While many think that bonsai is a type of plant, the truth is that it is a technique by which a tree or shrub is transformed into its miniature version that looks older than it actually is. Although not the same size, a tree sculpted with this technique will have all the qualities of its “regular” version. And what is perhaps even more interesting is that most species of trees or shrubs and even some tropical plants can become bonsai specimens. In this article, let’s talk bout flowering bonsai.
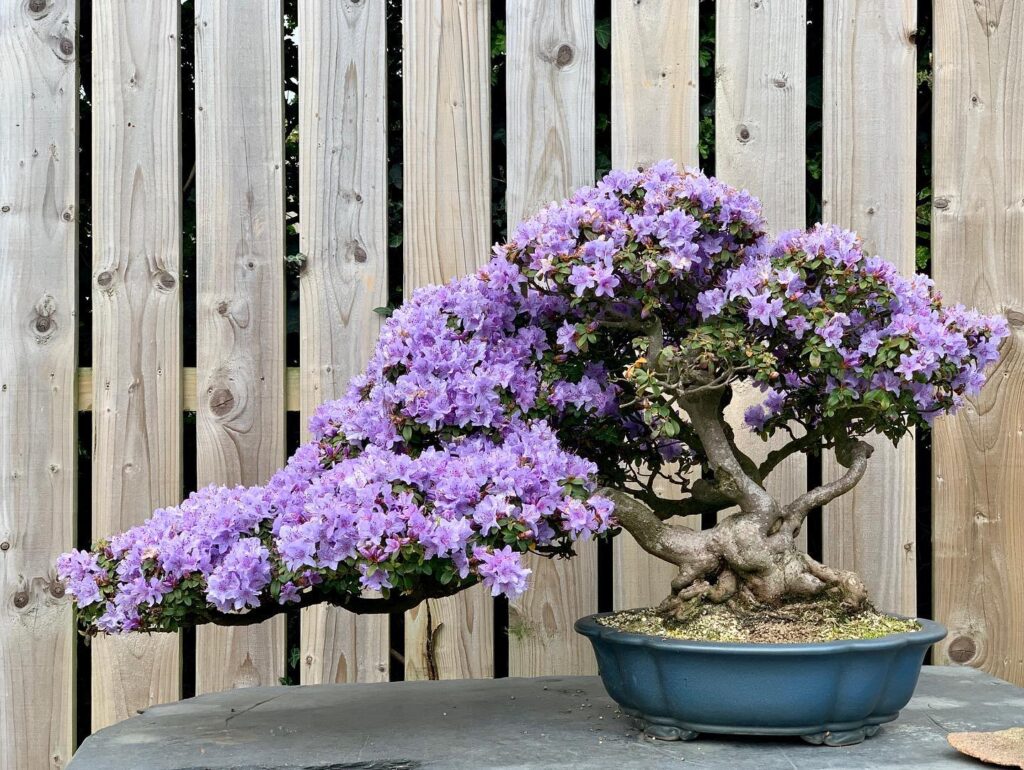

Bonsai trees are very easy to fall in love with because of their adorable and magical appearance. But flowering bonsai trees create an even more spectacular sight since they combine twisted and weird shapes of non-flowering trees with enchantingly colored blossoms of the flowering ones. Even though they are miniature, flowering bonsai trees require a lot of effort, patience, and knowledge.
Because of this, creating and maintaining a flowering bonsai tree has a positive psychological effect since through caring for the dwarfed plant, the grower improves creativity, relieves stress, and calms the mind. In this way, dedicating yourself to bonsai growing is similar to practicing meditation.
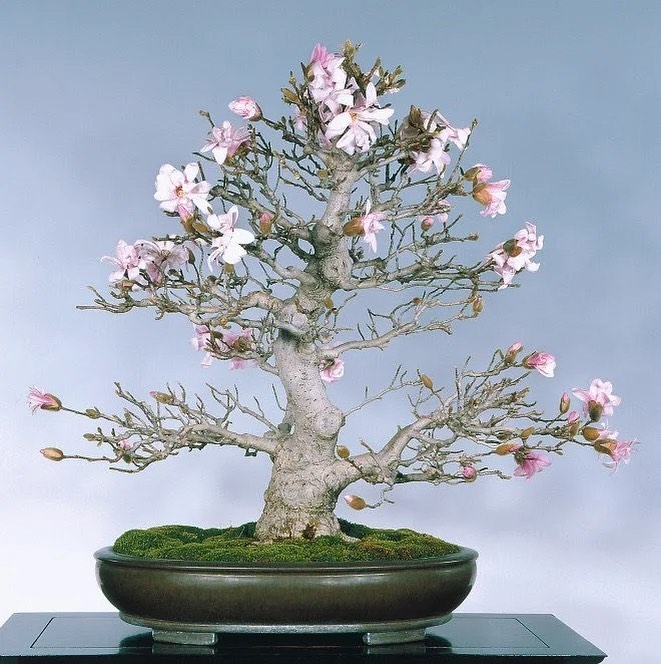

Origin And History Of Bonsai
Although commonly linked with Japan, where it is most popular, bonsai’s roots are actually in China.

