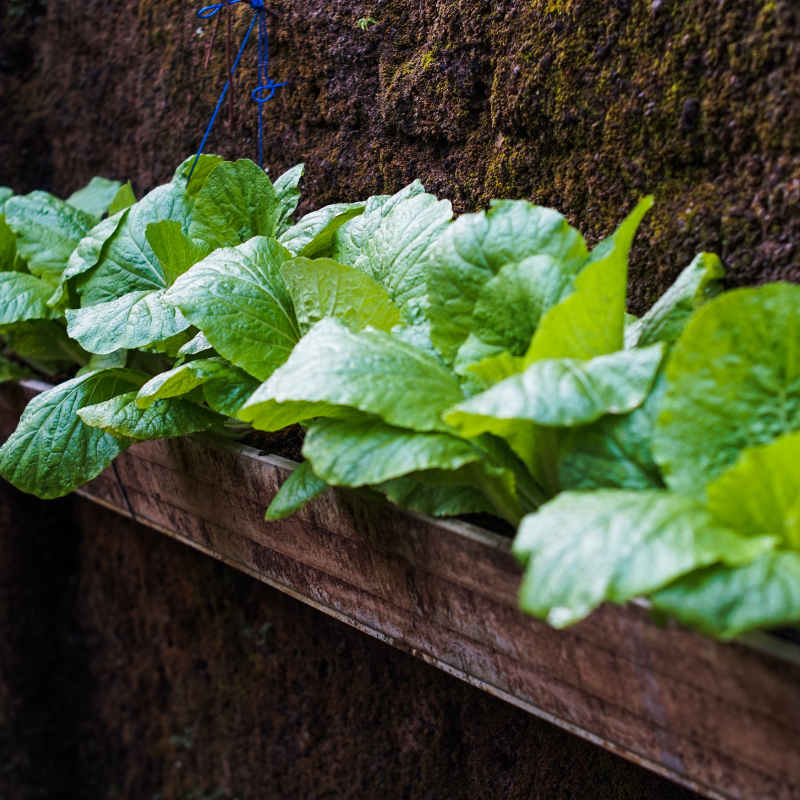

Siberian mustards are members of the Cruciferae family. They are usually grown for their seeds rather than their greens. The most common varieties include B. napus, B. oleracea, and B. rapa.
These plants produce seeds with high levels of erucic acid, a fatty acid that is toxic to humans if consumed in excess. However, these plants do provide some nutritional benefits when consumed in moderation.
16. Mizuna Mustard
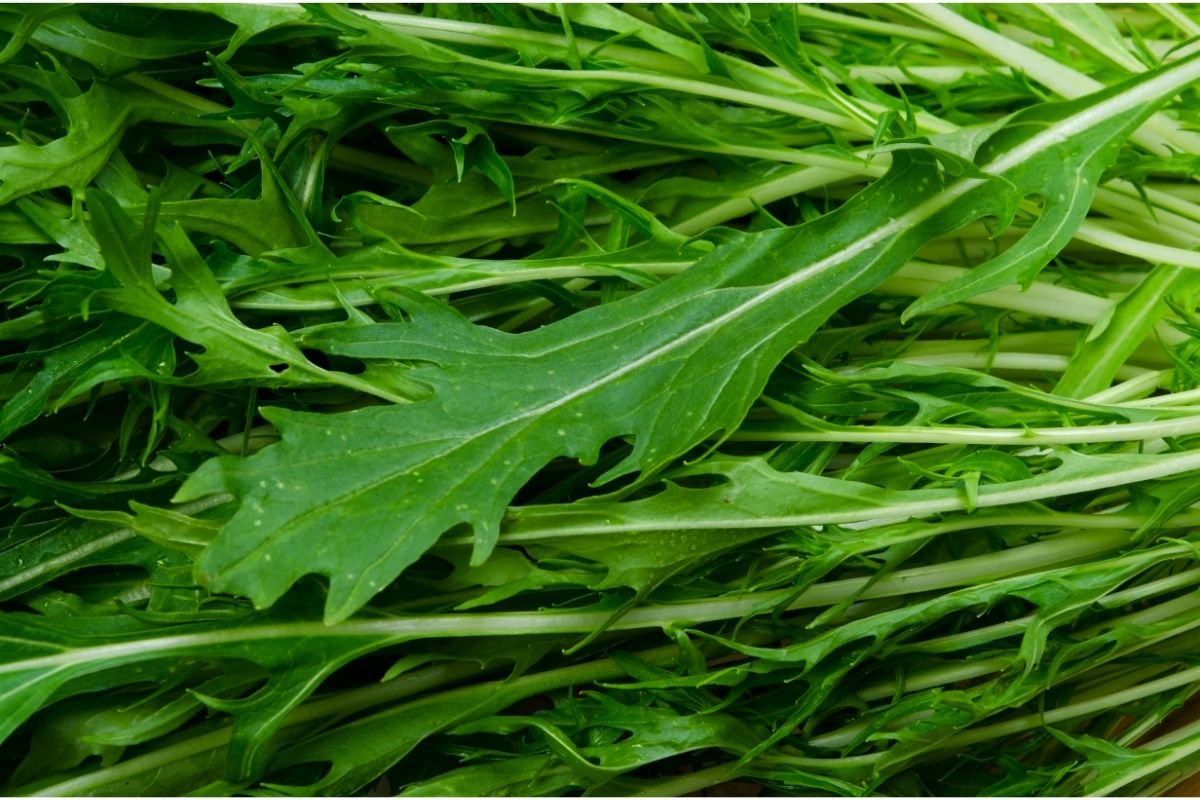

