The Corn Plant, scientifically known as Dracaena fragrans, is among the well-known house plant, with beautiful and elegant, shiny, attractive foliage. This plant is a broadleaf evergreen and perennial blooming plant with distinctive white-yellow stripes around gray-green centers on its leaves. In this article, let’s talk about corn plant care.
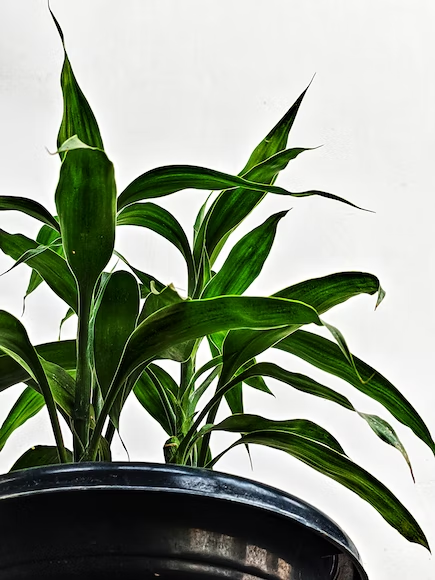

A young Dracaena fragrans is characterized by glossy yellow-green leaves, which will eventually turn to brighter lime-green as they mature. It definitely makes any space they are in have a good and bright ambiance.
If you are considering owning this simple yet gorgeous indoor plant, then you are in for a treat. In this article, we will show you the best approaches to care for this plant. In no time, you will surely be a master of your own Corn Plant.
Corn Plant Profile
General Information
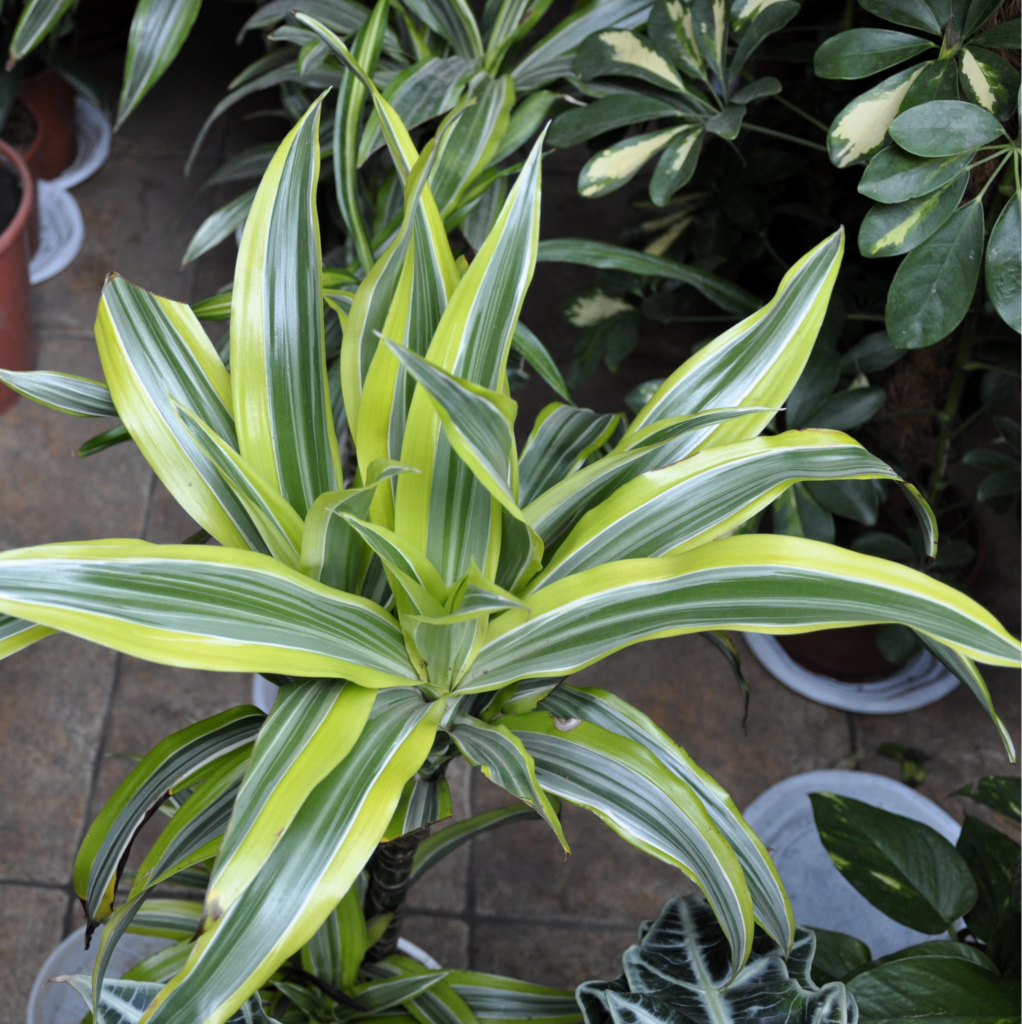

