Rainforests are probably some of the most recognized biomes in the world. Home to probably more species of flora and fauna than any other environment on the planet, there is so much we don’t know about them yet.
But something that we certainly do know, is that they have some of the most awe-inspiring and jaw-dropping plants ever!
To help you find your favorite types of rainforest trees, whether that’s just to admire them or to attempt to grow them in your greenhouse or backyard, we have compiled this list of 10 different tropical tree species that are out there in those dense jungles right now.
1. Kapok Tree
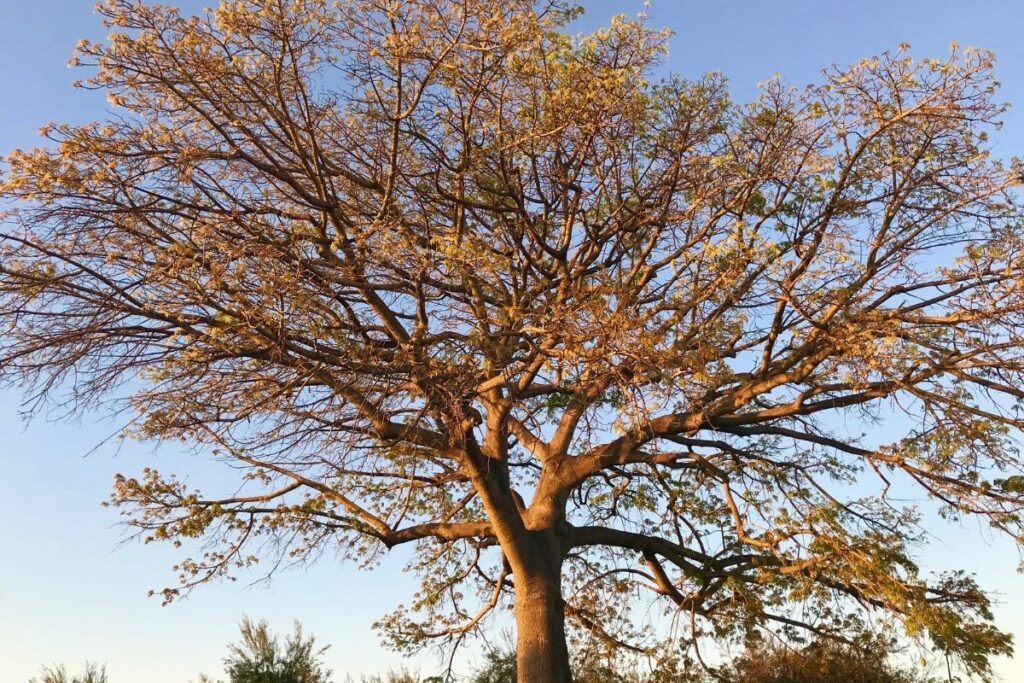

A species that is found in many forests across Central and South America, the kapok tree is probably one of the most distinctive trees found in tropical rainforests across the Americas. The soft, fluffy seeds inside the pods are used to make pillows, mattresses, and insulation.
The flower buds of the kapok tree are used to make oil and candles. The flowers are also used in traditional medicines across the region that it grows in.
Kapok seedlings are propagated easily by cutting off branches. They grow quickly after germination, reaching heights of up to 240 feet in the most exceptional examples.
Cultivars of kapok trees have been developed in many countries.
