Indoor plants are a great way to create refreshing and attractive interior settings. They also clean the indoor environment (convert carbon dioxide into oxygen). In addition to that, houseplants absorb toxins and purify the air.
To successfully grow and maintain houseplants, preventing them from insect pests is essential, such as mealybugs, fungus gnats, whiteflies, thrips, etc. These pests of houseplants suck the sap and damage their foliage, stems, and roots.
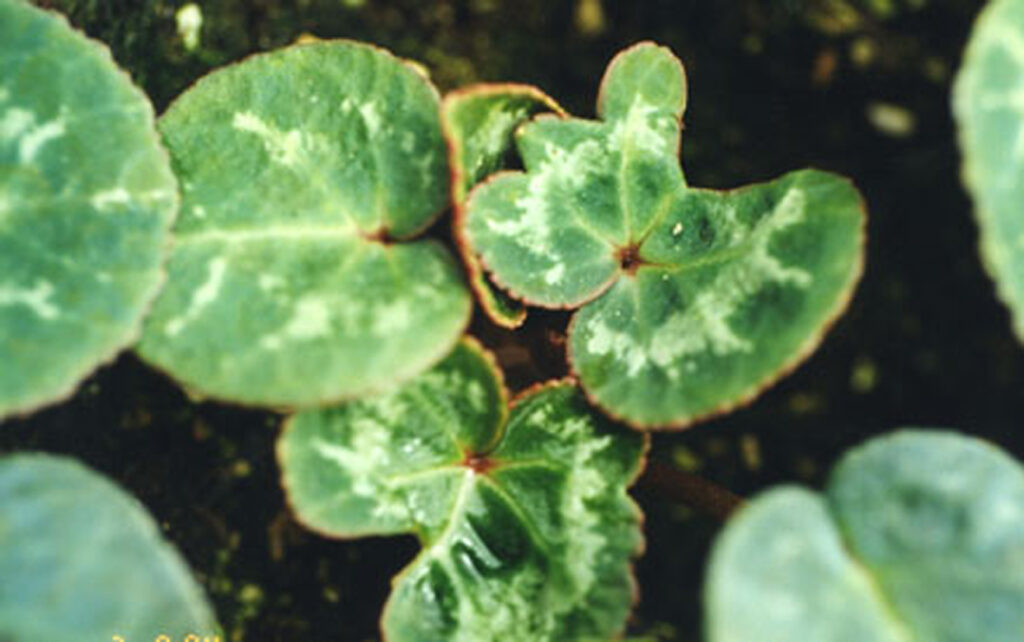
Thrips infestation in indoor plants causes discoloration of leaves. They produce a varnish-like excretion on leaves and deform the plant parts. Thrips on houseplants suck their cellular content and induce blemishes on leaf surfaces.
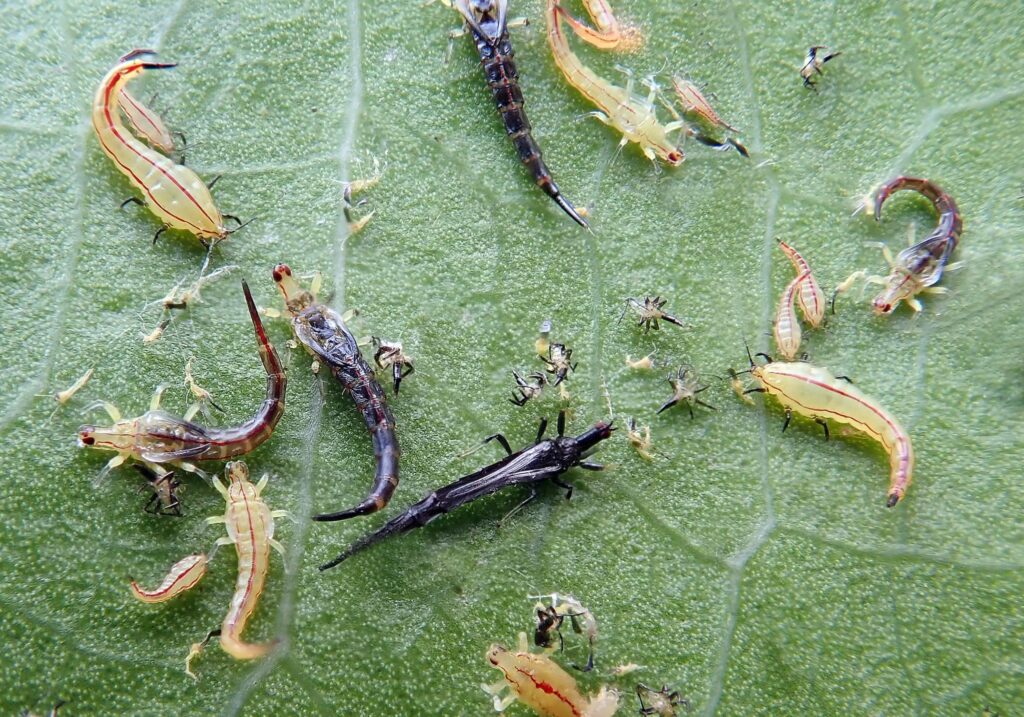
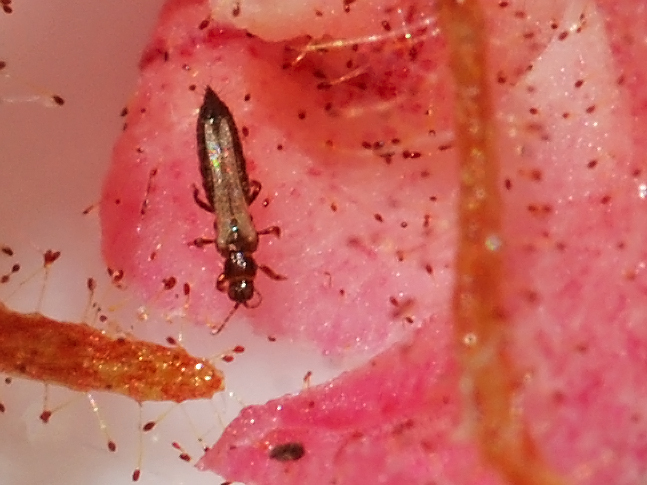


What Are Thrips?
Thrips are long, slim insects with fringed or feathery wings. These indoor plant pests have piercing-sucking mouthparts and suck sap from the outer layer (epidermis) of tissues and cells. Thrips on houseplants suck out their cell contents and cause silvering of the leaves due to their secretions. They are the most common insect pest of gardens, indoors and outdoors. Almost more than six thousand thrips species are there to suck plant sap.
