Believe it or not, those who have never seen a palm tree are surely familiar with its appearance. Most people believe that a palm tree and a coconut tree are interchangeable because palm trees produce coconuts. They belong to the same family of plants but are two separate species. In this article, let’s talk about coconut tree vs palm tree.
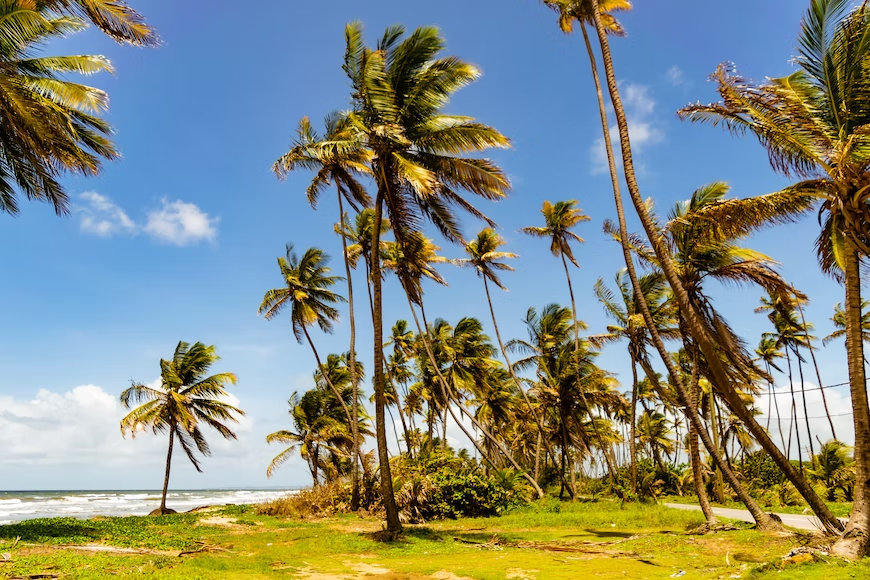

It’s possible that many individuals are unaware of the distinctions between a palm tree and a coconut tree. However, despite the fact that there are numerous varieties of palm trees, only one variety can yield coconuts.
What distinguishes coconut trees from palm trees, then?
In this article, we will show you the main differences and similarities of these two economically important trees. Read more and find out!
General View Of Palms And Coconuts
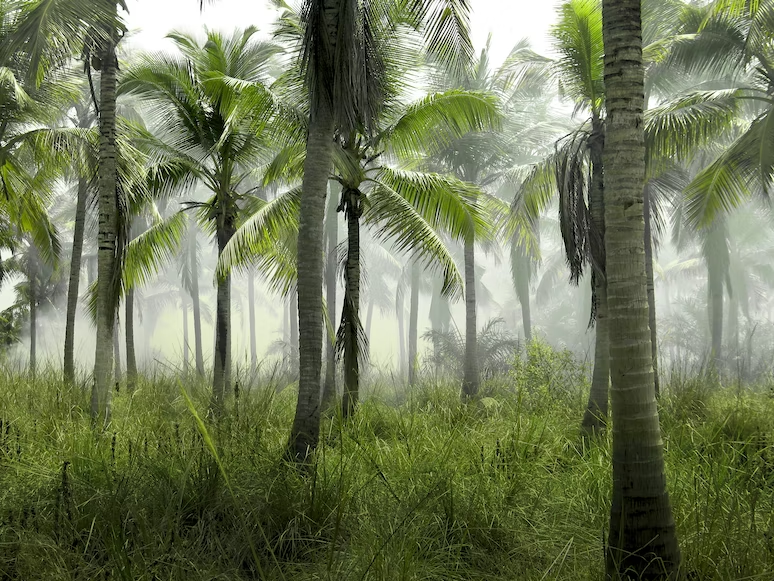

Although palm trees and coconut trees have many similarities, not all palm trees produce coconuts. The differences are greatest on the leaves. Palm trees have fan-shaped leaves, whilst coconut trees have broad leaves. Additionally, coconut trees produce coconuts, whereas palm trees produce palm oil.
Coconuts come in a wide range of varieties. These trees typically have a familiar appearance but differ in thickness and size. Most coconut trees grow to an average height of 80 feet and have thin trunks. Although fronds grow on the top, the bases are typically thick.