Mizuna is a type of mustard that originated in Japan. It is a member of the cruciferous genus Brassica. It is a cool season annual that is often grown as a salad green. It has a peppery flavor and a slightly sweet aroma.
Mizuna is commonly used in salads, sashimi, and misozuke dishes. It is sometimes referred to by the name of its cultivar, “Hara-kiri”.
17. Wasabi Mustard Plant
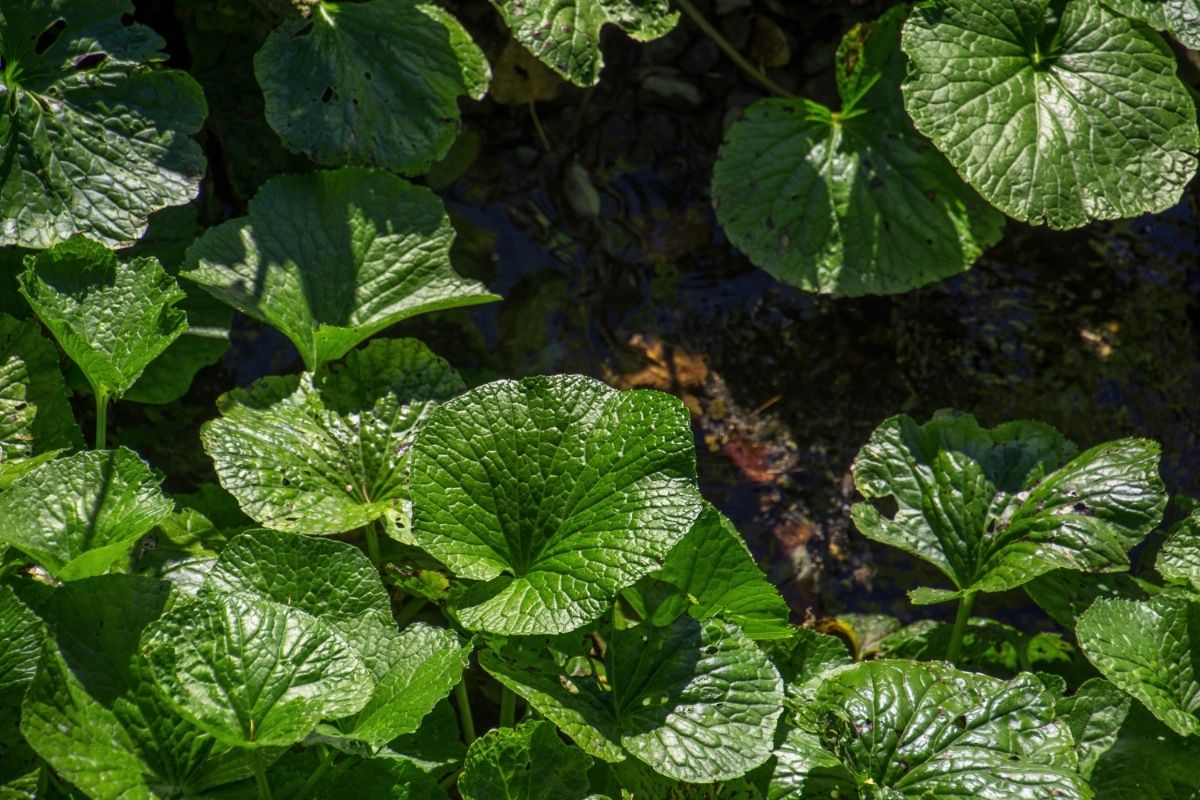

Wasabi is a member of the mustard family. It is native to East Asia, but is now cultivated worldwide.