Thrips feed on plants, and leaves turn pale, flecky, and silvery. Infested plants become distorted, discolored, and eventually die. Thrips belong to Thysanoptera and produce scars on outdoor plants’ leaves, flowers, and fruits.
They are also responsible for transmitting many plant pathogens. They are only visible using a hand lens. Without hand lenses, they appeared as black threads on leaves.
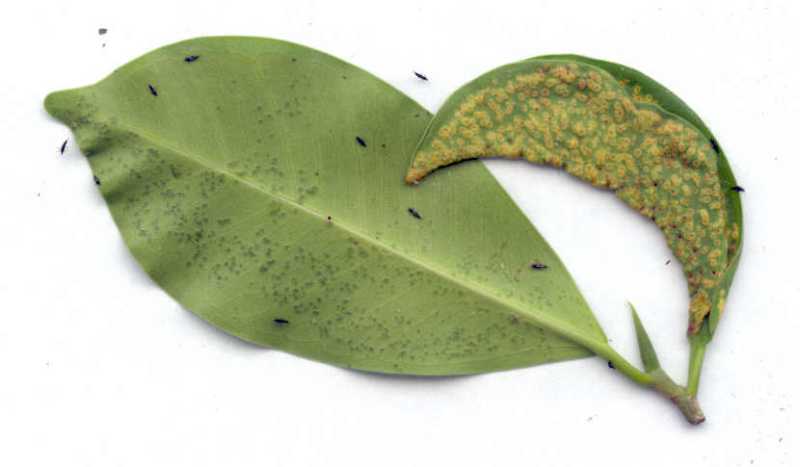

On the other side, many thrips species act as beneficial insects and feed on fungal spores. Thus, preventing plants from other deadly diseases. However, thrips feeding on plant pollens reduce flower longevity.
RELATED: Aphids Vs. Thrips | Which Is Worse And How You Can Get Rid Of Them?
What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Thrips Infestation?
Thrips are tiny insects of houseplants that are barely 5.08 mm long. These are the most little houseplant pests because they cast nasty secretions on foliage surfaces and leave appeared as scared. However, the African violet and Wandering Jew plants are prone to thrips attacks.