2. Rubber Tree
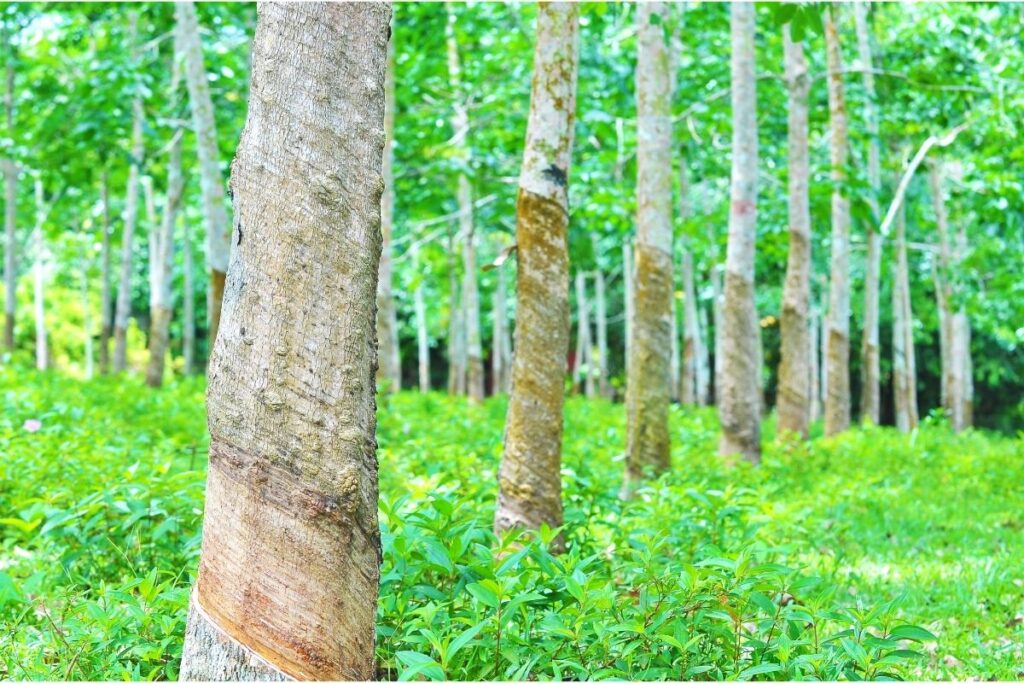

A rubber tree is a large tropical evergreen tree native to Southeast Asia. The latex produced by the trees contains natural rubber, which is used to produce tires, gloves, condoms, balloons, and medical tubing.
Rubber trees are grown commercially in many countries, particularly Malaysia, Thailand, Indonesia, Colombia, Costa Rica, China, India, Ecuador, El Salvador, Peru, Mexico, Nicaragua, and Sri Lanka.
A rubber tree grows from its seed. The seeds germinate in water. The seedling then sends out roots into the soil. The root system pushes up through the soil until it reaches the air.
Rubber trees grow quickly and produce large leaves. They grow tall and straight. The leaves are roundish and smooth, with a pointed tip towards the end of the leaf. Rubber trees are usually found growing near large sources of water, such as rivers.
Most rubber trees are found in tropical rainforests. However, some populations have been established outside their natural range, such as in the United States.
These exotics must be carefully managed to prevent them from becoming invasive. For example, rubber trees may escape into nearby forests where they could compete with native plants for resources.