Mother Nature created the first specimens of bonsai plants in mountainous regions of China, where certain trees’ growth would have their growth stunted due to unfavorable climate conditions.
According to legend, some 2000 years ago, Taoists were the first people who started practicing the technique of artificial downscaling as a spiritual practice after seeing these dwarfed trees in nature. They believed that this practice would allow access to mystical and magical attributes of nature. Thus, a new concept and art of growing miniature natural landscapes in pots was created.
Recreating small-scale natural scenery in small pots gained popularity when these containers started to be used as lids for incense sticks. The smoke, coming out through the holes in the pot, would create the impression of living and breathing nature that fascinated and captivated the observers.
However, the first recorded information dates from the 8th century, 706 AD to be precise, which is the year when Crown Prince Zhang Huai was buried. Two persons with pots containing miniature replicas of nature can be seen on one of the murals located at his burial site. During this time, the practice of creating the environment surrounding us on a small scale was prevalent among the elite, and the possession of such objects was a status symbol. It was called punsai, but later it got another name, penjing (pen – tray, jing – scenery), which is still used in China today.
In Japan, penjing arrived some 1,200 years ago with Buddhist monks, as China was exerting considerable influence on the surrounding countries, especially Japan. But instead of creating an entire landscape with trees, grass, rocks, and the like, the Japanese started carefully modeling only trees down to small specimens. In this way, the bonsai style as we know it today was born. The word comes from a combination of the Japanese words “bon” and “sai”, which means tree in a pot.
It was not until the 19th century that bonsai spread to the Western world, and the first bonsai tree exhibition in Europe was held in 1910 in London. Since then, bonsai growing has captured the imagination of a lot of people and is valued as a unique blend of gardening and art.
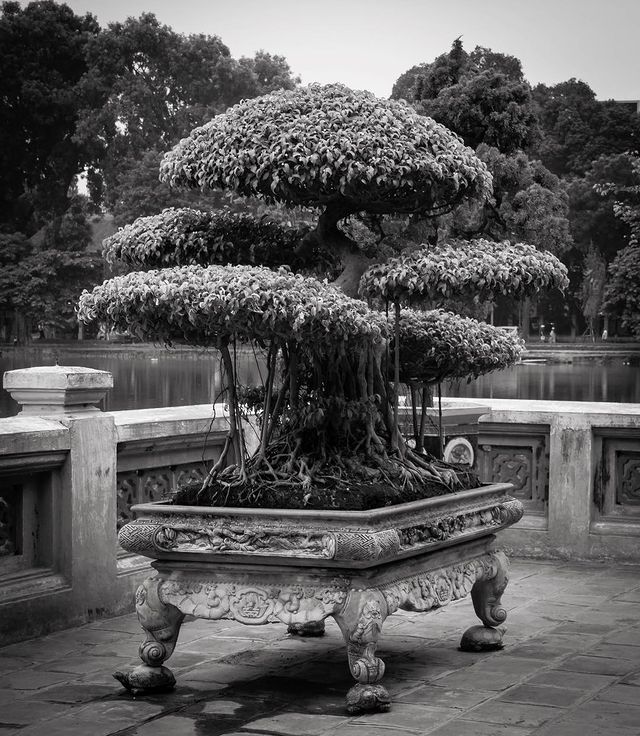

