Your all-in-one guide to the most common types of white spiders with pictures
Unlike most spiders which are brown or black, white spiders are, you guessed it right, white! But despite wearing the colors of a ghost, most white spiders are pretty harmless. Compared to other types of spiders which number around 50,000, there are only a few dozen white spider species on earth. They all vary in size and body patterns. But no matter, small or large, seeing a white spider crawling around is still too much for some, especially for the arachnophobes around us!
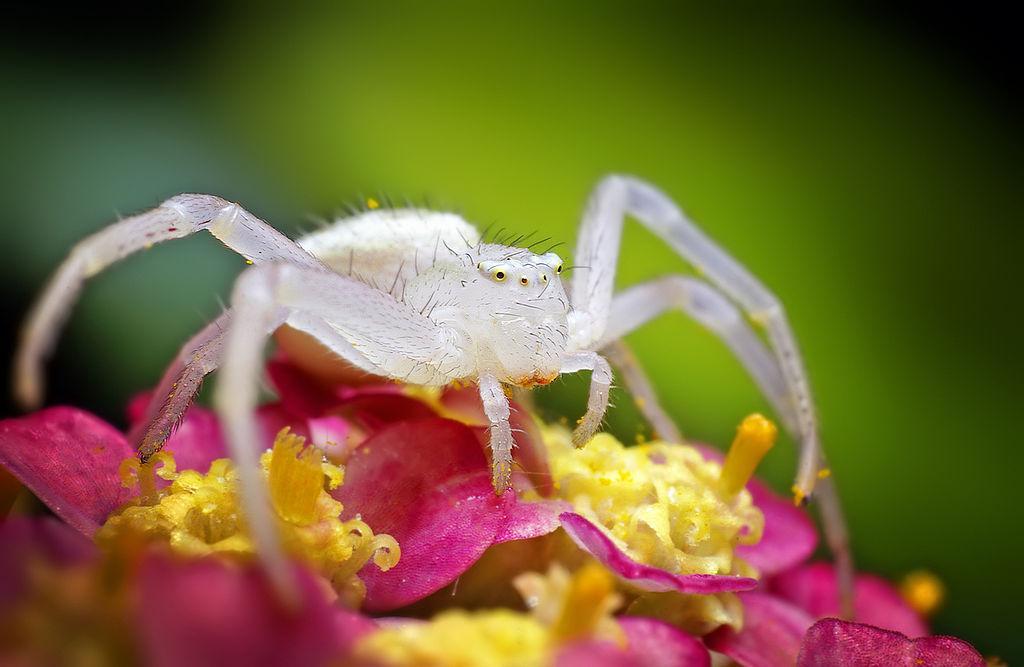

White spiders can live in a wide range of settings. Some even utilize the regions of human settlements such as houses, farms, barns, gardens, attics, basements etc., as their homes. So, next time you see a white spider jumping around and want to know a little more about it or just wondering, what white spider species is that? This article has got you covered! But before we go ahead and start throwing different types of spiders at you (not literally), let’s just get some FAQs about white spiders out of the way.
Are white spiders poisonous?
First of all, spiders are venomous, not poisonous. Their toxins work by being injected, not by being ingested. Nonetheless, most spiders generally have a small quantity of venom in their bodies, be it a common house spider or a white spider. However, the venom rarely causes any significant damage to humans because of the small quantity.
For example, the bite of commonly encountered spiders including house spiders and the common species of white spiders, the crab spiders only cause local swelling, redness and pain, much like a bee sting.
| Poison | Venom |
| Poison is inhaled, ingested or absorbed | Venom is injected through bites or stings |
| Snakes and Spiders are venomous | Amphibians, Plants and Mushrooms are poisonous |
| Example: Widow Spiders | Example: Poison dart frogs |
Do white house spiders bite?
Like commonly encountered spiders, white spiders have the potential to bite when triggered. But more often than not, a single bite is not a reason for concern or something that needs medical attention. Instead, the ones you need to worry about are the black widow spiders and brown recluse spiders.
Are white spiders rare?
They are not as common as many species of house spiders that you may generally encounter such as orb weaver spiders or grass spiders. Still, they cannot also be declared rare. The most common white spider species is the Flower crab spider which can easily be found hunting in the milkweed plants.
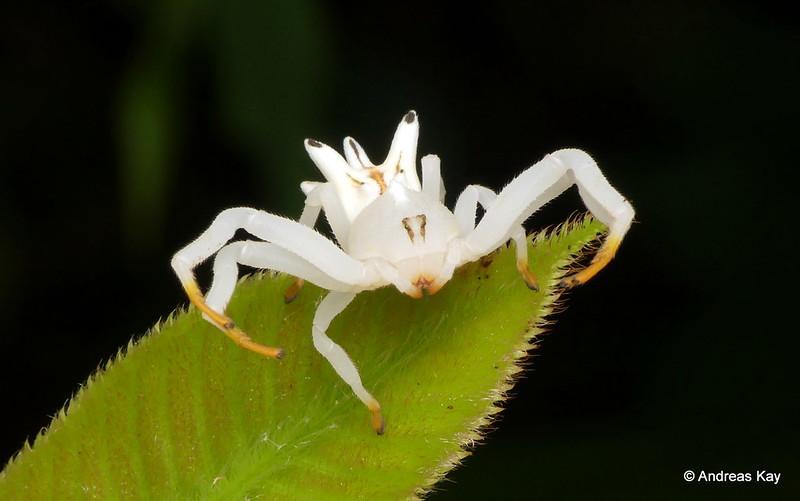

