Russia has a massive amount of territory. Whilst much of it is often buried under thick layers of snow, that doesn’t mean that the steppes and plains of Russia are bare of trees. Far from it Types Of Russian Trees.
There are forests in Russia, and they have been there since before humans started to call this place home. Even today, some parts of the country remain covered in dense woodland and packed with a wide variety of different species.
How many species? Well, that’s what this list is for! To show you just some of the many trees that call this place their natural habitat!
1. Oak
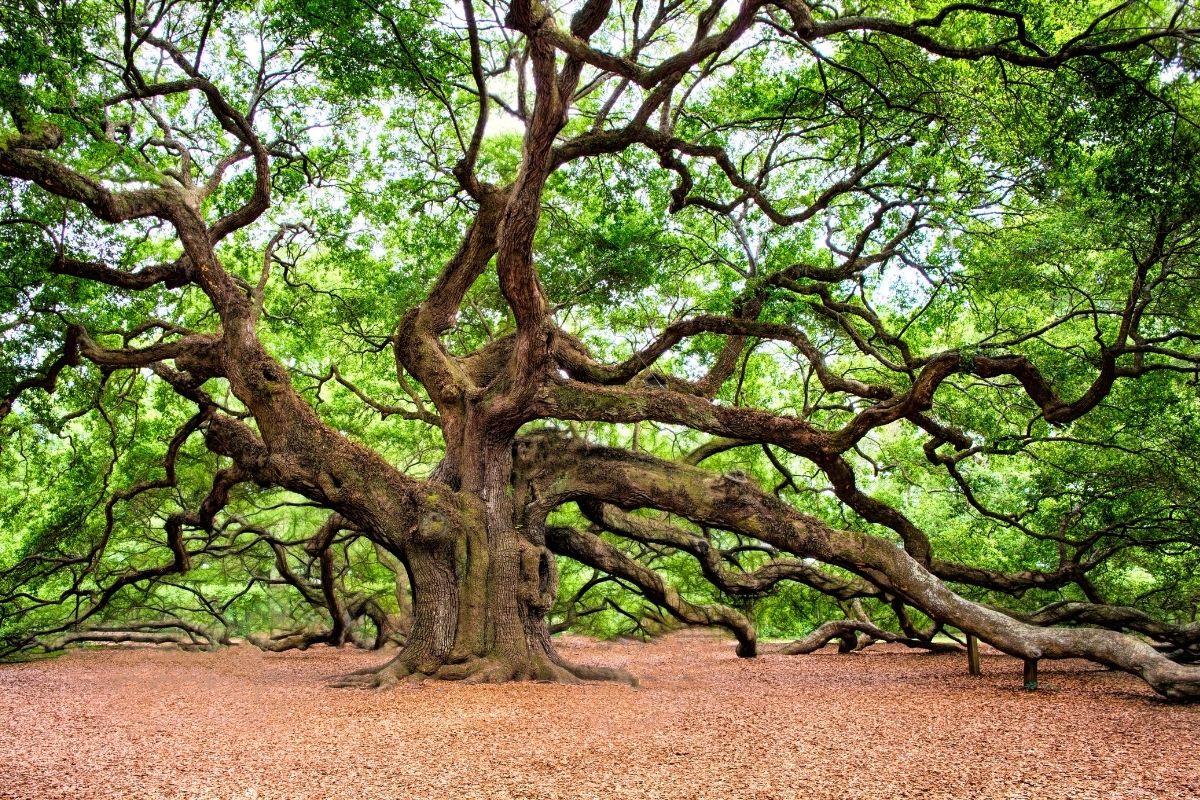

Oak trees. like in many other places where they grow, thrive in the more temperate climates of this large country
They provide shade and shelter for wildlife, such as squirrels, deer, rabbits, and birds. They also provide food for various species of birds and small mammals.
Without oak trees, Russia would be much poorer in terms of biodiversity. It would be difficult to sustain life without the protection provided by oak trees.
Oak trees cannot survive in the northernmost regions, however, and there are two main reasons for this. First, the climate is too cold for oak trees to grow. Second, there is not enough land available for the growth of oak trees.
2. Maple
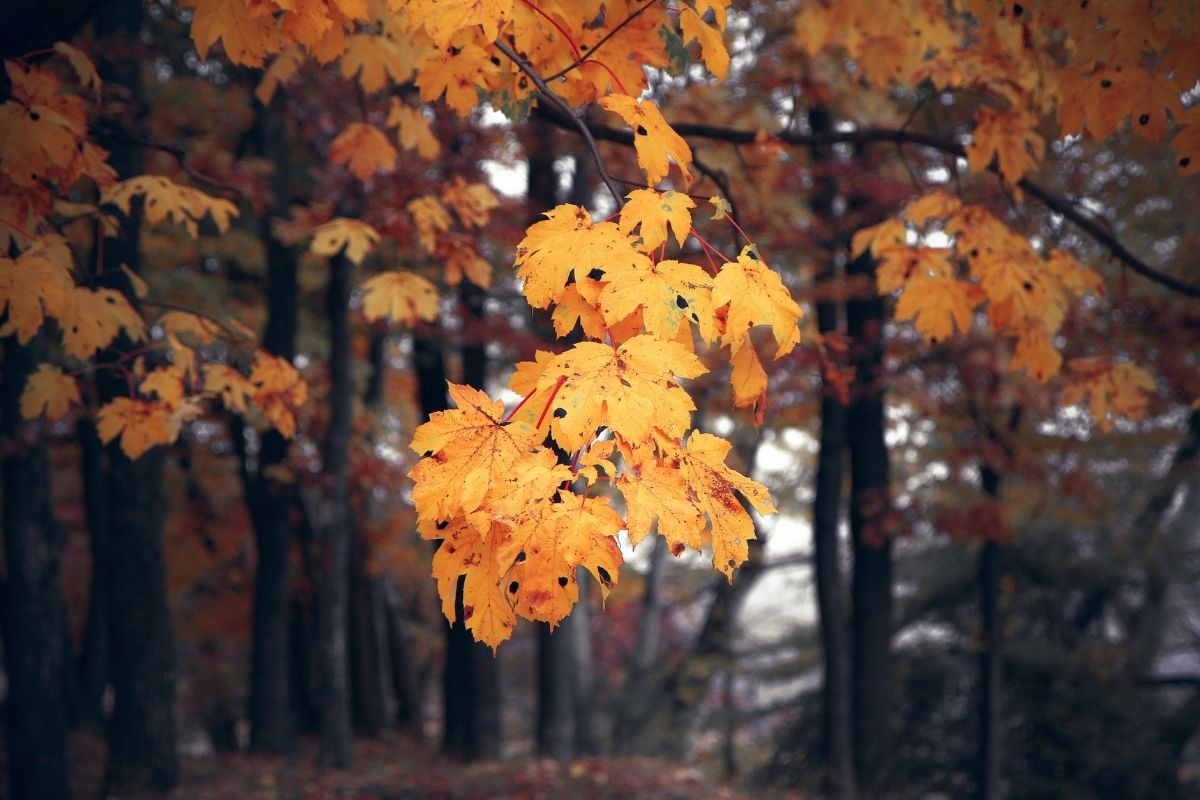

Despite their widespread fame and syrup that has made Canada famous around the world, Russia is also home to a massive number of maple trees.