How To Create A Flowering Bonsai Tree?
The most popular flowering bonsai trees are Azaleas (namely Satsuki azalea and Kurume azalea), Bougainvillea, Wisteria, Magnolia, Prunus mume, and Desert rose. All of these plants will look amazing in their bonsai form with proper care. Still, you should not base your decision only on the appearance of the plant – consider the climate conditions of your environment as well as the plant’s light, humidity, and temperature requirements.
Choose a suitable specimen, which mostly means a young tree. Bonsai can also be grown from stem cuttings or seeds, but if you go down that road, it can take a couple of years before you see any results.
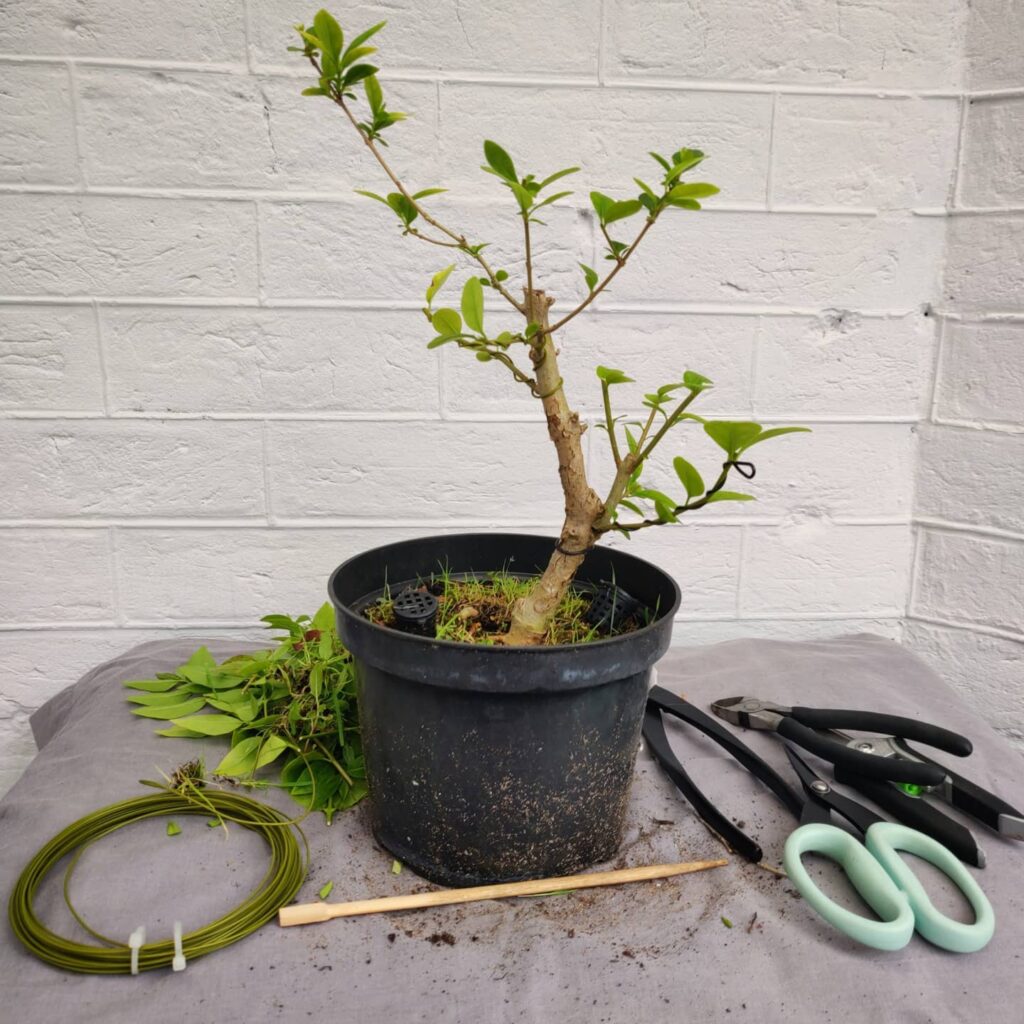