How do I get rid of white spiders?
Unlike what internet memes suggest, you do not need to burn down your house to get rid of these white creatures with eight legs. Just as with commonly encountered spiders, make sure to keep your home clean, regularly check the dark corners around your home, use spider nets, and you will be alright. You can check out this guide to learn further about eliminating house spiders from your home.
RELATED: Grass Spiders: How To Get Rid Of Them? A Comprehensive Guide
Do white spiders harm plants?
While healthy garden plants can tolerate small garden spider infestations, control is still essential as these creatures with eight eyes tend to reproduce and increase rapidly. Prolonged infestations can also cause significant damage to your garden. In addition, some hunting spiders might also catch and feed on pollinating insects which could discourage them from visiting the flowers.
Now that we have looked at some of the White Spider FAQs. Let’s look in more detail at various types of white spiders, which species are you most likely to find in your home or garden, and how could you identify them.
Types of white spiders
Many white spiders are commonly referred to as sac spiders, cellar spiders, jumping spiders and widow spiders. Following is a list of some common and some not-so-common white spiders worldwide.
1. Common Candy-Striped Spider
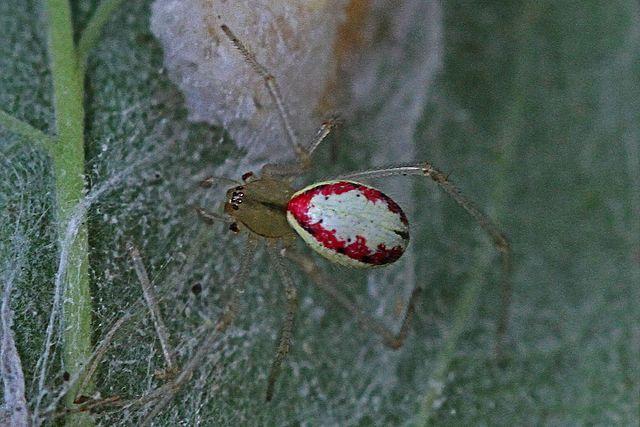

Sounds yummy or something you would like to eat, no? But a quick glance at this ghostly creature will immediately tell you that this spider is a stuff of nightmares. The spider has an inflated balloon-like abdomen with extremely long legs that look like thin filaments next to its big belly.
Although native to Australia, these spiders have now been introduced into the United States as well. They are only around 6 millimeters in size. But despite being tiny and sounding cute, they are formidable predators. Common Candy-Striped Spiders can catch insects that are many times their size.
Due to their appearance and colors, Common Candy-Striped Spiders are very well camouflaged in flowers. Here, they sit and patiently wait for the unlucky insect that will be their lunch. Their venom also acts rather quickly and is especially very deadly for the smaller bees.
Common Candy-Striped Spider Identification Guide
As you can tell by the above-attached picture, you will have a hard time confusing these ghastly creatures with any other spider species.
Common Candy-Striped Spiders have a swollen sac-like abdomen with very prominent red or pink markings. You will also see tiny black dots on their abdomen on a closer look.
Although it is more often than not white in color, some spiders may also be translucent green or yellow creamy in color.
Common Candy-Striped Spider Quick Facts
| Distribution | Native to Europe, introduced to North America, common in Lithuania |
| Habitat | Hedgerows, grassland and gardens. |
| Venom Strength | Moderate |
| Size (Average) | 5 millimeter |
2. White Spinybacked Orbweaver Spider
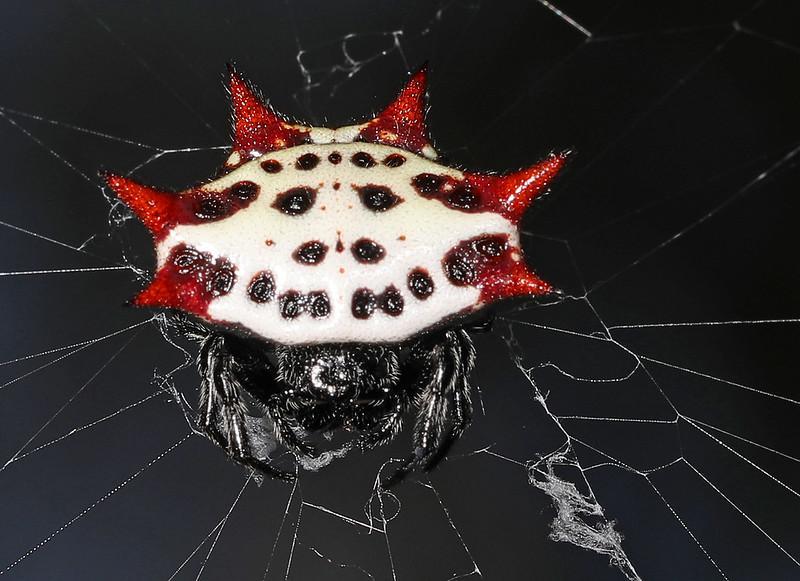