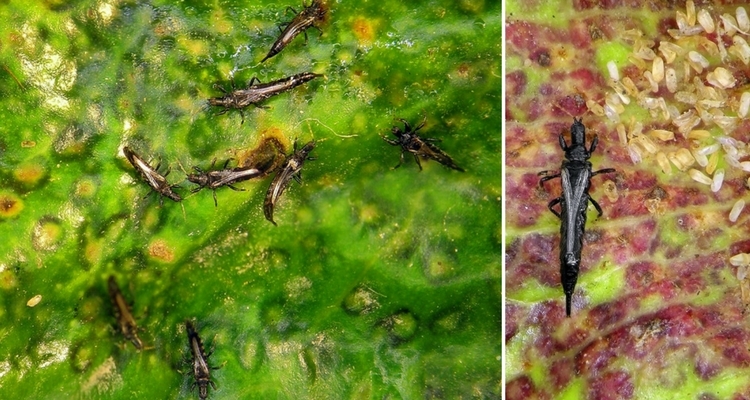


Thrips also secrete a black fecal material on leaves, flowers, and stems, which turns into dark spots. The continuous feeding of thrips on houseplants produces irregular white streaks on leaves due to sucking out of leave juices.


Life Cycle Of Thrips On Houseplants
Thrips life cycle consists of six stages which are:
- Egg stage
- Two larval stages (comprise of actively feeding larvae)
- Two non-feeding pupal stages ( a prepupal and pupal)
- An adult stage includes male and female adult thrips
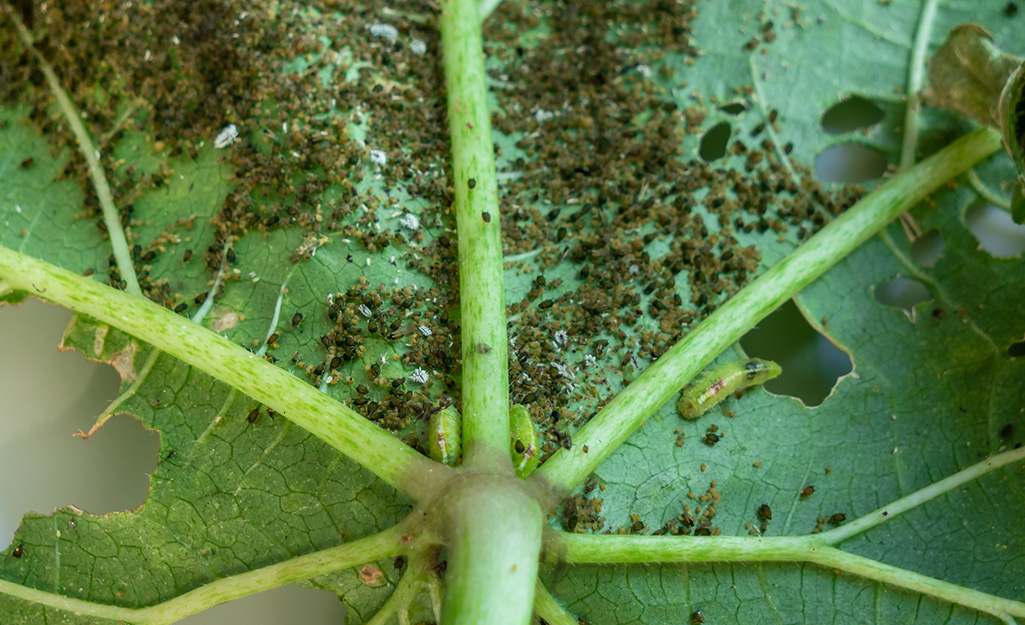
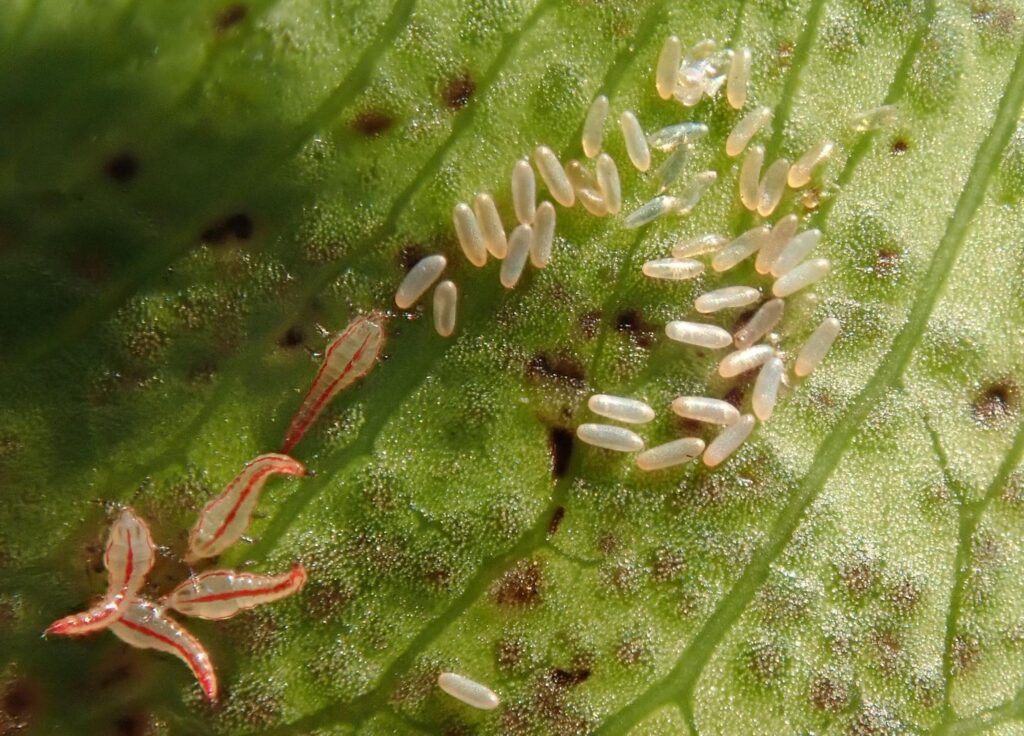
The female thrips lay their eggs in or on leaves, buds, flowers, and stems. Thrips eggs are long, cylindrical, or kidney-shaped that hatches within a few days in warm, dry, and indoor environments.