In Russia, maple trees grow wild along rivers and lakes and are used as a source of food and medicine.
Maple trees are extremely popular among homeowners and landscapers because of their beauty and versatility. Their leaves change colors throughout the seasons and give off a sweet fragrance when crushed.
The sap from these trees is used to make syrup, candy, and maple sugar.
In addition to providing beautiful autumn foliage, maple trees produce delicious wood products that can be used for furniture, flooring, and building materials.
While most people associate maple trees with fall foliage, maple trees bloom in spring and early summer. These flowers appear as small white blossoms that turn into large yellow fruits. The fruit ripens in late summer and fall.
3. European White Birch
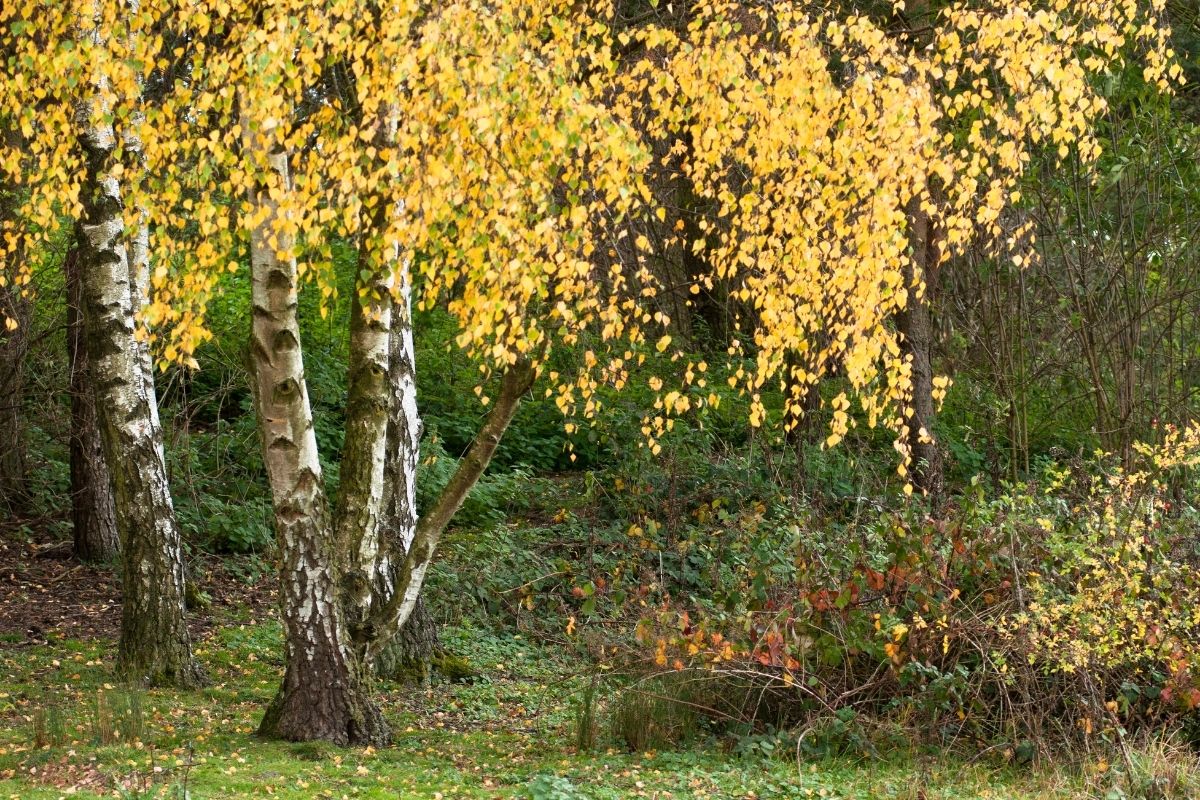

Russia shares as much of its floral life with Europe as it does with North America. One of the widest spread of the trees that occupy both of these landmasses is the European White Birch, also known as the Silver birch, thanks to its distinct shiny bark.
This tree grows quickly and provides excellent growth rates. It is also extremely resistant to pests and diseases. For these reasons, the European white birch is becoming increasingly popular in Russia.
It is possible to grow this tree in most climates, though it does require consistent moisture. It will thrive in well-drained soil with full sun exposure.