3. Banana
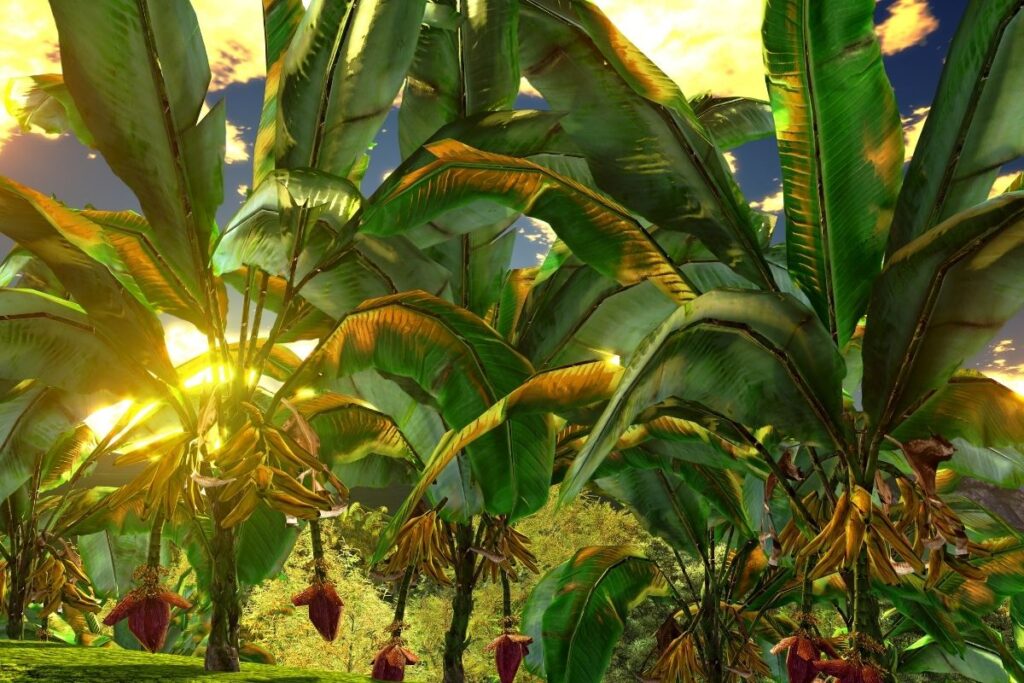

Bananas are one of the most popular fruits in the world. They grow pretty much anywhere where they receive enough moisture and a high enough temperature, so it’s no surprise that they are found in tropical rainforests.
Banana trees are native to tropical areas, such as Central and South America, Indonesia, Malaysia, and Australia. However, they are widely cultivated in warm countries.
Banana trees do well in warm climates and moderate rainfall. They require full sunlight and lots of water.
Thanks to the popular fruits that this plant grows, the banana tree is grown in a huge number of countries such as Indonesia, Kenya, the islands of Hawaii, Papua New Guinea, the Philippines, and Thailand.
There are hundreds of different varieties of bananas, each with its unique taste.
4. Ceiba

Ceiba trees are native plants native to Central America. They grow well in warm climates. Ceiba trees are often used as street trees.
They do well in urban areas where there is plenty of water and sunlight. These trees are popular because of their beautiful leaves, flowers, and fruit.
The fruit is called “ceiba”. The ceiba fruit is yellowish-green and looks like a small berry. The fruit contains antioxidants, vitamins A and C, and potassium. The fruit is commonly eaten fresh by most people.
There are different varieties of this tree. Some varieties may produce fruits with seeds, but most varieties do not.
The ceiba tree is often planted near houses and buildings. The roots of these trees are shallow. As a result, the soil does not dry out quickly.
When this tree is planted next to houses and buildings, it helps prevent air pollution. It cleans the air by removing pollutants such as carbon dioxide and dust particles.