Next on our list is one of the orb weavers. They are also called crab spiders sometimes because of their appearance. But that is not accurate, and these spiders are not related to crab spiders.
Although they are nowhere as large as some other orb weavers, their colors and body patterns make them very prominent. These orb weavers are most common in tropical Asia, especially Indian and Indonesia. Spinybacked Orbweaver Spider bites are generally harmless for humans despite their menacing looks. In the United States, these spiders are commonly sighted between October and January.
These spiders usually make their homes in trees and shrubs near nurseries or homes. Citrus field workers often come in contact with these spiders. Like all other orb weavers, these spiders use their nets to capture their prey which include flies, moths, and beetles.
White Spinybacked Orbweaver Spider Identification Guide
They have a brilliantly colored, primarily white abdomen that has dark spots all over it. There are also six huge black or red spines arising from the abdomen. The abdomen is unlike any other spider that you may have seen. It is broader than long, making it look like a crab spider.
White Spinybacked Orbweaver Spider Quick Facts
| Distribution | Tropical Asia, United States to northern Argentina |
| Habitat | Trees and shrubs, common in citrus fields |
| Venom Strength | Mildly toxic |
| Size (Average) | 7 millimeter long, 12 millimeter wide |
3. Goldenrod Crab Spider
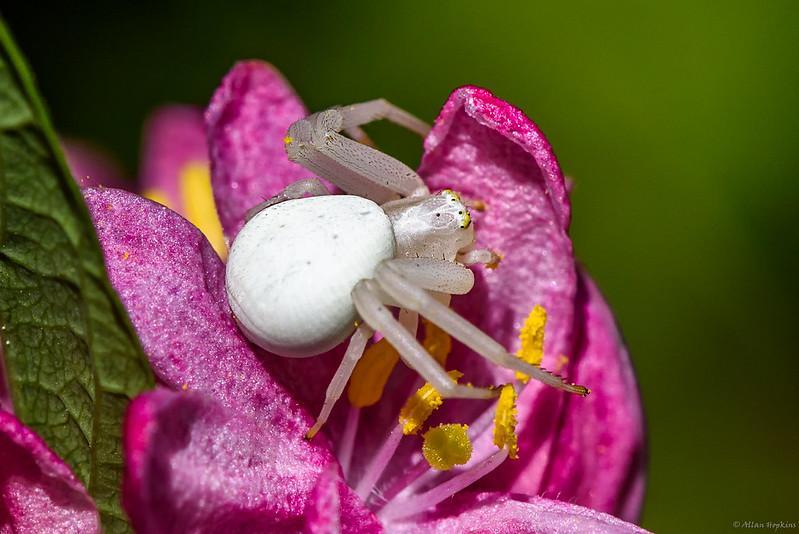