Because the European white birch offers such a wide variety of uses, there are many ways to grow it successfully. Some people choose to plant it in large groups to create a natural woodland setting.
Others prefer to plant individual trees in smaller groups.
4. Caucasian Fir
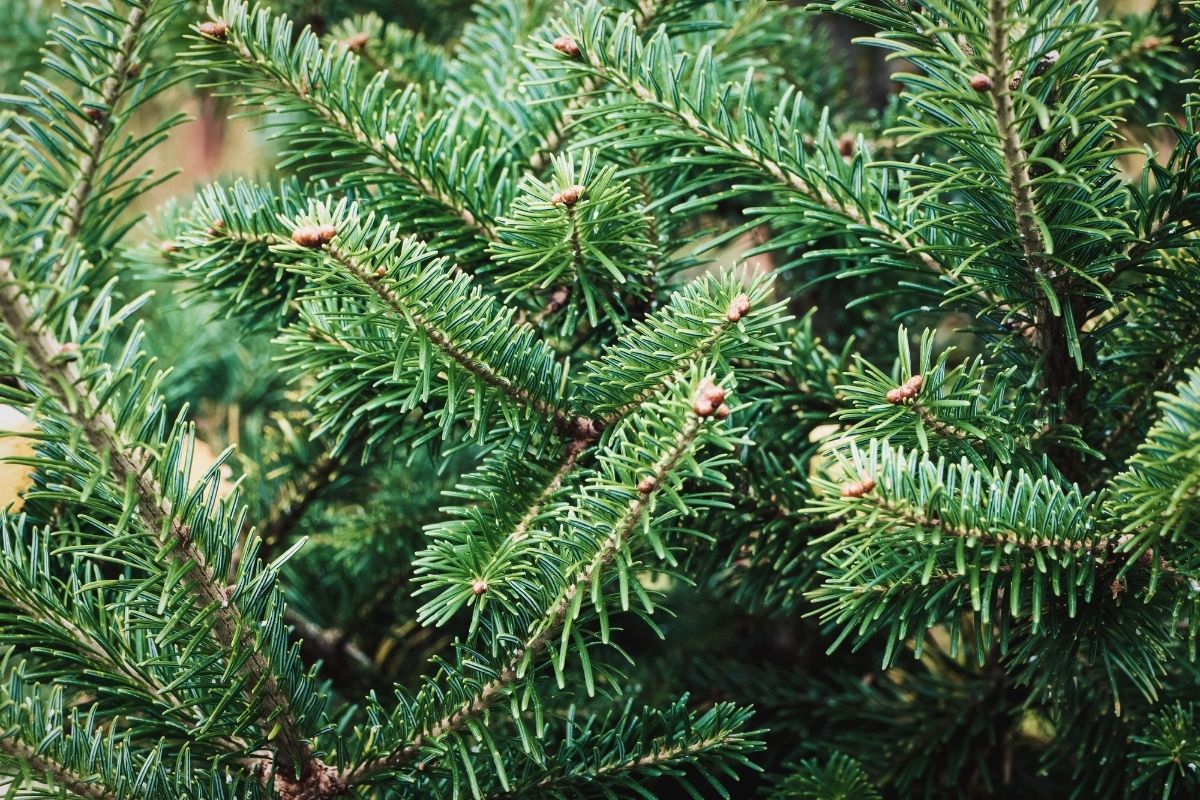

The Caucasian fir tree is another coniferous tree that Russia shares with Europe. Located around the Black Sea in Turkey, as well as the Russian Caucasus, hence the name.
Along with Western Russia, this tree is native to the mountains of Georgia, Armenia, Azerbaijan, Turkey, and even some regions of Iran as well.
They’re usually found growing in rocky areas and mountain meadows. These forests are home to many animals such as bears, wolves, lynx, foxes, deer, hares, squirrels, birds, and butterflies.
Because of its beautiful appearance, the tree is often used as a symbol of rebirth and renewal.
5. European Spruce
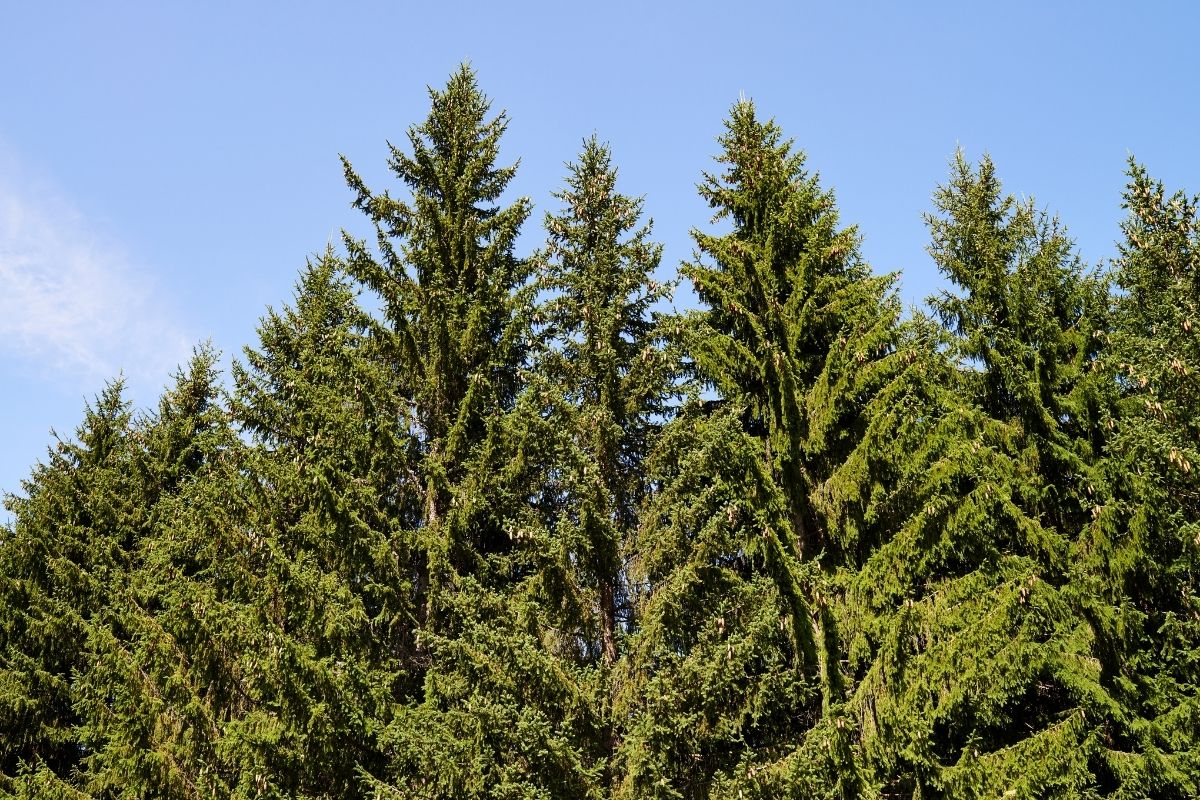

The European Spruce is another tree that Europe shares with Russia.