What Are Palm Trees?

Any tree that may be categorized as a member of the Palmaceae class is referred to as a palm tree. More than 230 families and more than 3,000 species comprise this tree group. Although these palm trees are found worldwide, they are primarily found in Florida and California in the United States.
Palm trees can be recognized by their leaves. All palms have “fronds,” which are fan-shaped leaves with a structure made up of pieces that branch out from a central point. Each type of palm tree has unique leaf lengths, some of which can reach ten feet.
Palm trees can range from tall, slender, reedy trees with small heads topped with fronds to thick, squat trunks coated with scales. Both planted, and potted conditions are favorable to them. Although palm trees have extraordinarily robust exterior trunks, they are mostly compared to almost all other tree species inside. Palm plants both produce fruit and flowers.
Related: Madagascar Palm Tree: The #1 Care, Propagation, and Watering Guide
Characteristics Of Palm Trees
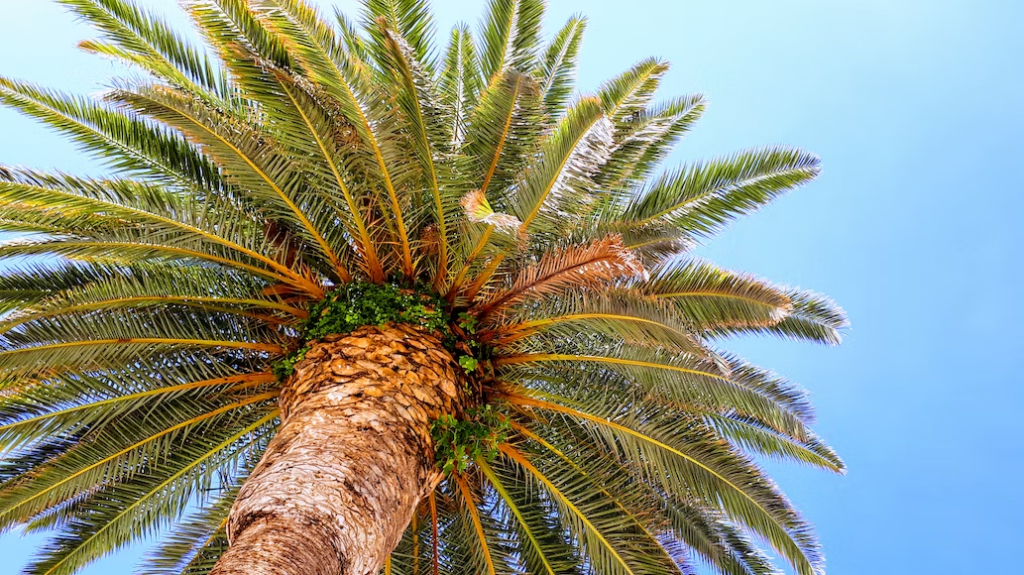

Perhaps surprisingly, not every palm tree resembles a typical tree. These species can occasionally develop as long vines or shrubs.
There are two types of leaves on palm plants. One of these cultivars grows in an oblong shape that resembles feathers. They develop from the stem in sharp, elongated forms that spread outward. The second type of palm tree leaf, which is bigger and almost like hands, is set at the very tip of the stem.
The largest species of palm trees can reach heights of up to 197 feet, though they come in a variety of widths as well. Although palm trees can only grow in specific regions, it is allowed to utilize in landscaping across the United States.
However, it can be challenging to manage them in the winter. Since palm palms are not deciduous trees, they remain evergreen throughout the year without losing their leaves in the winter.
Differences: Coconut Tree vs. Palm Tree
Due to the coconut’s frequent appearance in palm trees in popular culture, most people believe that all palm trees are coconut trees. But only a few types of palm trees bear coconuts. There are two different yet strikingly similar-looking palm trees: the coconut palm and the oil palm.
The most extensively planted palm tree in the world is the coconut palm tree. These coconut palm trees are robust, and their roots go far down into the ground. They are resilient trees that have a 100-year lifespan.
Only in Florida’s tropical climate are coconut palms produced in the United States. Not all palm trees are coconut palms, including those found in Arizona and California. For survival and growth, coconut trees require the wetness and humidity of a tropical or subtropical environment. The coconut fruits are not nuts, despite their name. The coconut tree fruit is a drupe type.