They are called crab spiders because of their unique ability to walk not only forwards and backwards but sideways as well. Goldenrod Crab Spiders have a ghostly white body and completely white legs when they are born.
But as they grow, they develop the ability to change their body color to blend in with their surroundings. Female spiders are bright white with light brown or tan stripes on the sides. Female goldenrod crab spider lives with her egg sacs and actively protects their territory.
While males are colorful spiders that are often very well camouflaged in flowers of daisies, goldenrods and milkweeds. Goldenrod Crab Spider is a common garden spider across northern Asia, Europe and North America. They primarily feed on pollinating insects, so you might want to keep an eye out for an infestation.
Goldenrod Crab Spider Identification Guide
These spiders can be identified with their large egg-like bodies. They have eight eyes in front of their heads which seems minuscule in front of their large abdomen. The male usually has a brown thorax and a small white or yellow abdomen.
Goldenrod Crab Spider Quick Facts
| Distribution | Only North America and Europe |
| Habitat | Forests as well as milkweed and goldenrod plants |
| Venom Strength | Harmless for humans |
| Size (Average) | 10 millimeter |
4. Caribbean Crab Spider
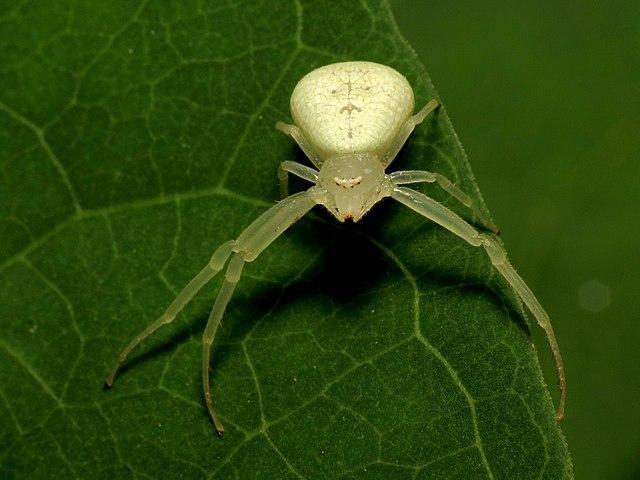

Caribbean Crab Spider is one of the many spiders in the animal kingdom that are known for their strange looks. The spider has a flat body, long legs and an enormous leg span. These spiders are roughly the same size as a Goldenrod Crab Spider, rarely exceeding 5 to 6 millimeters in length.
These spiders are found in America and Canada. They can be found in gardens, parks and woodlands. Like most spiders, the female Caribbean Crab Spider is always larger than her male counterpart. As they grow, the head and front parts of their long legs become translucent green.
These spiders are generally considered beneficial for the gardens. Even though they sometimes feed on pollinating insects, they also kill and eat flies and mosquitos. They are sit-and-wait predators that hunt in flowers, foliage, or leaves and strike their prey when it gets too close.
Caribbean Crab Spider Identification Guide
Caribbean Crab Spider can be easily recognized by its four front long legs and four short hind legs. They have a white abdomen with a characteristic dark violin-shaped mark. Eyes are in two rows at the front side of the head that look like faint black dots.
Caribbean Crab Spider Quick Facts
| Distribution | Mexico, Americas |
| Habitat | Gardens, parks, and woodlands |
| Venom Strength | Not Known |
| Size (Average) | 5 millimeter |
5. White Crab Spider
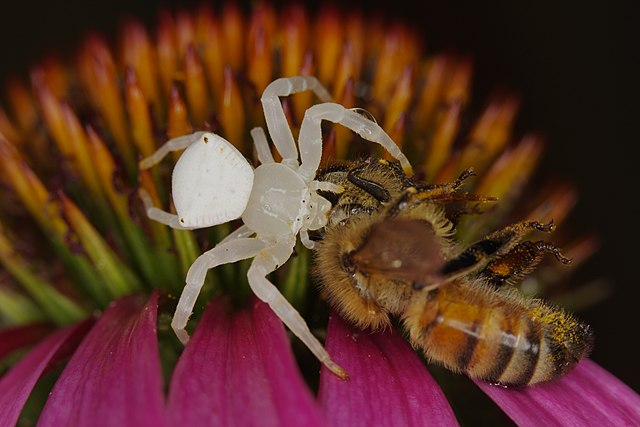