Whilst this tree mainly occupies pockets around colder, mountainous regions of Europe, such as in Scandinavia and the Alps, there are also great Swaths of forests made from this tree in Eastern Europe and Russia.
Spruce trees grow naturally in Siberia, Russia. They are found in abundance in the taiga forests of the country’s far eastern side. This species of tree is known for its magnificent bark, which is used for various purposes.
This type of tree grows rapidly in the taiga forests and produces large amounts of wood. The timber produced from these trees could be used for building houses, furniture, and other wooden products.
These trees grow massive. Heights of 180 feet are not uncommon, and one example of this tree in Slovenia is well over 200 feet tall!
6. Lobed Elm
Although this tree is usually associated with Japan and East Asia, the Lobed Elm also grows extensively on the Russian mainland.
Russian lobed elms have longer branches than those of American elms. Their leaves are smaller and rounder, and the bark is smooth and shiny.
The flowers appear first in spring, then later in summer. They resemble those of European red maples. This tree has been cultivated in Russia since ancient times and is found in parks and gardens everywhere.
The Russian lobed elm is used extensively for landscaping, especially in parks and gardens. Its fast growth rate makes it ideal for such use. The tree is easily propagated by grafting.
The Russian lobed elm is one of the most popular types of deciduous trees in Russia.
It is well suited to urban conditions, and it can withstand pollution and drought better than other species, though it does prefer to grow at higher altitudes where urban centers aren’t usually located.
Elevations between 1000 and 2000 meters are ideal for this tree, but it can be grown outside these ranges as well.
7. Manchurian Walnut
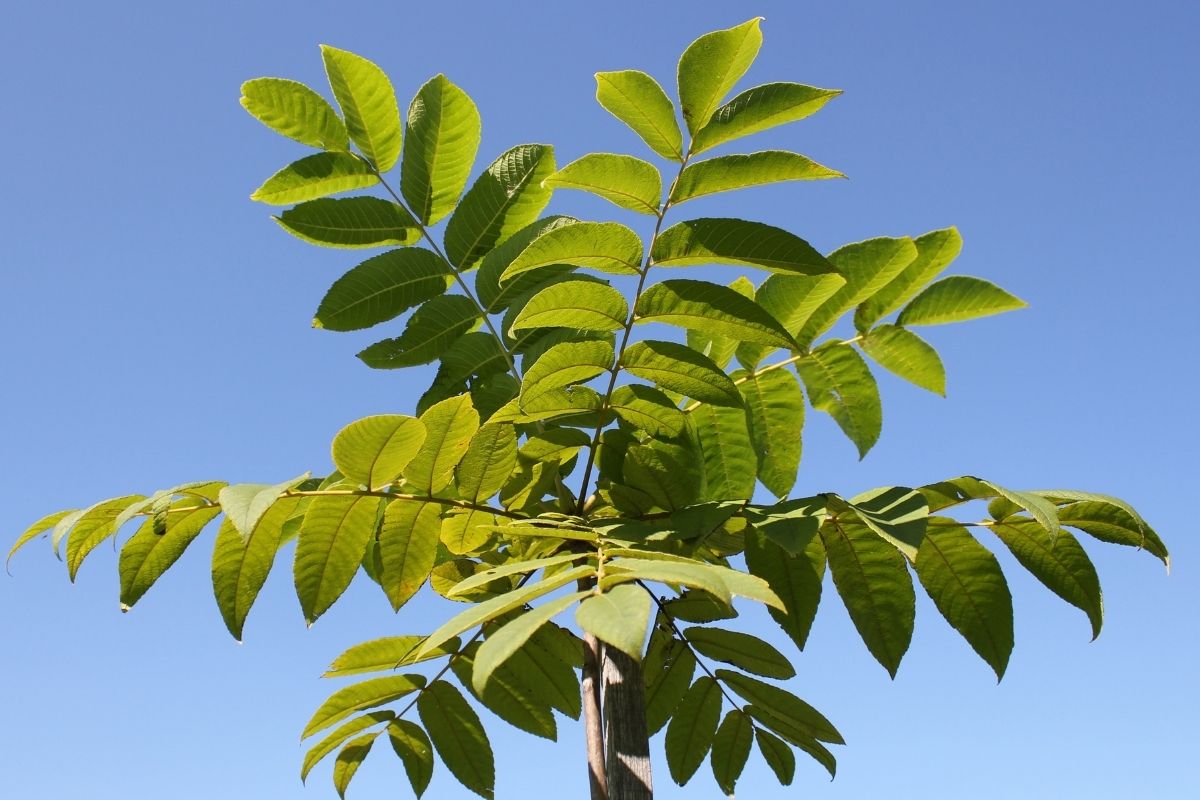

Being one of the many countries that are located next to China, it is unsurprising that these two countries would also share several species, both animals and plants.