The coconut palm bears fruit, just like the other palm trees in the family. The coconut has a wide range of benefits that humans have benefited from since the dawn. Coconut fruit can be used to make various items, including coconut flesh, water, and oil.
Whole civilizations have survived on the fruit of the coconut tree. The phrase “the tree of a thousand uses” refers to coconut trees in Malaysian culture. People drink the water from coconuts, consume the flesh when it is dried, use the oil for various things, and even use the husk. Cattle can be fed even the parts with an excess of dietary fiber that would be difficult for a human digestive system to process.
Related: Golden Leaves? 5 Reasons Why Your Majesty Palm Is Changing Color
A Coconut Tree:
- Produces coconut fruit
- Has wide-spreading leaves
- Coconut trees often live for 60 to 80 years. Since it can support three generations, it is frequently referred to as a three-generation tree. However, it usually takes six to ten years for it to start bearing coconuts.
- It has deep roots that can reach a diameter of 1 cm
- Grows best in hot, humid areas in the tropics. This means that for them to thrive, they need enough warmth and moisture.
A Palm Tree:
- Produces palm oil
- Has fan-shaped leaves
- Some palm trees live for 150 years or more. However, a palm tree’s lifespan ranges from 7-8 decades on average. In the meantime, a palm tree’s longevity depends on its kind. While some palms live for more than a century, those grown in tropical environments only live for 70 to 100 years.
- To give the palm tree solidity, tree roots stretch out on the base up to 36 inches.
- Palm trees perform better in a warm, tropical climate. Although resilient and adaptable to many environmental situations, shallow temperatures often damage them, particularly in the winter.
Comparatively, the climatic conditions under which coconut and palm trees grow differ. The inequalities in characteristics and attributes are a result of this. While palm trees come in various forms and sizes, coconut trees are recognized for producing coconuts. Palm trees have some critical differences despite being members of the same family. Despite the abundance of coconut plants, only the coconut palm can produce coconuts.
Do Palm Trees Produce Coconuts?
Even though they are members of the same family, only one species of palm tree produces coconuts. However, there are numerous varieties of coconut trees.
The only species of palm that produces coconuts is Cocos nucifera. Some are unrelated to coconuts, while others are known to have palm oil. People assume that a palm tree and a coconut tree yield coconuts due to their similar appearance. However, the palm tree comes in two separate species.
What Palm Tree Produces Coconuts?
The only species of palm tree that can yield coconuts is the Cocos nucifera species. Therefore, the only remaining member of the genus Coco is this species. Additionally, there are two types of coconut trees, tall coconut trees, and dwarf coconut trees.
There are numerous coconut trees under the two categories of coconut trees. The types of trees vary according to where they can be found. As a result, the coconuts that the trees produce vary in hue, size, and shape. This is based on how old and healthy the coconut tree is.
Another interesting fact is that this category includes approximately 80 different types of coconut trees. Although there is only one kind of coconut tree, there are wide different varieties of trees that produce coconuts.
Let’s start with the taller kind of coconut because it differs from the shorter variety. Cross-pollination is possible in the taller type. This implies that it can exchange general data with other trees.
However, the ability of its flowers to increase depends on pollination from other trees. The tall and dwarf palm trees, which produce various coconuts, are the reason why they are both in existence.
Below is a list of palm trees that yield coconuts:
- West Coast Tall coconut can grow in any soil and produce 80 coconuts yearly
- Eastern Coast Tall coconut has 70 coconuts a year and thrives in sandy soil
- The Macapuno coconut is highly nutritious and grows in deserts.
- The Malayan yellow dwarf coconut, a common dwarf coconut, yields the most coconuts recorded in the annals of palm trees.
- The Maypan coconut is cold-hardy and produces enormous coconuts. It is also resistant to yellowing sickness.
- King coconuts are green and grow in 30 bunches.
- The Fiji dwarf coconut has long fronds and is very disease-resistant.