The female lays 60 to 100 eggs per cycle and is present throughout the year. After hatching, the young larvae emerge similar to adults but are small in size and do not have wings. The larvae actively feed on leaves, twigs, and flower pollens. The young appear cream to pale and only visible through a hand lens or magnification. These two larval thrips remain active for seven to fourteen days and feed copiously.
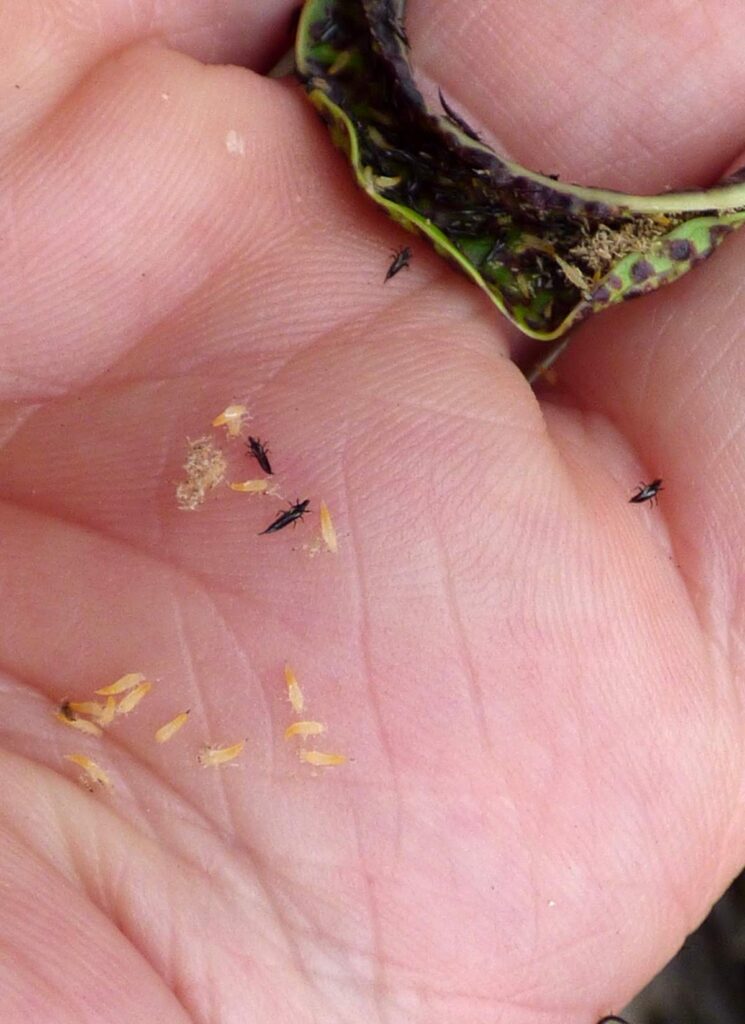
After 7-14 days, the fully grown nymphs drop to the soil or leaf litter and pupate. The pupal stage is immobile and found beneath leaf litter or soil in dark places. After two to five days, the adult appears. The adult thrips are light yellow to dark brown and 1 to 2 mm long. The males are lighter in color and slightly smaller than females.