These venomous spiders are also known as Australian crab spiders. But other than Australia, they are also present in far east Asia. Females are larger than males with an average body length of 10 millimeters.
It is a common species in Australia. Not only is the spider white, but its egg sacs are also white-cream colored which the female lays in folded leaves.
Australian crab spiders tend to be more aggressive than other species of crab spiders. They have a higher biting rate than other common species of crab spiders. Even though the bite is not lethal, it can still cause local swelling and redness.
Australian crab spiders are not web spiders and do not spin webs. Instead, they ambush and actively chase their prey which are tiny insects, including some pollinating insects.
White Crab Spider Identification Guide
They are bright white but can also change their colors to pale yellow to match their surroundings. The bulbous abdomen is whitish but the legs can be translucent which helps them camouflage. In fully grown White Crab Spiders, legs also have small black colored spines.
White Crab Spider Quick Facts
| Distribution | Australia and far east Asia |
| Habitat | Flowering plants |
| Venom Strength | Not lethal, but painful |
| Size (Average) | 10 millimeter |
RELATED: How To Get Rid Of Spider Eggs From Plant Soil For Good? The Ultimate Guide
6. Yellow Sac Spider
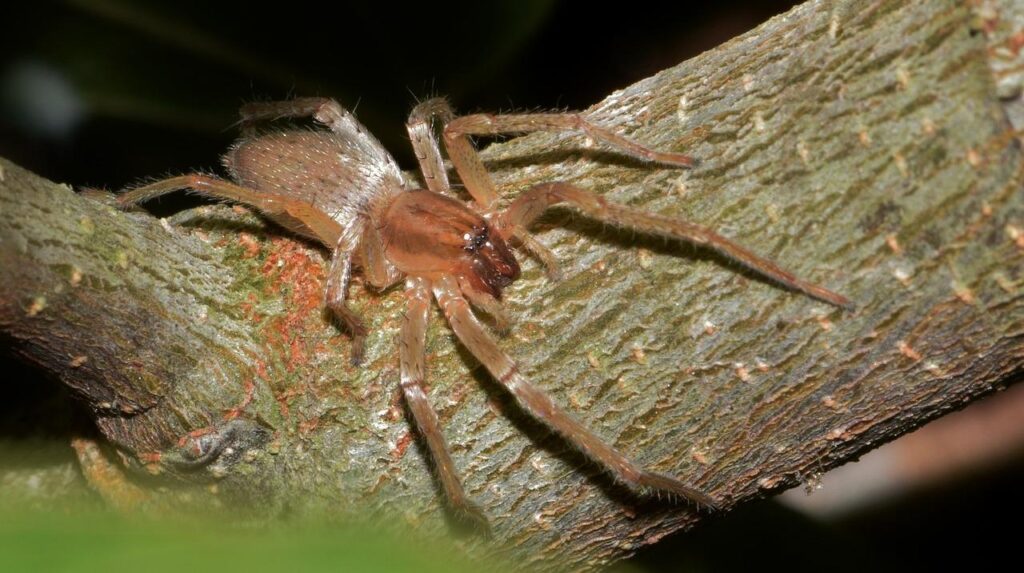

A type of garden spider that can be found under leaf litter, stones as well as in the ceilings of homes like cellar spiders. These spiders are probably responsible for more bites than any other spider species. These spiders are indigenous to much of the US and Europe.
These spiders deposit their egg sacs in spider silk, and females always remain near the eggs to protect them. When eggs hatch, baby spiders spend their days hiding in silken retreat protection and only coming out at night to feed. Unlike orb weaver spiders, these spiders actively hunt their prey.
Also, unlike many other species of spiders, these sac spiders are known to bite without provocation. Symptoms are similar to Brown recluse bites but less intense. The symptoms usually last for about ten to twelve hours. Some people might show an allergic reaction in which case medical attention must be provided.
Yellow Sac Spider Identification Guide
Females are 5 to 10 millimeters in size, while males are much smaller, averaging around 4 to 6 millimeters. They have a yellow sac-like abdomen and a light brown body. It is noteworthy that unlike what their name suggests, yellow sac spiders are not always yellow in color.
Yellow Sac Spider Quick Facts
| Distribution | Widely distributed in the United States |
| Habitat | Leaf litter, underground, ceilings |
| Venom Strength | It can cause lesions and swelling in humans |
| Size (Average) | 5 to 10 millimeter |
7. Dancing White Lady Spider
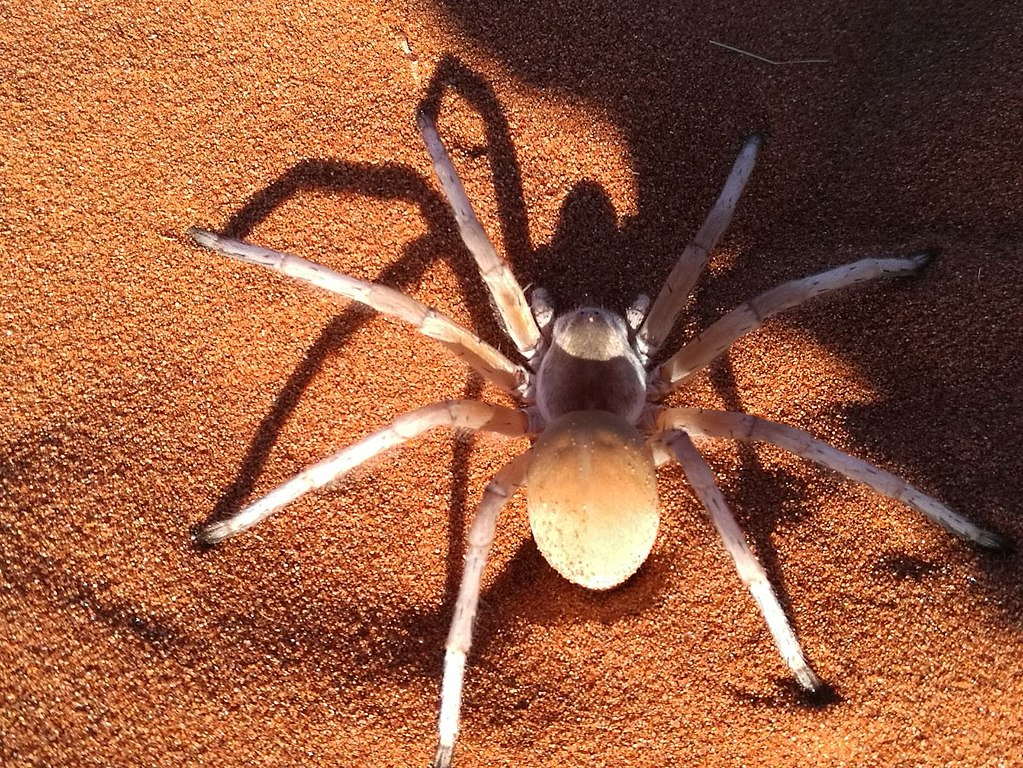