5. Custard Apple Tree
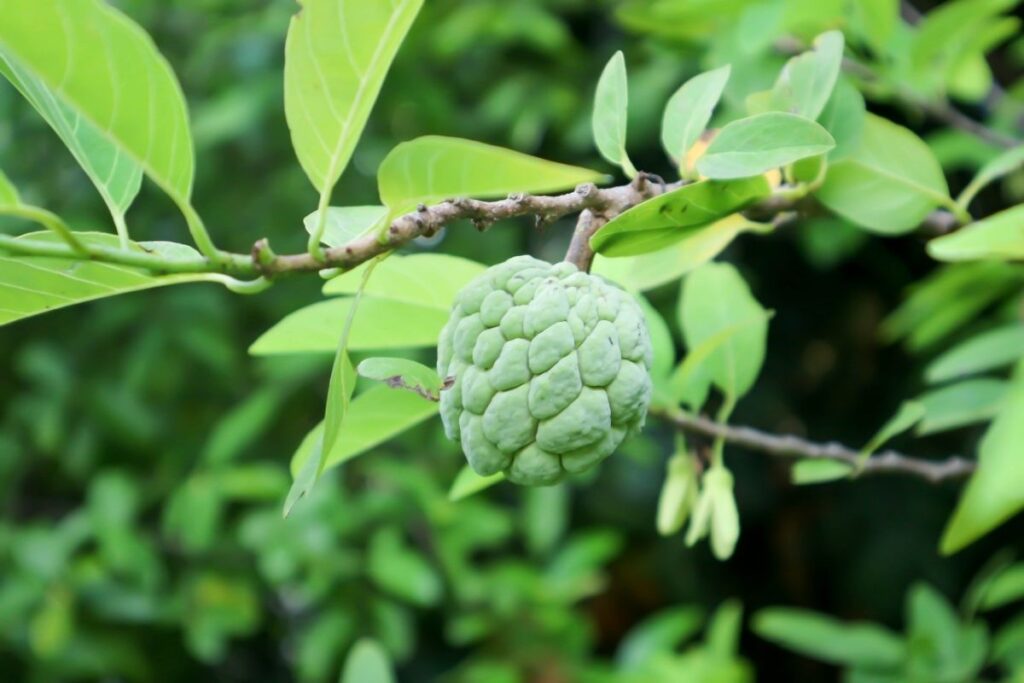

The custard apple tree grows in North, Central, and South America, although several other variants have since found their way across the world. They can now be found growing in groves across South East Asia.
The blossoms are white and there are usually four flowers per cluster. Each flower produces one large round fruit. In the United States, many people call these fruits “custard apples” because they are similar to the apples found in supermarkets.
In the spring, custard apple trees blossom and produce fruit. Fruit ripens between June and August. Custard apple trees bear fruit again after three years, producing a second crop. This makes it possible to harvest two crops each year.
Custard apple trees are among the first trees to bloom in spring. They begin blooming about five weeks earlier than other apple trees.
RELATED: 28 Awesome Tropical Rainforest Plants (Including Pictures)
6. Oil Palm
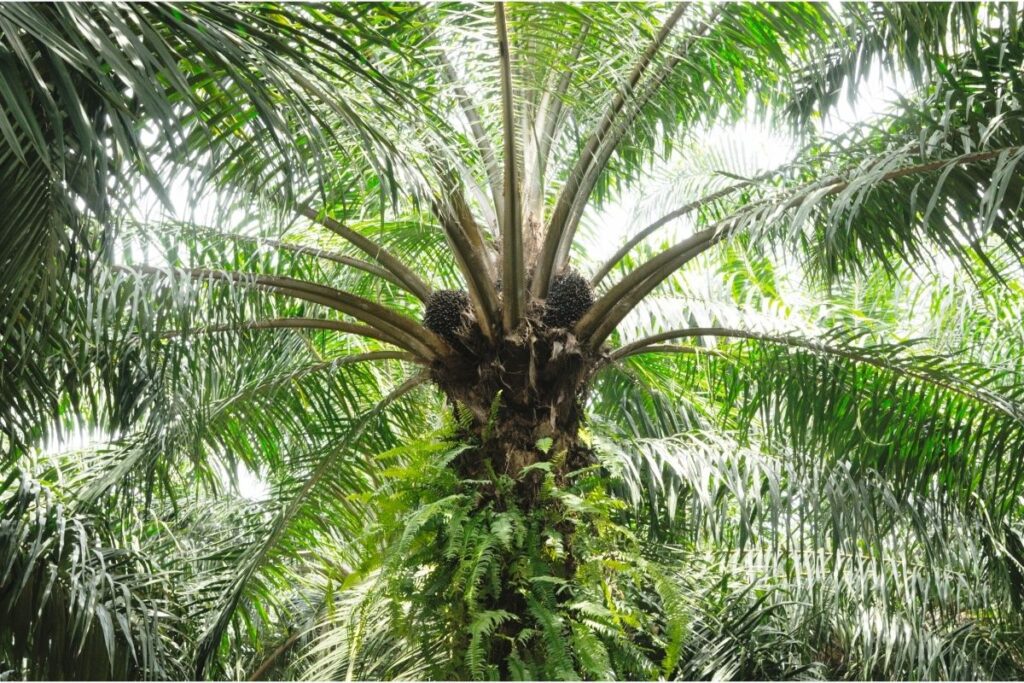

One of the most widespread tropical rainforest trees in the modern-day, oil palm trees are grown in pretty much every tropical region around the world, both in the wild in Africa where it originates from, and in many plantations in South and Central America, South Asia, and in the southwest Pacific.