Uses of Coconuts
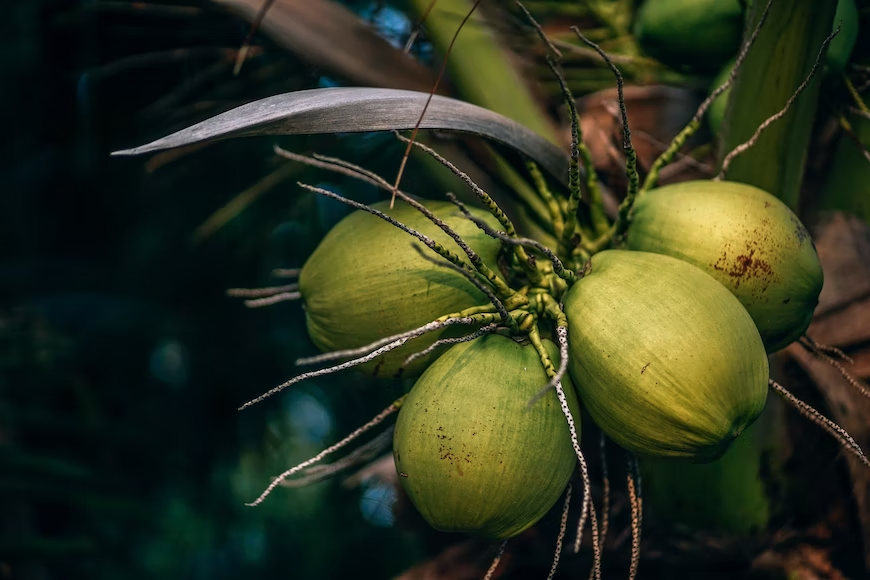

Coconuts are a fruit with a husk that contains both water and meat. Although the two by-products of the palm tree that are most well-known to people are these two, there are more than a hundred other uses for this fruit. The tree is called “The Tree of Life” in the Philippines.
Coconut Lumber Uses
Beyond construction, coconuts are employed in practically every industry, including medicine, flooring, and cosmetics. The coconut contains various parts that are used in numerous ways. Trade in coconuts is a major component of the economies of many nations, and it plays a significant role in daily life on practically every continent.
Coconut Husk Uses
There are various uses for the coconut shell’s outer layer. The fiber outside the husk, known as coir, is used to create ropes, bags, compost, brushes, and even a waterproof joint sealant for boats. The fibers can also be used to make tea, served in nations like Brazil, to treat inflammatory diseases. The husk itself is utilized for skin exfoliation, charcoal, fuel, floor polishing, and insect repellant. Bird feeders, plates, decorations, and crafts are made from shells.
Coconut Water Uses
Finally, there is coconut water inside the shell. In the tropical regions where the fruit grows, coconut water is frequently drunk. It offers a good amount of sugar, fiber, antioxidants, and vitamins. Because it may mix safely with blood, it can be administered as an emergency infusion and restores the body’s electrolyte balance. Kidney stones are also removed by it. Cutting off the top and sticking a straw inside a coconut is all it takes to drink from it.
Coconut Oil Uses
Coconut oil is well renowned for its ability to soften, hydrate, and minimize wrinkles. It can get rid of head lice, lessen the visibility of varicose veins, condition the hair, and enhance the tone and elasticity of the skin. Coconut oil has medical uses in addition to cosmetic ones. It can aid in reducing acid reflux symptoms, supporting the liver, enhancing nutrient absorption, and easing the signs of chronic weariness.
Related: Not Down With The Brown: Tips For Saving Your Majesty Palm’s Tips
Identifying A Coconut Tree
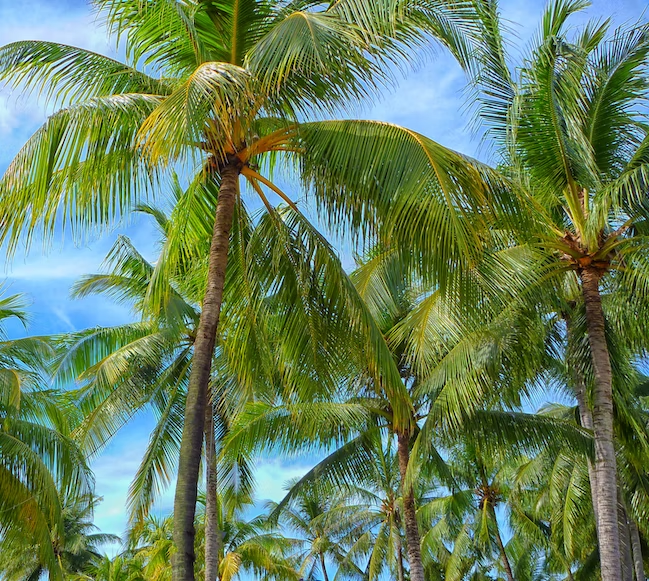

There are numerous techniques to identify coconut trees. Despite having many unique traits, coconut trees share several universal characteristics that make them simple to recognize:
- Typically, the columnar trunk is 15 to 17 feet long.