Pruning
Before you get your hands dirty, you should know that every action involving pruning the plant is very stressful and takes time to recover. The time required for the progress of bonsai is measured in years, and sometimes even in tens of years, which just highlights how crucial the human factor is in the successful care of bonsai.
Prune any broken or crossed branches and dead foliage both on the inner and outer part of the tree. Branches that intersect can leave damage that will facilitate the development of diseases. The same goes for broken branches, which need to be carefully removed so that the tree can direct all its energy into new growth.
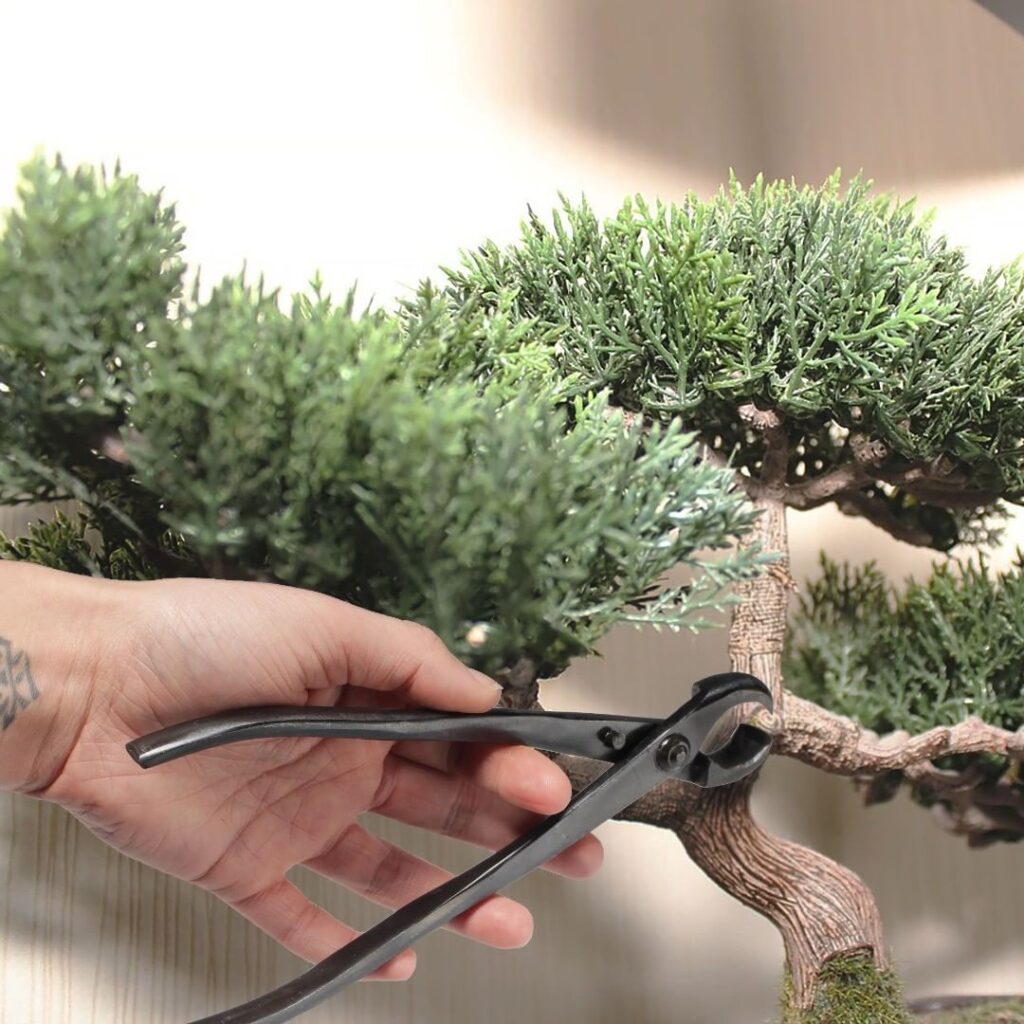

Aesthetical Pruning
This part does not have any strict rules as to precisely which branches you should cut, but in most cases, the lower branches are removed so that the lower part of the trunk (up to one-third of the total length of the tree) is clearly visible.
Any upward or dangling growth should also be cut to ensure proper and healthy growth in the future. In addition, healthy branches that will undermine the overall appearance of the future bonsai specimen should also be removed.
At this stage, it is important to consider the three-dimensionality of the plant and where you would like to see the plant grow branches. Depending on the density of the tree, you can cut up to one-third of the branches.

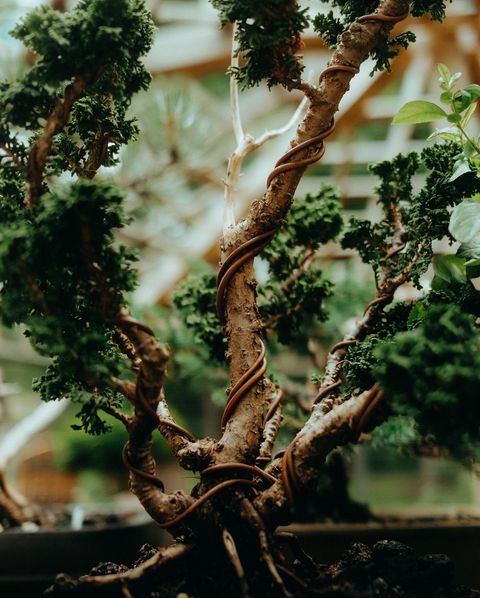
Wiring
The perplexing appearance of the bonsai we all admire is achieved partly through pruning but also by means of wiring. We shape the branches through wiring, effectively deciding which growth patterns we would like the branches to adopt.
We wire the plant using the same techniques for the wiring of non-flowering trees, but one should be slightly more careful when dealing with flowering trees as their branches are usually more fragile.
Carefully wrap the wire around the trunk and branches to hold them in the desired position and direction. When wound in this way, the wire serves as a splint – the branch grows in the direction that the wire allows it to grow. After around six months, remove the wire, so it does not grow and cut into the branches.