Oil tree fruits usually take 6 months to ripen. Nuts are picked up after the fruits are ripe. To pick the nuts, workers must climb the oil palm trees. Workers use mechanical tools to remove the nuts from the trees.
7. Kauri Trees
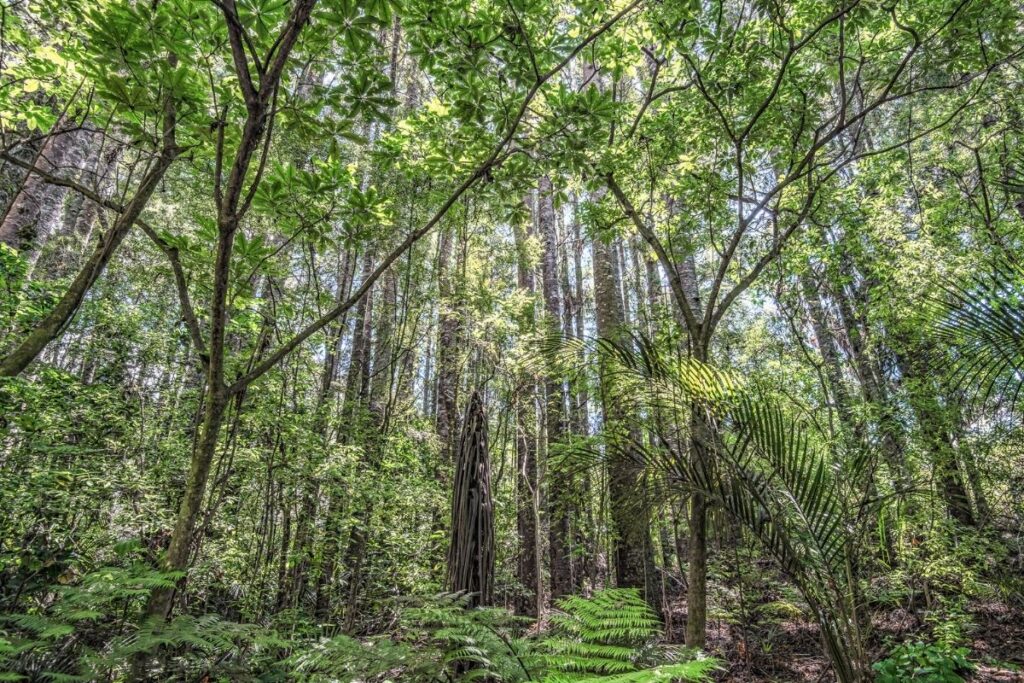

One of the largest trees in the area that it grows, the Kauri tree is found in the Northern islands of New Zealand.
They grow in coastal areas and are often found along the beaches. They are slow-growing trees, and most people don’t realize that kauri trees can live over 200 years.
The wood of this tree is durable and has been used for centuries for furniture, flooring, boat building, house construction, and many other things.
Kauri trees produce a yellow sap called kaurin. This yellow sap is sticky and can be removed easily from the trunk. The Maori people of New Zealand have been using the sap as a natural treatment for insect bites and stings for hundreds of years.
In addition to its medicinal properties, the sap from kauri trees makes excellent glue. For example, kauri gum is used to create waterproof surfaces such as raincoats, boats, and rubber products. It is also used to make shoes and clothing.