- Four feet broad leaves with feathery shapes.
- Fruit with fibers on it.
- Their trunk is thin and rough.
- The majority of coconut tree species can grow up to 80 feet tall.
- The base is thick, while the top is covered with frond growth.
Identifying A Palm Tree
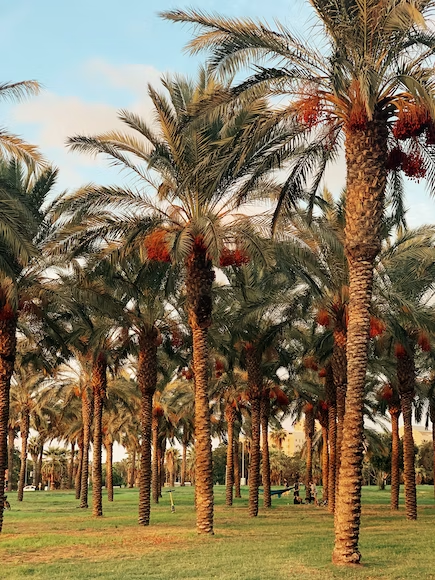

Even though a palm tree’s characteristics may be nearly identical to those of a coconut tree, you may tell a palm tree apart by its following characteristics. Most palm trees have:
- Leaf fronds resemble fans.
- The single trunks of certain species are longer and thinner.
- Short, plump palm trunks are characteristic of dwarf palm trees.
- Some dwarf palm trees have bushy pinnate fronds that burst out without any trunk, whereas smaller palm trees have clustered trunks with three to four trunks growing together.
- There are certain palm trees with smooth, thin trunks.
None of these species yield high-quality firewood made from palm trees. While some palm tree varieties have trunks covered in trunks, others have a graying, brown hue. The distinctive feature is that most houses use the dwarf and shorter palm varieties to grow in the compound.
Because palm trees have shallow roots, most people who grow them in their yards prefer a shorter and dwarf variety of the trees.
These are the typical dwarf, bushy, and tiny palm varieties that most households prefer:
- Pygmy Date Palm – This palm is tiny and doesn’t get much taller than 10 feet. Due to its single stem and bushy, pinnate-shaped fronds, it is easily recognized. The tree is a typical flowering ornamental tree that is perfect for subtropical landscaped gardens. Dates are produced by the plant, although they are not as good as dates that are produced by taller palm trees.
- Pindo Palm – The palm tree is a type of cold-tolerant palm commonly referred to as the jelly palm. They typically grow slowly, reaching a maximum height of about 20 feet when completely extended. They are, therefore, perfect for gardens that call for shorter palm palms. In addition, this species’ ability to thrive in soil and the full sun makes it unique.
- Triangular Palm – It suits small to medium size palms that can be utilized for a small garden and is commonly known as Dypsis decaryi palm. The palm tree is recognized by its pinnate fronds, which can reach a height of 8 feet. The leaves of the fronds point at a 120-degree angle, which is an intriguing characteristic. As a result, the palm tree has a triangular cross-section. Tropical gardens are suitable for the aesthetic variety of palm trees.
- Mediterranean dwarf Palm – It is a flowering palm frequently referred to as the Mediterranean palm tree. Because of its clustered trunks, the palm tree resembles a shrub. The palm tree often reaches a height of 20 feet in warm regions. It is prized for its beautiful appearance, resistance to cold, and vibrant hues.
Final Thoughts
Upon one glance, palm and coconut trees have a similar appearance but in closer look, they definitely differ in several ways. They are distinct with one another although they come from the same family of plants, Palmaceae.
Both the Coconut trees and Palm are economically important plant species as they are utilized in many products we use in our day to day lives. That is why they are heavily cultivated and distributed widely around the world.
Editor’s Recommendations
27 Fruits With High Water Content (Including Pictures)