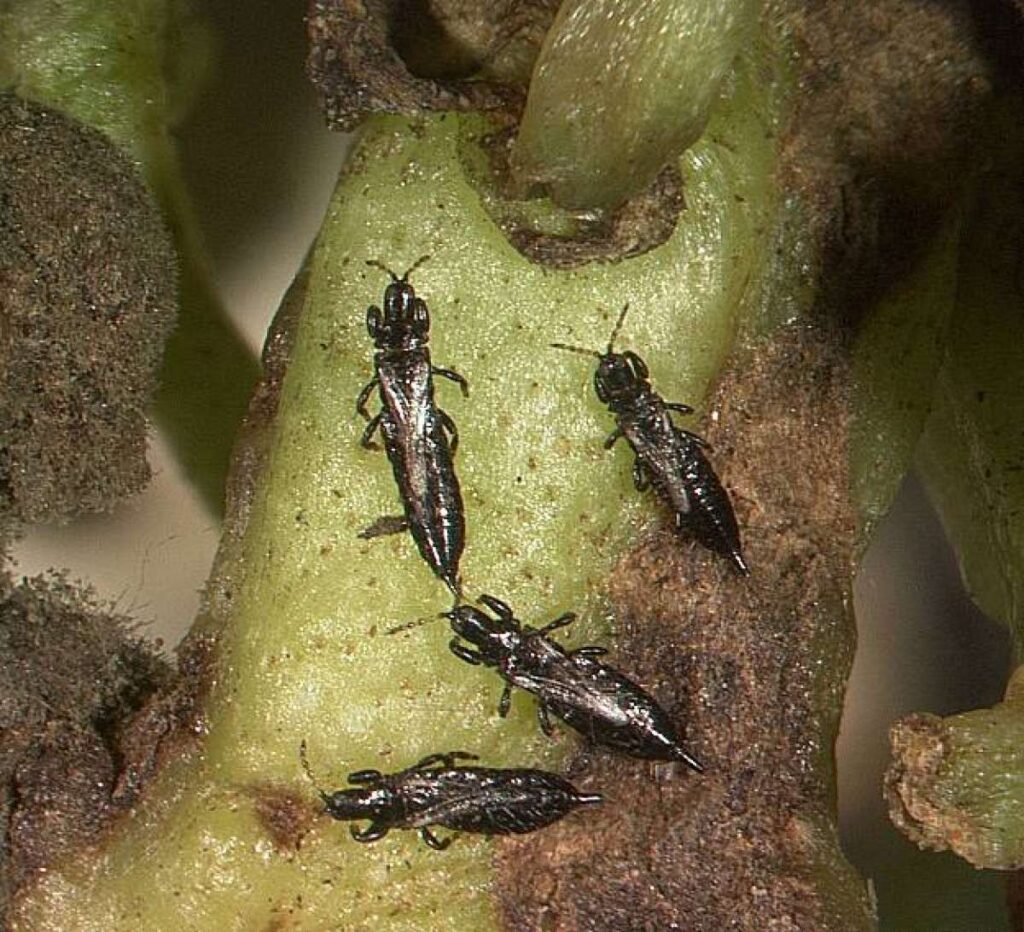
The adult thrips have two pairs of wings and three pairs of legs. The wings are fringed or hairy and narrow. Adult thrips have several generations through the entire year. The life cycle completes within two weeks under favorable conditions, such as warm and dry weather. The complimentary temperature range for their life cycle is 20-26ºC. And they have up to eight generations per year.

RELATED: How To Get Rid Of Thrips From Your Garden For God? The Ultimate Guide
Thrips Damage To Houseplants
Thrips reduce the cosmetic value of houseplants, leaves, fruits, and stems. However, flowering plants are more susceptible to thrip injury because they feed on pollen and threaten flower life. The houseplant thrips also transmit viruses and put pressure on their survival.