When the first Europeans arrived in New Zealand, they saw kauri trees everywhere. Some of these trees were so tall that they could be seen from ships offshore.
These trees became famous among sailors and explorers for their height and strength. However, due to deforestation, these majestic trees are becoming rarer and rarer.
8. Xate
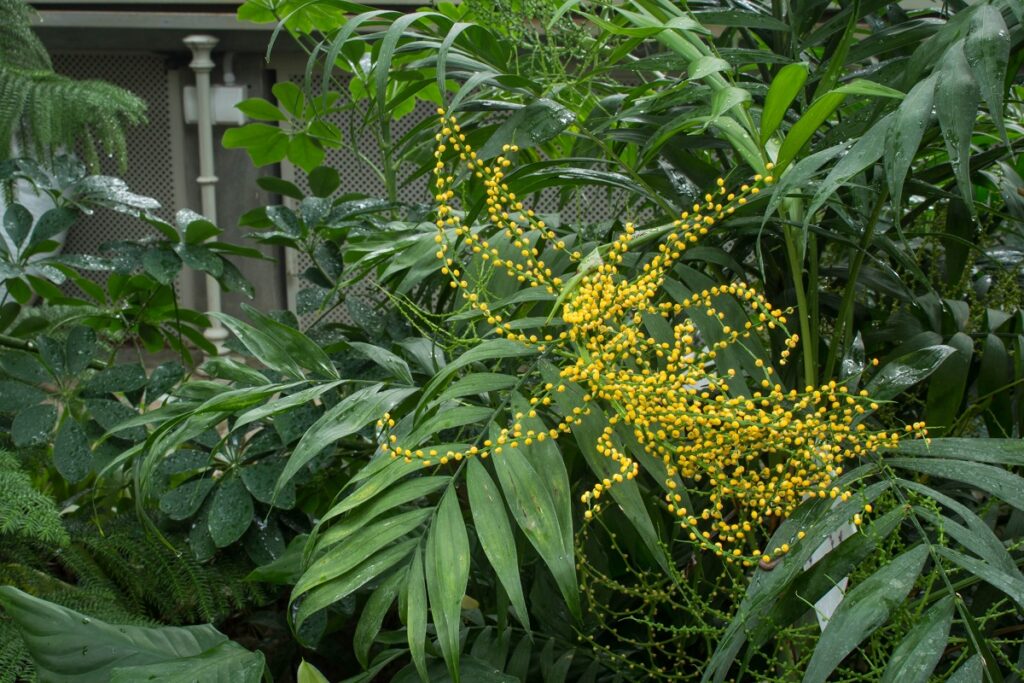

Xate trees are native to Central America, Mexico, and South America. They grow up to 30 feet tall and can live for 300 years.
They are deciduous and usually have a single trunk, although there may be multiple trunks. The leaves are dark green and shiny, and the flowers are white or yellowish.
There are different varieties of xate trees, including the common xate, which grows in northern Mexico, Guatemala, Honduras, and El Salvador.
Other types of tropical rainforest trees include the blue xate, which grows near San Francisco and California, and the huetamo, which grows in the jungle regions of Peru, Ecuador, Colombia, Venezuela, and Brazil.
The bark of the tree is used to produce the dye xato, which is black. This dye is sometimes called caxte.