It is a type of huntsman spider known for its speed and agility. It is found in the deserts of Namibia. It gets the word “dancing” in its name from the tapping movements it makes while walking. They have really poor eyesight, but they somehow manage to use starlight for navigation.
Before mating, the male finds the burrow of a female. Then, he makes careful vibrations on the sand with his legs to not be mistaken for prey. But, all this still cannot save him from his gruesome fate. Like many spiders, Dancing White Lady Spider also eats the male after mating.
Dancing White Lady Spiders are giant spiders that are average 13 centimeters in length and have a leg span of around 25 centimeters. To avoid extreme temperatures, these nocturnal creatures usually keep themselves buried in the sand. Therefore, it is tough to spot them.
Dancing White Lady Spider Identification Guide
These are giant spiders with creamy white bodies. Their bulbous abdomen is somewhat raised from the rest of the body. Also, there are spines of black color arising from all over their eight legs. Eyes are located right in front of the head in three pairs.
Dancing White Lady Spider Quick Facts
| Distribution | Namibia |
| Habitat | Desert |
| Venom Strength | Requires medical attention |
| Size (Average) | 10 to 12 centimeters |
8. Short-bodied Cellar Spider
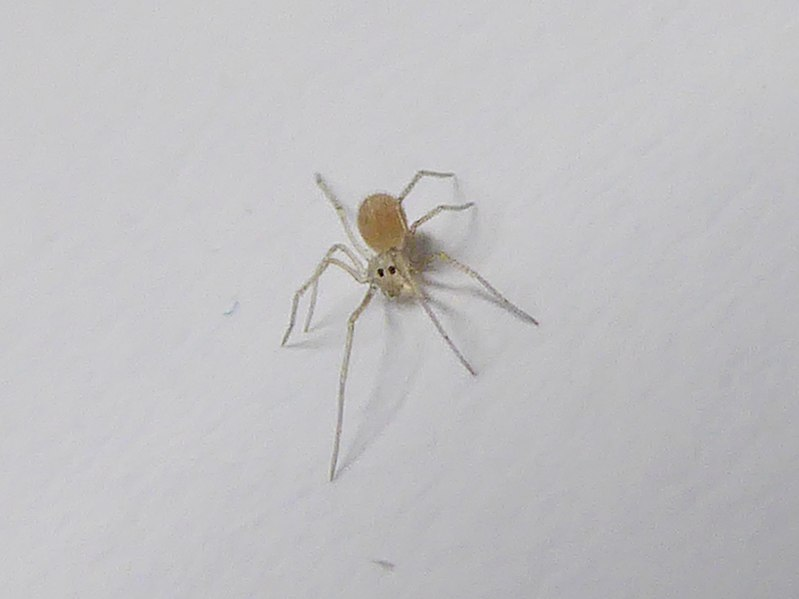

As their name suggests, short-bodied cellar spiders are commonly found in damp and dark places such as basements and cellars. Despite having a short body, these cellar spiders have long thin legs. These long legs have also earned them the name of daddy long legs.
The female is larger than the male with an average body length of 2 millimeters and a leg span of 8 millimeters. Short-bodied cellar spiders only produce three egg sacs throughout her life. Unlike web spiders such as the cobweb spider or the funnel-web spider, these spiders do not attach their eggs to a web. Instead, they carry their eggs in their mouths.
These spiders do not consume their old webs before weaving a new one. That is why cellar spiders often become a nuisance in homes as they keep on haphazardly adding new webs, one after another over time.
This spider is a common house spider in Asia, but it can also be found in the southern states of the United States and some Mediterranean regions.
Short-bodied Cellar Spider Identification Guide
They have a whitish body with skinny and long legs. The abdomen is the most significant part of the body with a round shape. The spiders sometimes also have thin brown stripes on their body which could help you identify them quickly.
Short-bodied Cellar Spider Quick Facts
| Distribution | All over the world, except Antarctica |
| Habitat | damp cellars, basements, and crawl spaces |
| Venom Strength | Not venomous |
| Size (Average) | 2 millimeter |
9. White Widow Spider