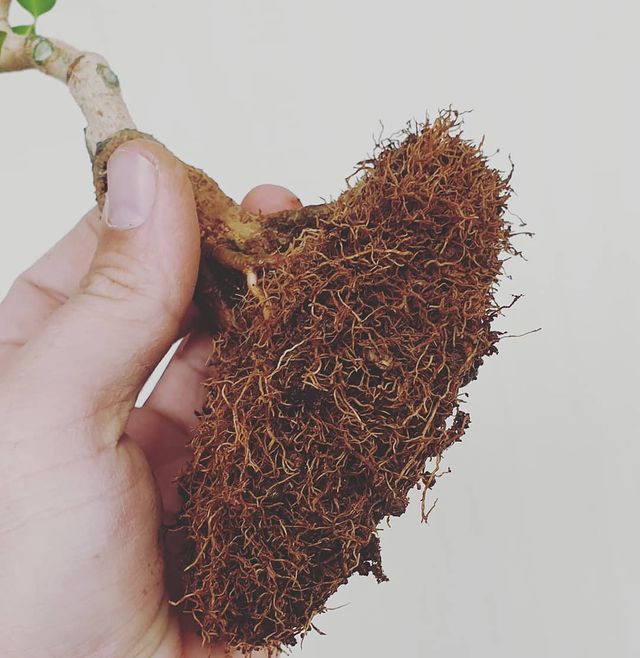
Root Pruning
In addition to branch pruning, bonsai also requires pruning the roots since flowering bonsai trees are placed in smaller pots in which the space for root growth is limited. One of the basic rules of growing bonsai dictates that no more than a third of the roots be removed during the initial pruning.

Defoliation
Another vital thing for shaping a bonsai tree is defoliation – a technique with which we remove leaves from the tree. It is done during the summer when the leaves emerge to stimulate the development of young foliage. As a result, smaller leaf growth and additional branching occur, giving your tree a more compact shape.
Choosing The Right Pot
Although they have an aesthetic function at first glance, pots play one of the main roles when growing flowering bonsai trees.
First, they must be the right width and height in relation to the tree’s size. The pot’s dimensions influence the way the roots of the bonsai tree grow, but they also nurture it to stay in its diminutive proportions.
The general rule is that the ideal pot length should be two-thirds the height of the tree. In addition, the width should be slightly smaller than the width of the tree.

A Few Care Tips
Since all kinds of flowering species can be reshaped into bonsai, there is no one size fits all type of care guideline, but there are still some practices that you should adhere to.
Most of the popular flowering bonsai tree species are sun-loving plants. Hence, position them in a place where they will be getting full sun. If you plan on growing some of the indoor bonsai plants, be sure to put them next to a window that gets tons of sunlight.
Regular and aesthetical pruning we mentioned earlier will achieve more even growth of the tree and leaves, thus a greater trunk density. But, flowering bonsai trees should be pruned at least once a year to maintain their size and desired form. However, be careful not to prune them at the wrong time – spring and summer, when the plants are actively growing, is the best option.
The proper watering regiment is also essential for bonsai care. To make sure your bonsai plant needs water check the top half-inch of the soil – if it is dry, it is ready for watering.
And to ensure the plant produces flowers prolifically, use a special fertilizer that contains low nitrogen levels but is high in phosphorus and potassium.