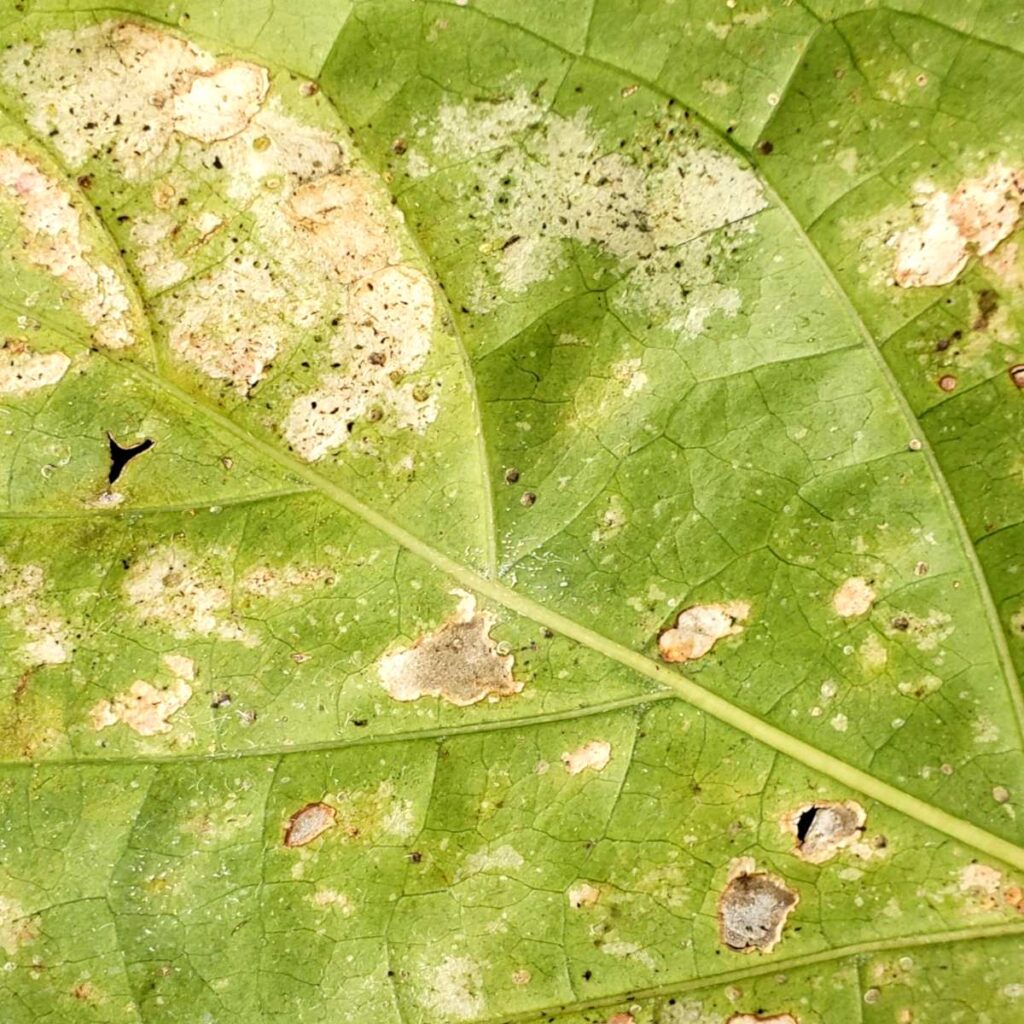
Thrips feeding on houseplants also stunt and distort their growth. Because of this, leaves fall off from plants prematurely. The plant leaf surfaces become brown and silvery due to thrip secretions. Thrip infected plants develop silver flecks on leaves and flowers.
Many thrips species feed on flower buds and kill them before it opens. And their feeding on leaves causes podlike leaf structure, appearing as “galled foliage.” In addition, while in garden plants, thrips feeding transmits tomato spotted wilt virus, severely damaging plant leaves and yield.
Thrips cause a scar on different fruits, such as citrus thrips impacts the fruit surface but do not harm the fruit quality internally. Similarly, the citrus thrips feed on blueberry tissues and avocado plant tissue, thus reducing the flower and fruit yield.
Another essential factor for plant damage is thrips spread easily over long distances. Thrips travel long-distance through wind and water to exotic places. For example, myoporum thrips are responsible for severe galling in myoporum laetum. This thrip species was introduced into Southern California from New Zealand.


How To Get Rid Of Thrips On Houseplants?
Thrips infestation is difficult to control on houseplants and other plants. However, a combined approach can control thrips and prevent plants from their damage. These practices include insecticidal soap, horticultural oils spray such as neem oil, chemical insecticides, and cultural practices.
Cultural Practices
Cultural practices help in controlling thrips infestation not only in orchards gardens but also in houseplants. Thrips spread over long distances and feed on many different species of plants. Therefore, try to avoid planting susceptible plants prone to thrips attack. Do not plant alternate hosts of thrips. Instead of this, try to grow well-adapted plants to resist thrip injury.
Always keep houseplants in proper sunlight conditions and not position them in dark places. Because in shady areas, plants are more prone to pest attack.
Keep plants in clean and well-aerated areas and instantly remove any dead infected leaves from the site. Then, properly apply irrigation and fertilization with the required amounts. Do not overfeed the plants with nitrogen fertilizer because the over-application of fertilizers will promote vegetative growth, attracting the thrips on houseplants.
Remove the old, dead, and fallen flower leaves around the houseplant area and ultimately dispose of them to avoid heavy population infestations. Always use resistant plant cultivars to discourage insect pests (thrips).