The White Widow spider is also known as the white steppe spider. It is a rare orb-weaver spider that is present in the grasslands and deserts of Central Asia, the Middle East, and North Africa. Unlike black widows or brown widow spiders, white widow spiders are not very venomous.
But a bite can still be dangerous for children or individuals with poor health. Also, compared to black widows and brown widow spiders, this species is relatively rare, with only a few confirmed sightings to date.
During mating season, adult spiders cohabit with each other for a very long time. Males after reaching maturity, do not actively forage and spend the rest of their lives searching for adult females. After finding a suitable partner, males engage in very energy-demanding courtship displays. And then, after a successful mating, the female white widow spider eats the male.
White Widow spider Identification Guide
Unlike brown widow spiders and black widows which are dark in coloration, white widow spiders are light-colored. Typically, they are beige to white and have darker legs or dark stripes on the legs. They are only 5 millimeters in size. Their most notable body feature is their big balloon-like abdomen which makes their head look minuscule.
White Widow spider Quick Facts
| Distribution | Central Asia, Middle-East, and North Africa |
| Habitat | Grasslands and deserts |
| Venom Strength | Dangerous for infants or weak individuals |
| Size (Average) | 4 to 6 millimeter |
10. Colonus puerperus
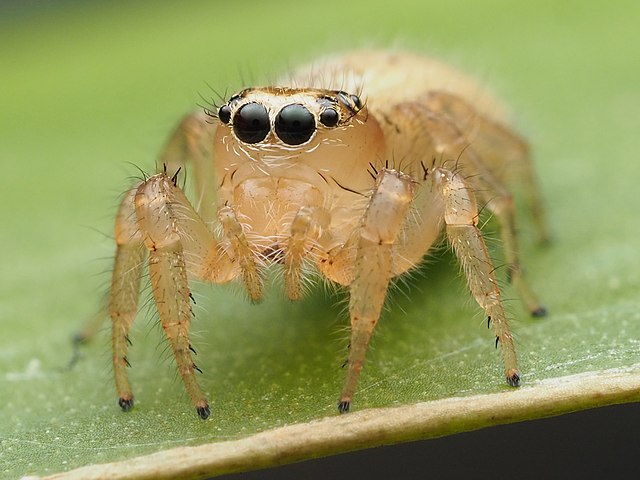

They are unique jumping spiders that are present in the eastern parts of the United States. They can be found throughout Florida, Texas, Illinois, Kansas, and Pennsylvania. These jumping spiders like warmer temperatures, so they can be found in grassy areas with other grass spiders.
Since these tiny jumping spiders do not have a common name, they are usually referred to by their scientific name. Despite being jumping spiders, they move slowly. Nonetheless, they have advanced predatory tactics that allow them to stalk and capture prey. Usually, they feed on flies, butterflies, crickets, and other smaller jumping spiders.
Like other jumping spider species, Colonus puerperus are friendly creatures. They do not bite unless threatened or roughly handled. Many spider enthusiasts also keep this jumping spider as a pet, and they do very well in captivity.
Colonus puerperus Identification Guide
Colonus puerperus jumping spider has a fuzzy white body due to the presence of numerous hair on its body. Females are 8 to 10 millimeters, while males are between 7 and 8 millimeters. At a closer look, you can see that this jumping spider species also has red to orange areas as well on the anterior side of its body.
Colonus puerperus Quick Facts
| Distribution | Gulf Coast, eastern United States |
| Habitat | Grassy areas |
| Venom Strength | Not dangerous |
| Size (Average) | 8 millimeter |
11. Hibana incursa
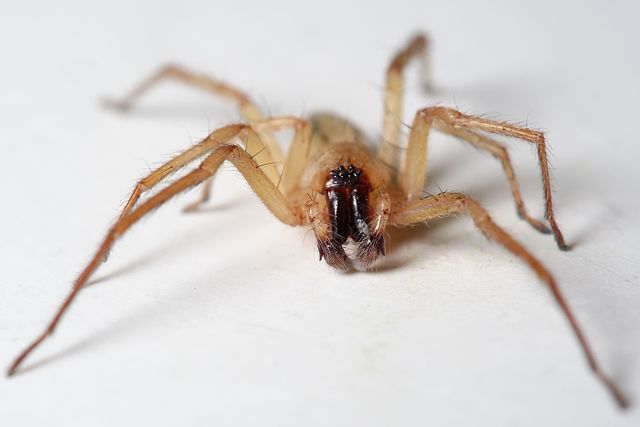