The Manchurian Walnut tree is a clear example of this sharing of flora and fauna.
They are quite a large species of tree, being about to grow to heights of over 75 feet tall in some cases.
Manchurian walnuts were found in Siberia, where they grew in abundance on the banks of rivers, lakes, and ponds.
They had a nut about three inches in diameter and a shell that protects the nut inside. The fruit was edible but bitter.
8. Siberian Spruce
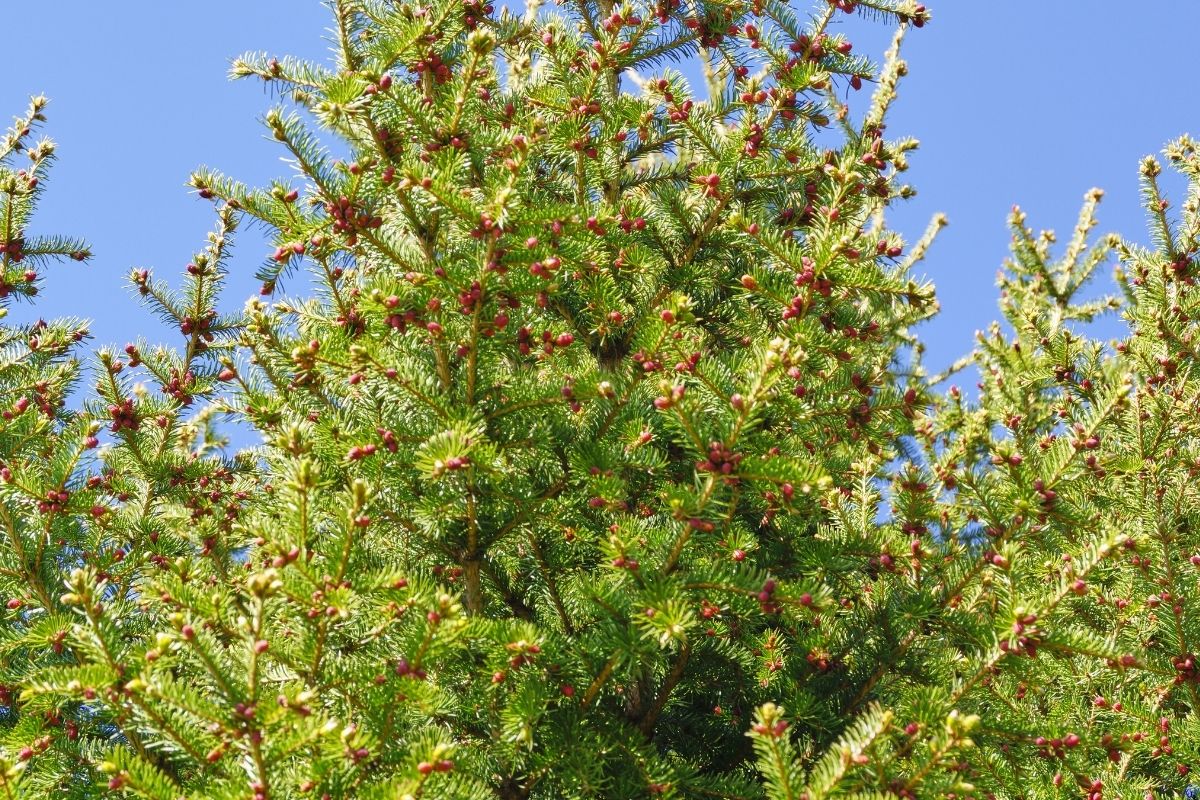

A close relative of the European Spruce tree, the Siberian Spruce is a species of tree in the Siberian Ural Mountains. They are slow-growing trees and can live up to 500 years.
The wood of these trees is used to manufacture lumber products.
The Siberian pine tree grows rapidly to a height of 50 meters. The trunk diameter of these trees ranges between 1 and 2 meters.
The leaves of the Siberian pine trees are glossy green and grow up to 2 meters long. The Siberian pine trees bear cones that contain seeds.
These Russian Spruce nuts are known to be rich in vitamin B and minerals such as iron, phosphorus, and potassium. There are several species of pine nuts that are grown in different parts of the world.
Some of the most popular varieties include Asian white pine, Japanese black pine, European red pine, Chinese white pine, and Russian white pine.