If you want to learn about the art of creating a bonsai tree, check out the video below!
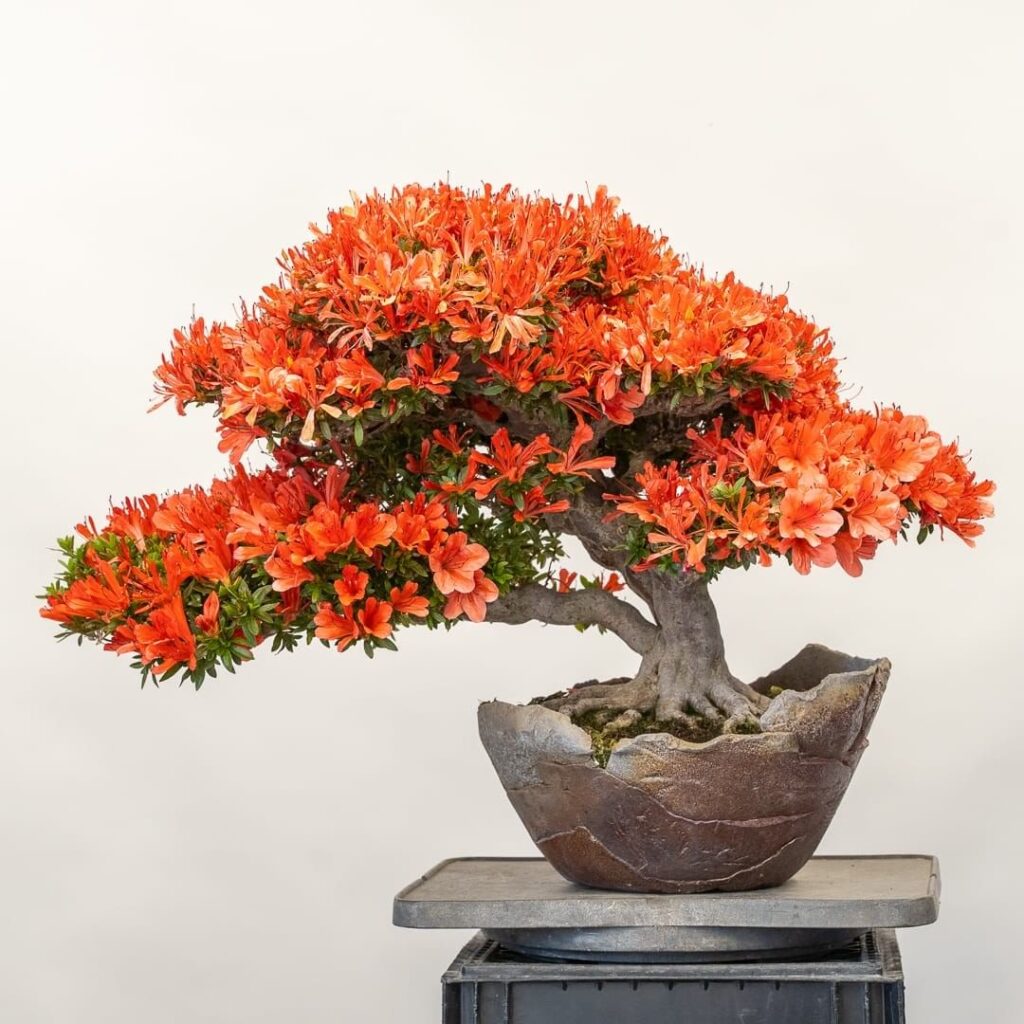
Satsuki Azalea
When it comes to flowering bonsai trees, azaleas are second to none. And the variety that reigns among thousands of azalea types is Satsuki azalea.
Satsuki azalea is an evergreen shrub that belongs to the genus Rhododendron. Its “usual” form grows from two to three feet, which, together with the tendency to produce smaller flowers in charming colors, makes it an excellent candidate for flowering bonsai species.
Satsuki azalea bonsai mostly has round or lance-shaped glossy green leaves that grow to 2 inches. Although bright foliage definitely contributes to the appeal of the Satsuki azalea bonsai tree, breathtakingly colored petals will blow away anyone. Truly a spectacular sight, Satsuki azalea has purple, red, orange, white, or pink flowers that also range in shapes, which adds to the plant’s attractiveness.
Satsuki azalea bonsai blooms in late spring – in Japanese, satsuki means the fifth month.

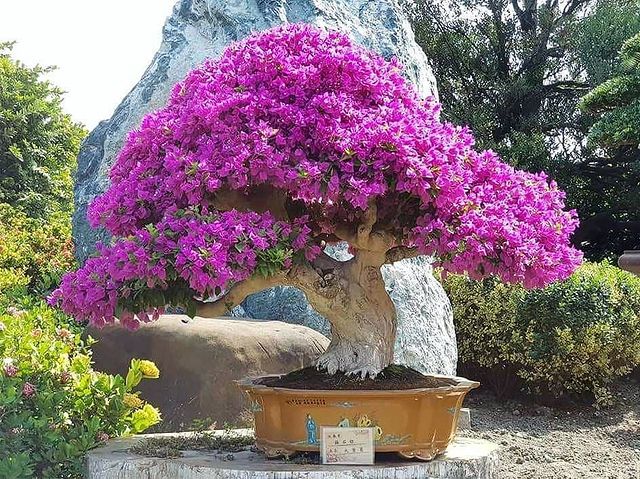
Bougainvillea
Excitingly colored, a tropical vine that can grow up to 30 feet is certainly not among the first candidates to consider for sculpting flowering bonsai plants. However, Bougainvillea is a popular choice thanks to the beautiful “flowers” and low maintenance requirements.
Another thing that makes Bougainvillea a great bonsai plant is that it doesn’t take long to grow into its new form. It is possible to get them to take on the shape of a bonsai tree within just one growing season.
Bougainvillea is adorned with dark green, elliptical leaves that are slightly hairy on the upper side and trumpet-shaped, tiny, white flowers. But the flowers are surrounded by large pink bracts, making this plant a beautiful bonsai. Magenta is the most common color of bracts, but they also come in pink, purple, orange, yellow, and white. In addition, Bougainvillea blooms several times from April to November, which is yet another reason to turn this beautiful plant into a bonsai.
Usually, pretty hardy plants, Bougainvilleas shaped into bonsai are susceptible to low temperatures and frost, so they are best suited as indoor bonsai plants during the winter. Besides that, care is pretty straightforward – lots of sunlight, so it keeps producing flowers and regular watering and fertilizing.