These medium-sized spiders are commonly known as ghost spiders. By taking a quick look at them, you can quickly tell why they are called ghost spiders. They are present in Panama and the United States. Like with most spider species, females are larger than males.
The average size of an adult female is around 7 millimeters, while it is about 5 millimeters for males. This species has a very restricted range and is not usually found outside it. They are common American house spiders and can be found in citrus fields as well. These spiders are generally sighted in December and January.
Hibana incursa Identification Guide
These spiders are easily identifiable by their pointed, oblong abdomens. In addition to their abdomens, their legs are also pointy. They have a creamy white body with slightly pale legs.
Sometimes, up close, you can also see a stripe running across their back. Also, on a closer look, you might also find very fine and thin spines arising from their legs or the rest of the body.
They have eight eyes on the front of their heads. These eyes are arranged in two rows of four eyes and are clustered in a dark spot.
Hibana incursa Quick Facts
| Distribution | United States, Panama |
| Habitat | Homes, citrus fields |
| Venom Strength | Not known |
| Size (Average) | 7 millimeter |
12. Yellow Ghost Spider

Among American house spiders, there is also the Yellow Ghost Spider. Like other ghost spiders, this American house spider also has a pointed abdomen. There is also a pronounced spinneret at the tail end of its abdomen. Yellow ghost spiders are often found in foliage and houses.
This American house spider is also found in citrus fields. And they are thought to be beneficial as they feed on harmful insects such as the citrus leaf miner. These spiders are often sighted most often in the outdoor environment during the summer months.
These spiders are often mistaken for brown recluse spiders. But unlike black recluse spiders, which are dark brown in color, Yellow Ghost Spiders are pale yellow or cream-colored.
Yellow Ghost Spider Identification Guide
As already stated, they are often mistaken for brown recluse spiders. But Yellow Ghost Spiders are smaller than these dark brown spiders. You can identify them by looking for pale markings on their pale yellow abdomen.
Also, like other ghost spiders, the Yellow Ghost Spider has spines like hair arising from all over its body. These spines are usually very prominent on their pointy legs which are just as sharp as their abdomens.
Yellow Ghost Spider Quick Facts
| Distribution | North America |
| Habitat | Homes and houses as well as foliage |
| Venom Strength | Causes irritation |
13. Garden Ghost Spider
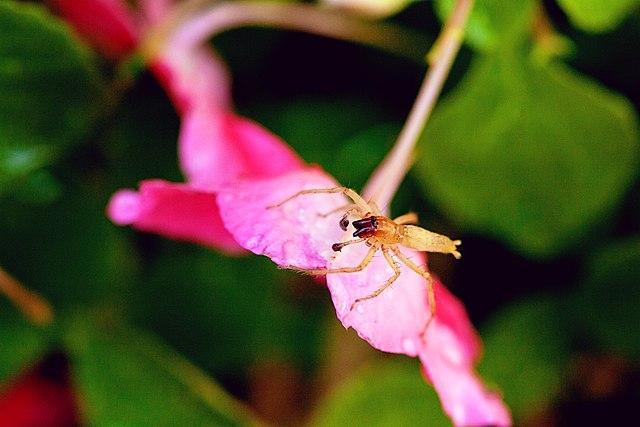

Next on our list is another ghost spider that is commonly found in the northeastern United States. This species is sometimes mistaken for brown spiders, especially the brown recluse spider. In addition to the United States, Garden Ghost Spiders are also present in some regions of Canada.
Not much is known about these elusive and secretive creatures. Also, very little information is available about their lifestyle and behavior. Nonetheless, they seem to be nocturnal, which means they are most active during the night. Also, they do not seem to be much indulged in making and maintaining webs.
They are ambush predators that sit and wait for their prey. Sometimes, they have also been known to chase their prey actively. They feed on small insects such as flies, some species of pollinating insects and other tiny spiders as well from time to time.
Garden Ghost Spider Identification Guide
They have a bibulous cream-colored body that varies in color from white to light brown. Other features that you could use to identify them include two rows of eyes, pointy and spiny legs and dark spots on the abdomen.
Garden ghost spiders are on average 7 millimeters in length, and as with many spider species, females are larger than males.
Garden Ghost Spider Quick Facts
| Distribution | The United States and Canada |
| Size (Average) | 7 millimeter |
Links for Further Reading
- Eliminating Spiders Around Homes and Buildings | Entomology. (2022). Retrieved 13 March 2022, from https://entomology.ca.uky.edu/ef623
- Spiders in the Home – 5.512. (2022). Retrieved 13 March 2022, from https://extension.colostate.edu/topic-areas/insects/spiders-in-the-home-5-512/
- Spiders. (2022). Retrieved 13 March 2022, from https://extension.umn.edu/insect-relatives/spiders
Now that you know about the types of white spiders, make sure to also read our other plant bugs articles:
How to Get Rid of Wireworms Effectively?
Fungus Gnats vs. Fruit Flies: How to Get Rid of Them on Houseplants?