9. Willow
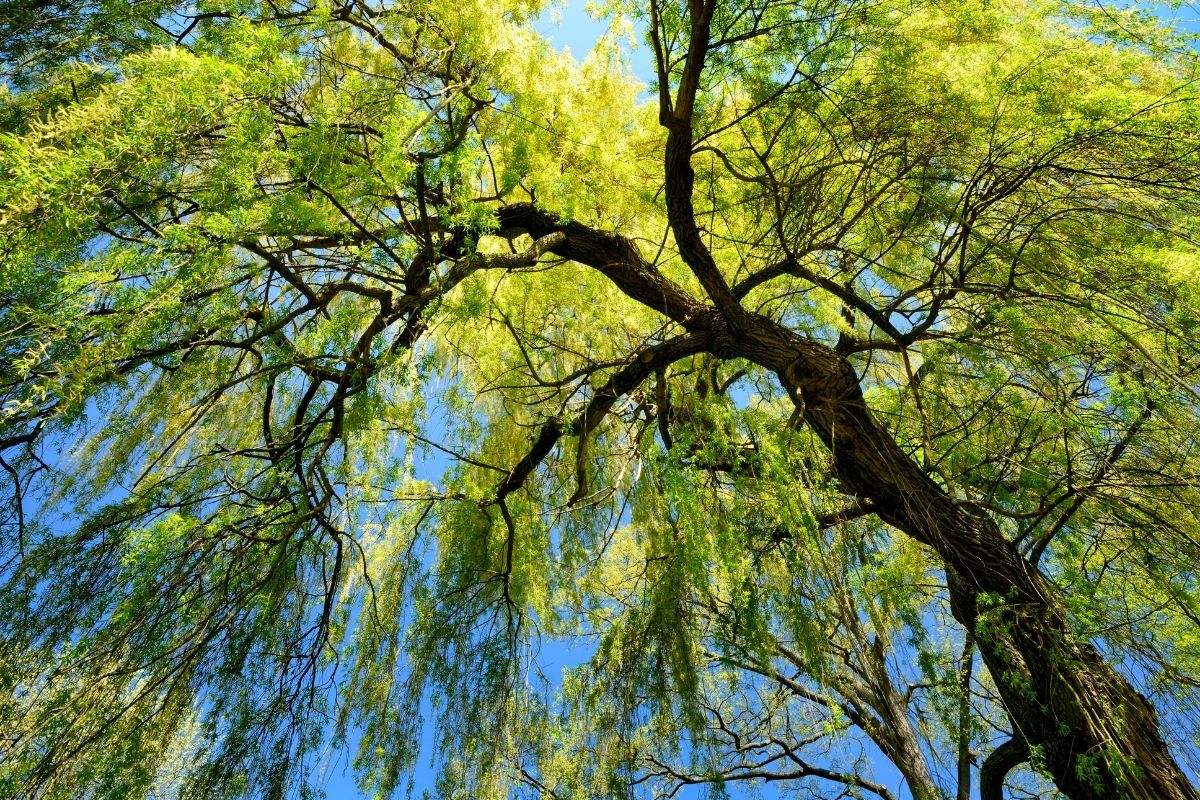

Willows are native to Europe, Asia, North America, and northern Africa. However, it is in Russia where the biggest natural forests of willows grow.
Because willow trees are technically considered non-native plants, they are often used as landscaping items and natural decorations. Willows are commonly planted along riverbanks, where they provide a beautiful shade for wildlife and people.
In addition to providing a pleasant place to sit, willow trees are known to have medicinal properties. Some studies suggest that willow bark contains chemicals that may help treat fever and coughs.
10. Poplar
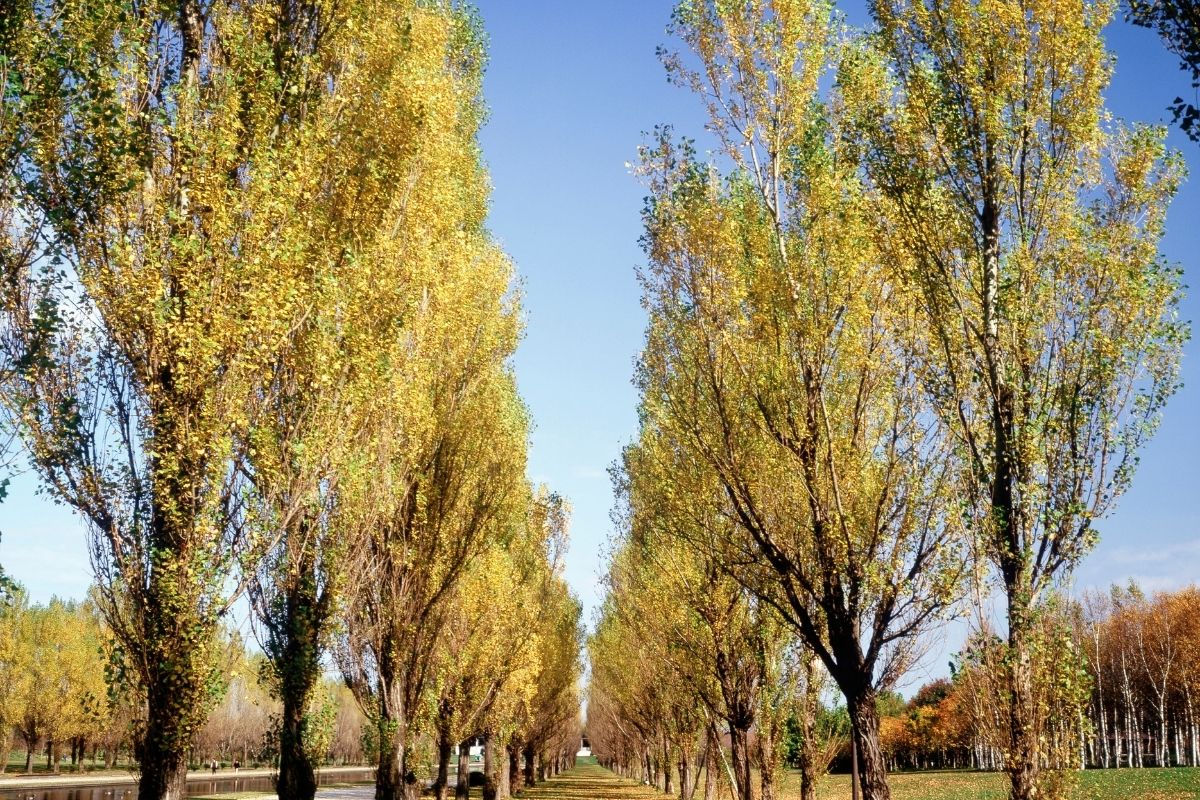

Next to Willows, Russia is also home to a massive population of poplar trees.
Poplars are native trees to Europe, Asia, and North America. They grow well in many climates and conditions, and their ability to tolerate colder climates allows them to thrive in the colder regions of Russia, particularly Siberia.