Pruning
The second-best approach to eliminating thrips is pruning—removing dead and infected plant parts by cutting. Do not over clip the plant foliage because it may attract thrip larvae towards new growths. Instead, prune the galled foliage, the leaves with thrip secretions and streaking. In orchards, the pruning in January prevents thrips damage. It also helps reduce fruit and leaves scaring because, during this time, thrips larvae only feed on new growths and do not move to fruit.
Pruning in January also induces new growth and increases the populations of predatory or beneficial insects such as spider mites that feed on thrips. This practice will benefit the growers by not reducing the quality of yield.
Use Of Insecticidal Soap
Insecticidal soaps kill thrips and control their population on houseplants. The foliar treatment of the houseplants and gardens by insecticidal soap deter thrips. These chemicals penetrate the insect body by breaking protective coatings. The insecticidal soap interferes with insect membranes and normal functioning. An example of insecticidal soap is Safer Houseplant Insecticidal Soap RTU.
Make dilutions of insecticidal soap, vegetable oil, and water. Apply dilution evenly on flowers and leaves. Also, ensure the frequent applications until the problem (thrips) is gone.
The applications of insecticidal soap are non-toxic to humans, birds, and pets.

Use Of Horticultural Oils
Horticultural oils such as Bonide All Seasons Horticultural and Dormant Spray Oil will prevent the thrip damage. However, the application of this oil suffocates the thrip populations and kills larvae, adult thrips, and eggs. Mix the horticultural and dormant spray oil with water and spray on houseplants and garden plants.
Do not apply when temperatures are above 90 degrees F. Also, avoid applications within 30 days of sulfur spray.

Biological Control
Thrips on houseplants can also be controlled through environment-friendly methods. The biological control involves the use of beneficial insects which prey on plant-feeding thrips—for example, parasitic wasps, green lacewings, and spider mites. To control thrips on houseplants, encourage the populations of beneficial insects in houseplants. In addition, maintain proper cleaning conditions around indoor plants (remove any dirt or dust from houseplants) and grow various plants.


Chemical Control
Pesticides can also be used to control thrips on houseplants. However, the application of chemicals along with predatory insects proves more effective control. So the contact insecticides can effectively control thrips on houseplants. Such as neem oil, azadirachtin, and pyrethrins.
Another example of chemical control is Spinosad. It appears more effective than pyrethrins in the management of thrips. However, it is harmful to beneficial insects. Spinosad gives the best results in controlling thrips when applied with horticultural oils.
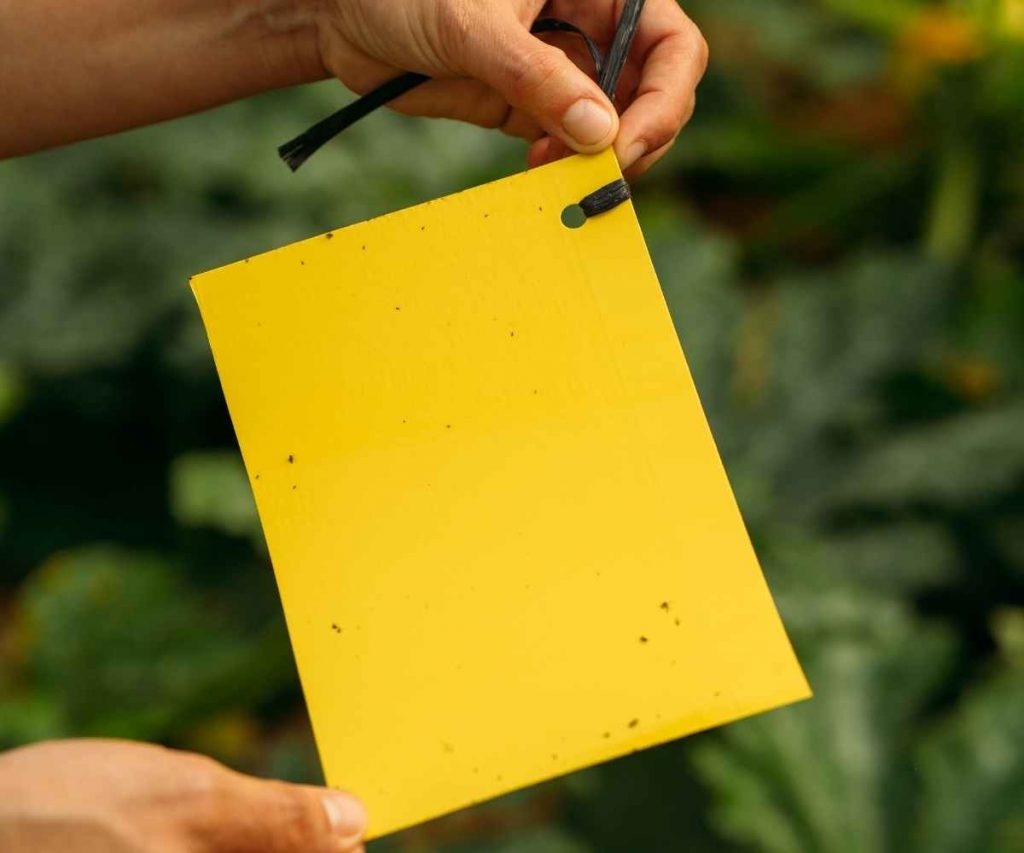
Monitoring
Monitoring for thrips also prevents potential damage. Adult thrips and larvae can be monitored in houseplants by slightly shaking the flower and foliage. They can also be monitored by hanging bright yellow sticky cards in or near plants.