RELATED: Money Doesn’t Grow On Trees: The Price Of A Bonsai Tree
Prunus Mume
Prunus mume bonsai is probably one of the most graceful flowering fruit bonsai species. It is the one tree where the seemingly incompatible combination of lifeless-looking trunks and branches and enthusiastically colored flowers adorning many flowering bonsai plants is most noticeable.
Prunus mume bonsai is one of the few plants in full bloom mid to late winter. It is a beautiful sight to witness as the white, red, or pink flowers blossom for a couple of weeks at a time when most plants look bland.
However, it is not just flowers that give people reason to grow this deciduous plant as a bonsai tree. Longevity, hardiness, and especially fragrance add to its uniqueness and separate it from other bonsai tree species.

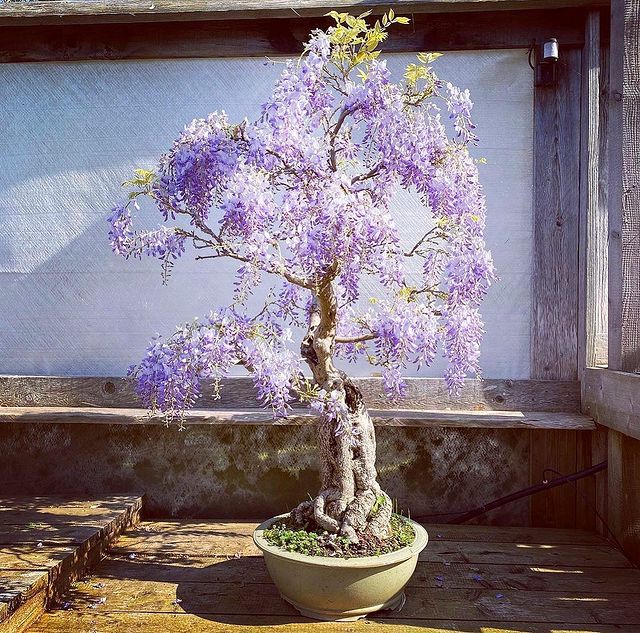
Wisteria
If we were to describe growing Wisteria bonsai with one sentence, it would be “Patience is a virtue” since it takes at least ten years for this magnificent plant to bloom when grown as a bonsai tree. But, the purple, violet-blue, and white flowers gathered in hanging clusters are a worthwhile reward for anyone prepared to care for this plant diligently.
The genus Wisteria has over ten species, but the most famous and commonly used to make Wisteria bonsai specimens are Chinese Wisteria (Wisteria sinensis) and Japanese Wisteria (Wisteria floribunda).
Wisteria grows naturally in the Far East (Japan, Korea, China) and East America. This vining climber can grow up to 60 feet in its natural environment, but this does not stop people from transforming it into a beautiful tree in bonsai form.
When it comes to caring, one of the essential things is daily watering – Wisteria bonsai is quite a thirsty plant, especially during the growing season, so be careful not to leave the soil completely dry.
And if you want to achieve a healthy and full bloom of the gorgeous flowers cascading down from the branches, be sure to provide it with lots of sunlight.
Wisteria bonsai also needs a low nitrogen fertilizer because the bacteria located at its root fixes nitrogen in the soil. Having high(er) amounts of it would encourage foliage development to the detriment of the flower growth.