These trees are planted in urban areas where they provide shade and shelter for birds and wildlife.
Poplars produce large quantities of pollen, which makes them useful for pollination, unsurprisingly.
When cut down, the wood is typically used for furniture, among its many other uses, such as for nectar production, fishing nets, and for its medicinal purposes.
11. Rowan Tree
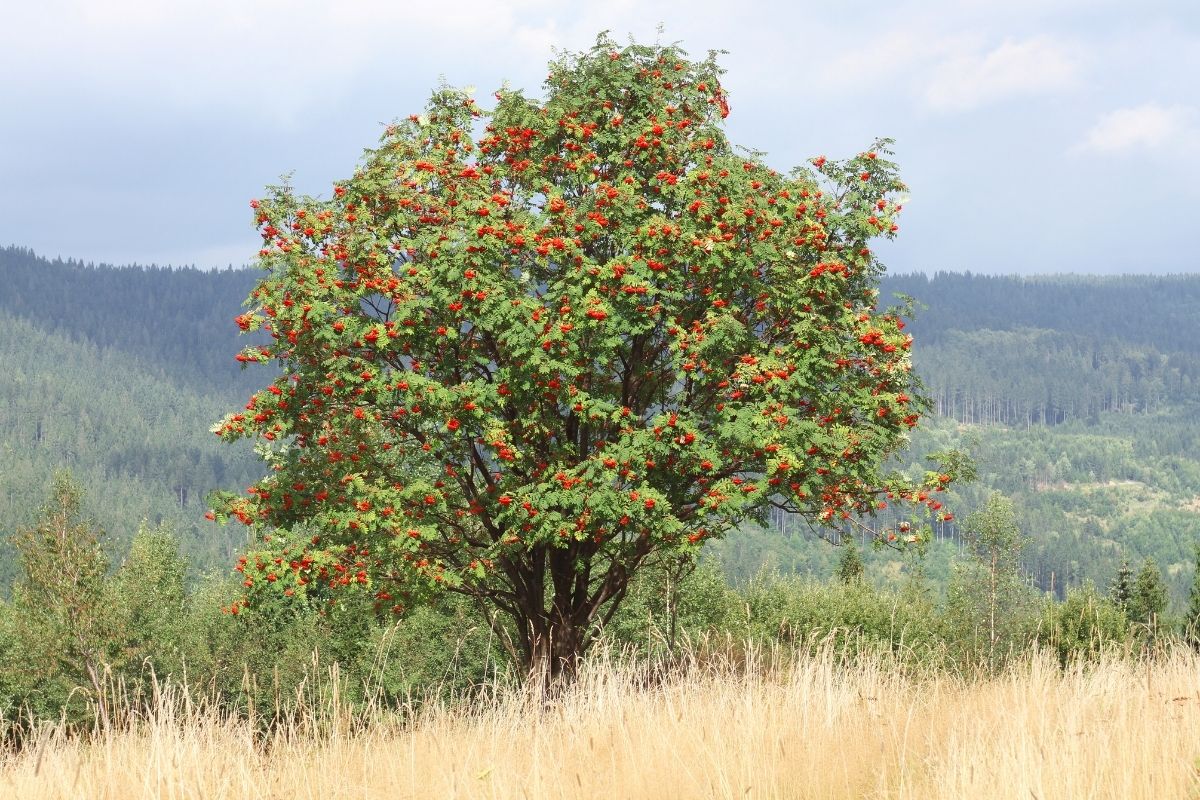

The Rowan tree is most associated with the regions of Tibet and China, but this type of Ash tree grows in many places around the world, including Russia.
It is believed that the root bark of the rowan tree contains an active ingredient that helps protect against colds, flu, stress, and fatigue.
In addition, the leaves of the rowan tree contain antioxidants, vitamins A and C, and iron. The leaves have been used for centuries to treat diarrhea and stomach cramps.
Nowadays, the roots of the rowan tree are being studied to determine whether they may help protect against certain cancers.
Interestingly, rowan trees were once considered sacred to the Norse god Thor. He believed that the rowan saved him on one of his adventures by clinging to its strong roots.
12. Scotch Pine
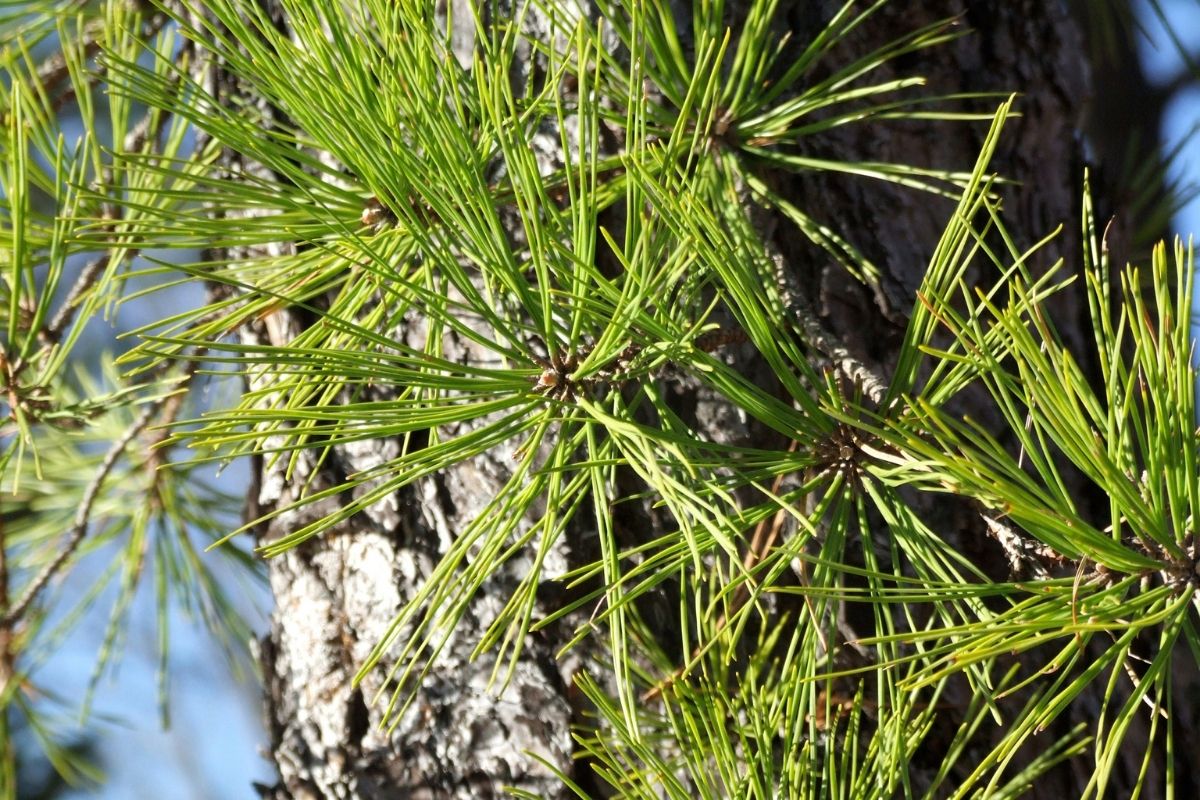

As the name suggests, the Scotch Pine is most often associated with the Scottish highlands. But this species is grown far and wide across Europe and Asia, and that includes Russia.