9. Ipe
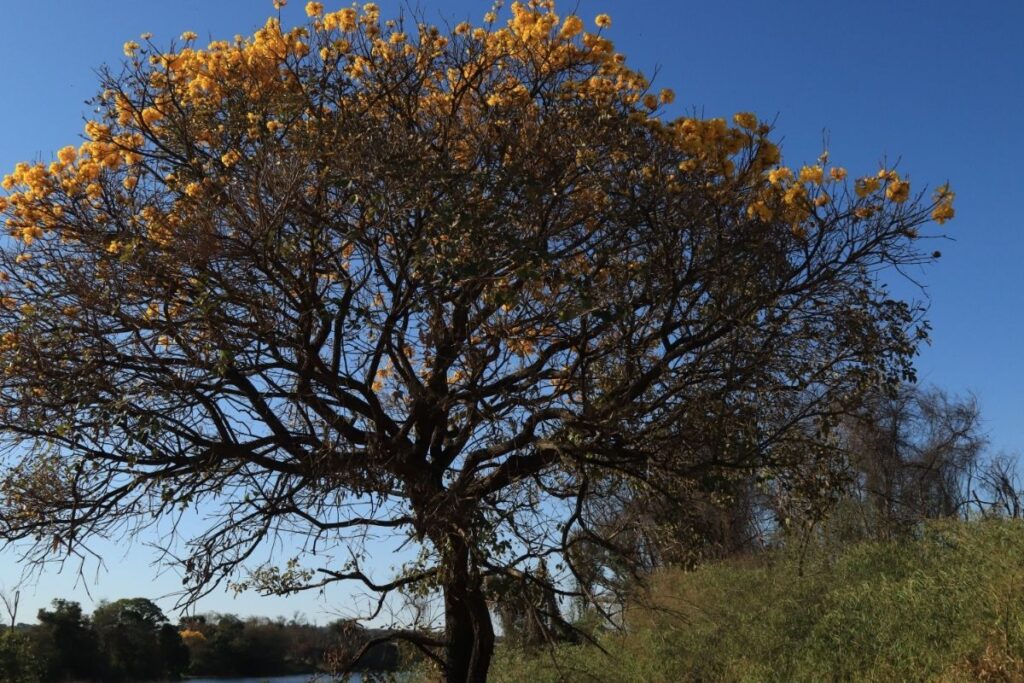

Ipe is one of the most common trees in Brazil. It grows well in tropical climates and is easily propagated from cuttings.
The wood is soft and white. Its sapwood is rich in tannins and contains large amounts of resins. These characteristics give ipe its typical black color.
Ipe is used extensively for furniture and flooring. It’s lightweight and resistant to moisture. Because of these properties, it’s often used in boats, railroads, and houses.
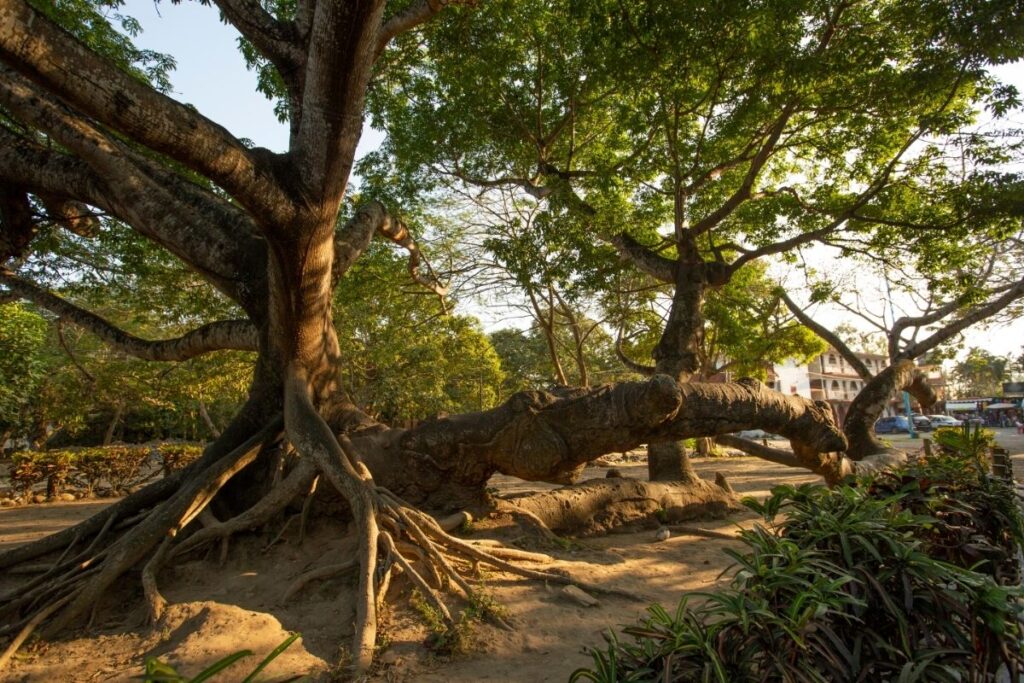
10. Strangler Fig Trees
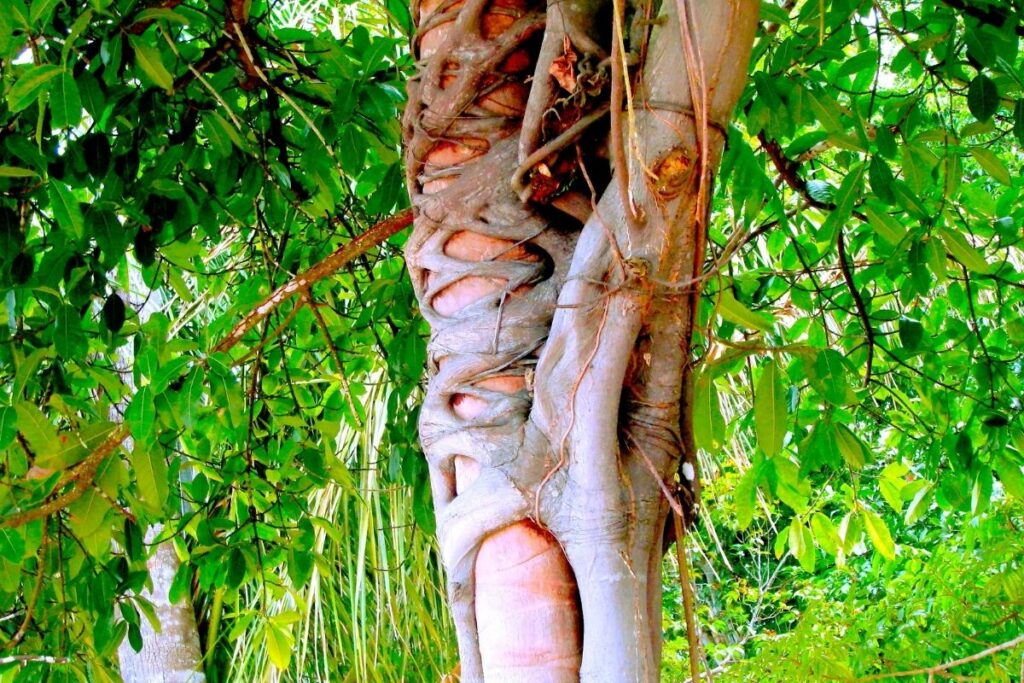

Strangler fig trees are native to South America. They are slow-growing trees and can live up to 200 years. The trunk of the strangler fig tree usually grows straight out from the ground, but occasionally curves to one side.
The strangler fig tree thrives in tropical climates and grows close to bodies of water. These types of tropical rainforest trees are most common along rivers, streams, swamps, and lakes.
Climbing fig trees are commonly used for ornamentation and privacy. Some people find these trees beautiful and peaceful. Climbing fig trees provide shade and shelter for birds and wildlife.
Strangler fig trees are often confused with oak trees. Both tree species can grow very tall, although strangler fig trees are much slower growing than oak trees.
Conclusion
So there you have it, 10 types of tropical rainforest trees that are grown in the tropics, but also across the world.
With such an ecological hotbed as these super-densely packed forests, there are thousands of species out there that we haven’t even begun to scratch the surface of.