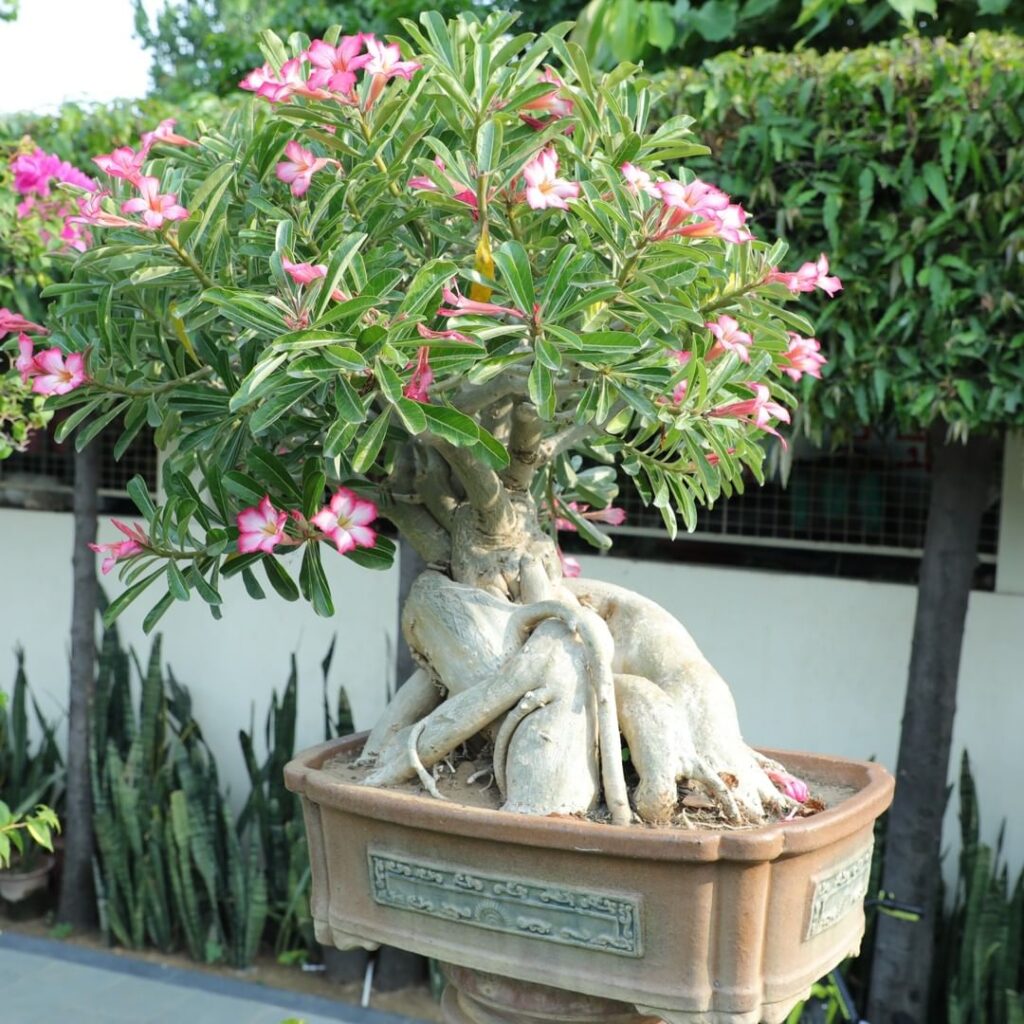
Desert Rose (Adenium Obesum)
When we see most flowering trees and shrubs, we do not immediately think how great they would look in bonsai form. However, Adenium obesum in its regular edition is irresistibly reminiscent of bonsai. For this reason, it is one of the most popular choices for creating flowering bonsai trees.
Due to its natural habitat – the Sahel, this plant is better known as the Desert rose.
Adenium obesum boasts a large, succulent trunk out of which a large number of thick branches grow. The fleshy leaves are densely arranged on the tips of the branches. When in full bloom, flowers made up of five white, red, or purple petals with creamy white inside appear.
Since it is bonsaiesque by nature, you will not have many obstacles trying to model a bonsai specimen in the desired shape. But the Adenium obesum bonsai tree is a slow-growing species, so patience is the key.
Evident from its name, Desert rose bonsai is a plant that requires a lot of light and heat and very little water. It is pruned in early spring to control the size of the plant, maintain its shape, and stimulate the development of new shoots that will bear flowers. It is fed one to two times a month with mild liquid fertilizer.
It is a poisonous plant that contains toxic glycosides, so you need to keep it out of the reach of children and pets.

Frequently Asked Questions
What are the most popular fruit-bearing species of bonsai trees?
Some popular fruit-bearing species commonly grown as bonsai trees are Snow rose, Chinese quince, Ilex berries, and some cherry trees.

Can you bonsai a rose?
Yes. Roses are small deciduous shrubs that are not usually grown as bonsai specimens as their trunk is thin. However, through frequent repotting and lifting the thickened part of the root out of the soil, it is possible to achieve a bonsai-like trunk. Miniature roses are most commonly used for bonsai.
Editor’s Recommendations
Top 10 Types of Elm Trees| Elm Tree Uses, Pictures and Identification Guide
Shrouded in Mystery: 37 Different Types Of Mystic Trees
La Naturaleza es Hermosa! 20 Different Types Of Mexican Trees