This type of tree grows quickly and produces large cones. If grown in a temperate climate, these trees do not require pollination and are self-pollinating. These trees are popular for use in parks, gardens, and front yards.
They are drought resistant and grow slowly. Most people prefer to cut them down after about seven years since they are prone to damage from insects, rodents, and deer.
13. Russian Larch
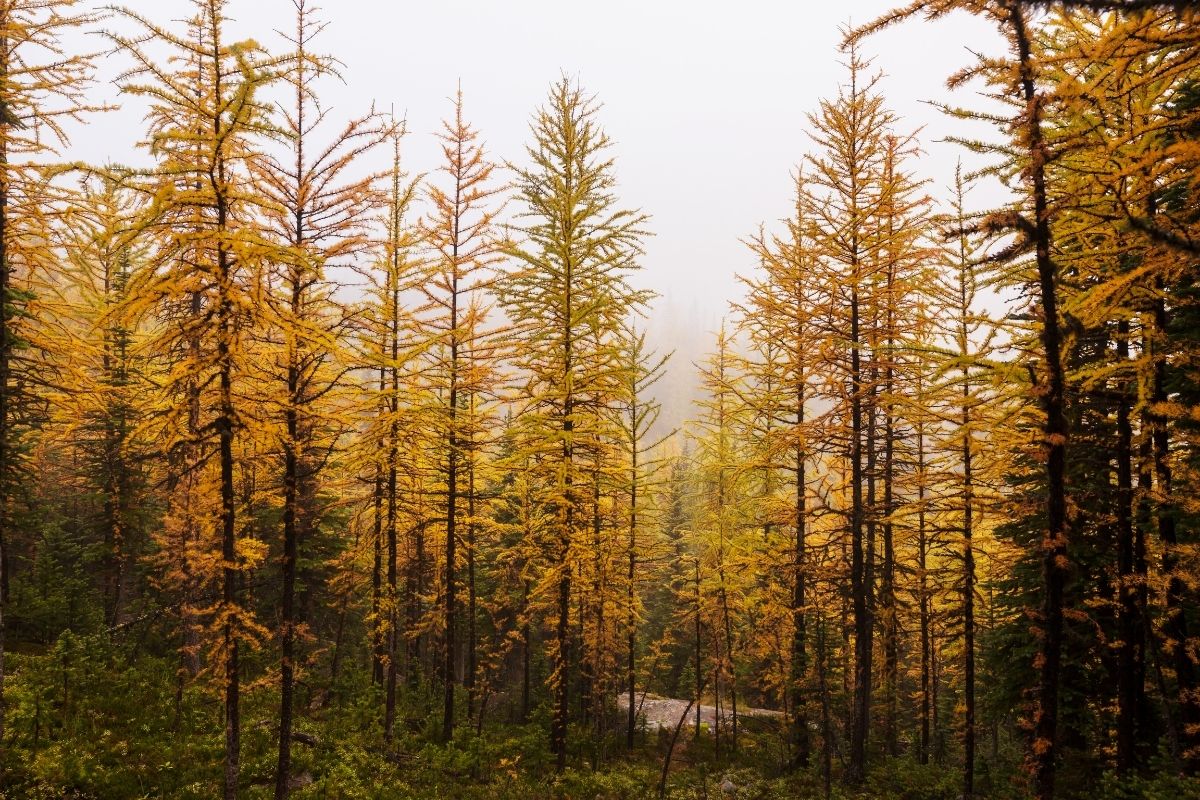

Russian larch trees grow in Siberia, Alaska, Canada, and parts of Europe. They are native to Eastern Asia, where they live in subarctic regions. The trees grow up to 100 feet tall, but most only reach about 40 feet.
They typically grow in thickets mixed with spruce, fir, pine, birch, and hemlock.
Some people think that the Siberian larch tree is related to the Scotch pine, which grows in Scotland. However, experts say that the two species aren’t closely related.
Siberian larch trees have dark green leaves with small white dots on the undersides. Their needles turn orange in the fall.
Final Thoughts
As you can see, having much of its most northern side covered in tundra and glaciers hasn’t stopped Russia from developing a wide array of plant and tree life.
And we hope our guide has given you some ideas to help you add a little Russian greenery to your home or garden!