Frequently Asked Questions
How Do You Repel Thrips?
Thrips on houseplants can be repelled by keeping plants moist. The thrips are more attracted to plants that are too dry. Therefore, to manage thrips, keep plants moist and maintain humidity.
How Do You Control Thrips From Plants?
There are many ways by which thrips can be controlled on houseplants, such as insecticidal soap, horticultural oil spray, and pesticides. For example, the application of insecticidal soap kills the thrips by breaking their protective body coverings. At the same time, the horticultural oils suffocate the thrip eggs, larvae, and pupae.
The pesticide applications work best when applied along with horticultural oils. The pyrethrins are plant-derived insecticides that effectively manage thrips than other chemicals. These insecticides are contact chemicals that block the oxygen supply of the insect bodies and kill them.
How Do You Keep Houseplants Free from Pests?
Following are the best practices to keep houseplants free from pests
- Keep the interior spaces clean to avoid any attraction for insect pests
- Instantly remove any dead fallen plant leaves and flowers to discourage protective hiding spaces for pupae
- Always drench the soil with organic pesticides to avoid egg hatching of houseplant pests. Use organic insecticidal soap (mix 1 tsp of mild liquid soap with one liter of water) to manage houseplant pests. Also, use neem oil solution to kell houseplant pests. The oils work as a systemic insecticide and kill the problem.
- Do not overwater and overfeed the houseplants.
- Keep them in well-ventilated and sunny areas indoors.
- Use pots with drainage holes to properly drain the water
- Remove egg sacs, webs, and pupae from the houseplant pots
- Always use clean, fresh, and disinfectant soil to provide a healthy environment for roots
- Always keep in mind the specific nutrient requirements of each houseplant
- Try to maintain the diversity of houseplants to encourage the population of beneficial insects
- Place Franch gold around indoor plants to repel whiteflies and aphids
Do Thrips Like Humidity?
Thrips do not live in higher humid conditions. They prefer dry, hot weather and young, immature leaves. In favorable conditions, they can produce many generations per year (like up to eight generations) and can complete their life cycle in a short span (within two to three weeks).
In contrast to fungus gnats and mealybugs, thrips enjoy dry environments. Therefore, to keep them away from houseplants, maintain higher humidity and wet the soil top layer.
Do Thrips Leave Poop?
Thrips secrete black, varnish-like excretions on leaf and fruit surfaces. This fecal material reduces the cosmetic value of fruits and plants and attracts other insect pests. At the same time, the thrips suck out sap from plant tissue and induce white streaks on leaves and flowers.
Sources For Further Reading
- Thrips How to Manage Pests Pests in Gardens and Landscapes—Thrips. (2021, August 1). University of California Integrated Pest Management. Retrieved January 18, 2022, from http://ipm.ucanr.edu/PMG/PESTNOTES/pn7429.html
- Planet Natural Research Center. (n.d.). Planet Natural Research Center. Retrieved January 18, 2022, from https://www.missouribotanicalgarden.org/gardens-gardening/your-garden/help-for-the-home-gardener/advice-tips-resources/pests-and-problems/insects/thrips/thrips-indoors.aspx
- Missouri Botanical Garden. (n.d.). Missouri Botanical Garden. Retrieved January 18, 2022, from https://www.missouribotanicalgarden.org/gardens-gardening/your-garden/help-for-the-home-gardener/advice-tips-resources/pests-and-problems/insects/thrips/thrips-indoors.aspx
Read and learn What are the Effective Ways to Fix Nitrogen Toxicity in Houseplants? and What Are Mealybugs? How to Kill Them on Succulent Plants?