Wasabi is one of the most pungent spices known to man. It is used as a condiment on sushi rolls, and is also added to various Asian dishes such as stir fries.
Wasabi comes from the root of the mustard plant, and contains several compounds that give it its unique flavor. It is notoriously difficult to grow because of its sensitivity to cold weather.
It needs a constant temperature between 55°F and 65°F to thrive. If you live in a place with extreme temperatures, then this plant may not work well for you.
18. Rosette Tatsoi Mustard
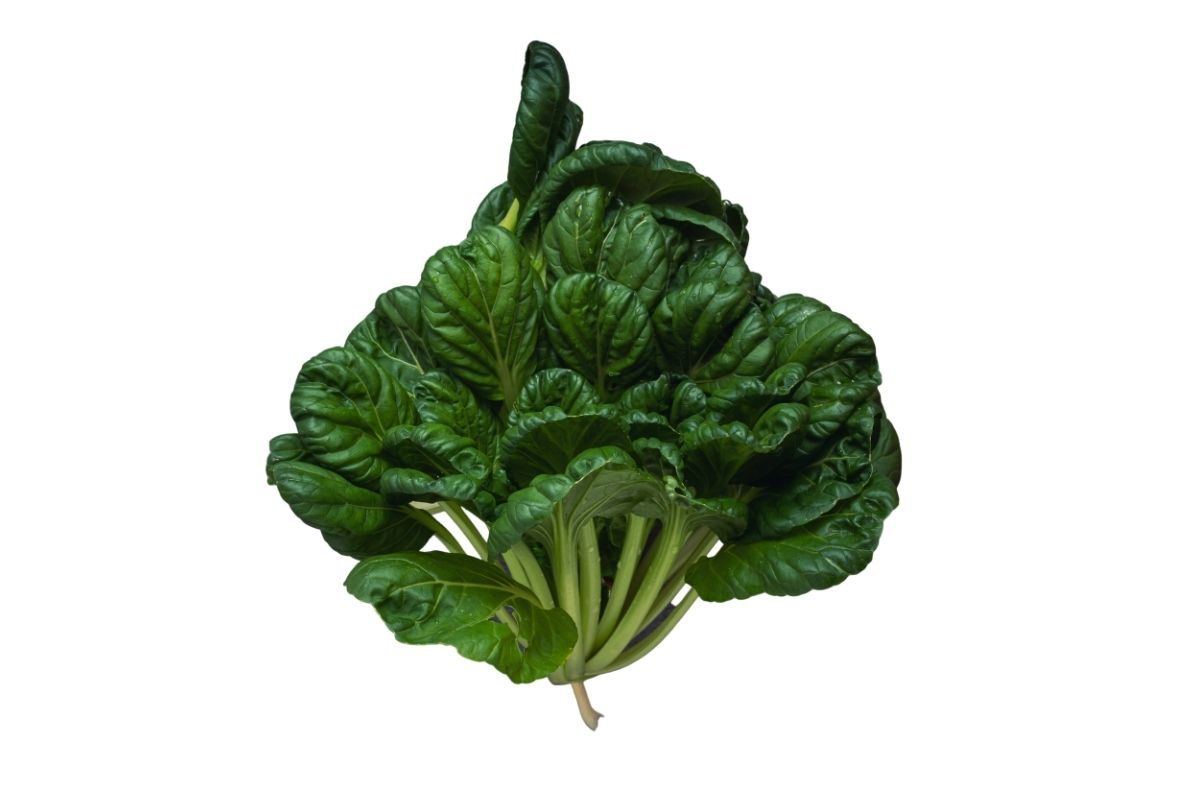

Tatsoi is a leafy vegetable that grows wild throughout Japan. It is often used in salads, and is also enjoyed raw in sashimi.
It tastes like watercress, and has a slight bitterness. It is a good source of vitamin C, potassium, calcium, and iron.
Final Thoughts
Our list is just a sample of what’s available to you. There are many other types of mustard plants out there, and we encourage you to explore them further.
Find something that suits your culinary preferences, your budget, and your environmental conditions. Good luck!
Editor’s Recommendations
16 Types Of Olive Plants (Including Photos)