The Corn Plant, scientifically known as Dracaena fragrans, is a species of flowering plant in the genus Dracaena that is an evergreen perennial. It is a species under the Asparagus family, Asparagaceae.
This plant is prevalent in the tropical regions of Africa, from Sudan south to Mozambique, west to Côte d’Ivoire, and southwest to Angola.
The Dracaena Corn Plant has been extensively cultivated as an ornamental plant in tropical and subtropical areas. The common name is due to its corn-like structure, bright green leaves, and woody stalk.
As it matures, it forms a solid stem and concentrates its leaves at the top of the stems, adding tropical elegance to the interior decoration.
Etymology
The genus name, Dracaena, is derived from the romanized version of the Ancient Greek “drakaina,” which means “female dragon.” The fragrans epithet name alludes to the fragrance of flowers and derives from a perception that the stem resembles a stalk of maize (Zea mays).
Flowering
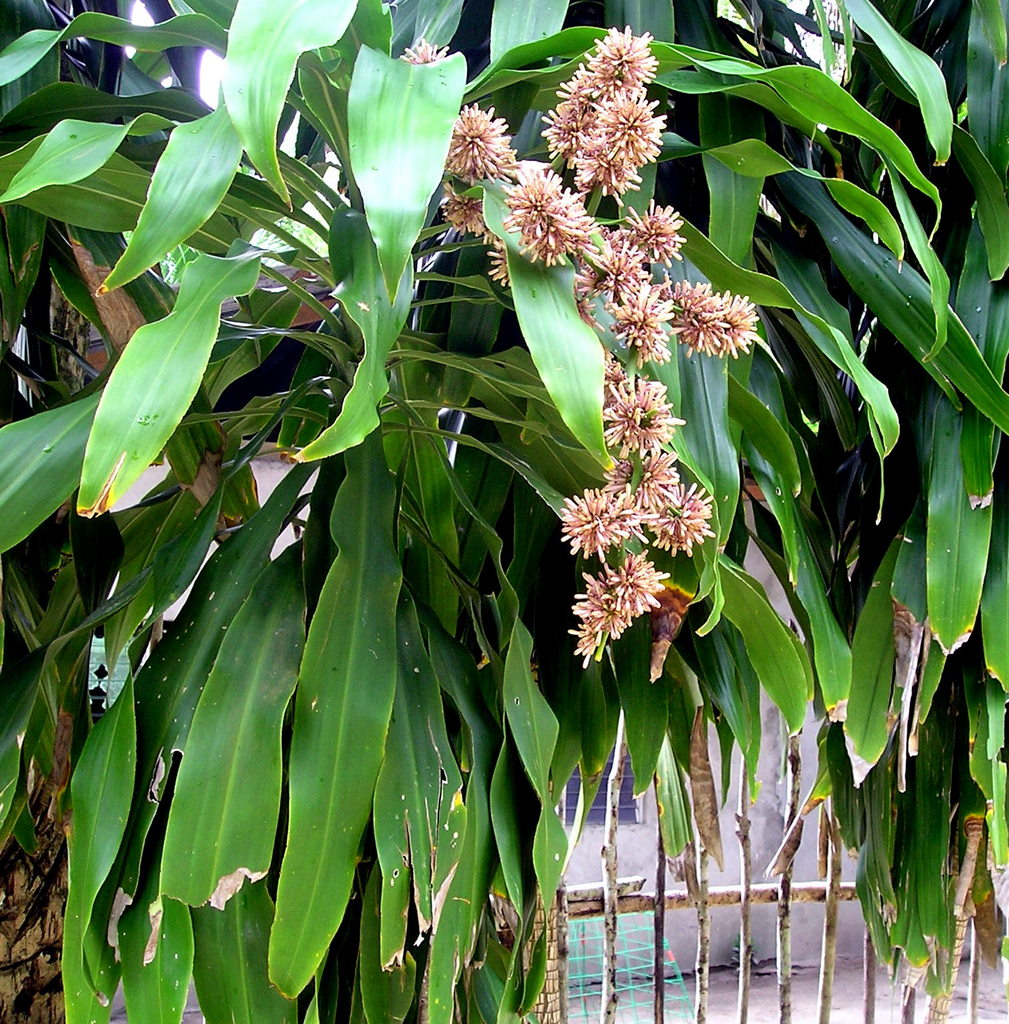

Dracaena fragrans massangeana will produce flowers on mature plants most of the time. These Dracaena plants can reach heights of more than 6 feet. If the conditions are conducive, it will produce a shower of fragrant white, pink, or purple flowers.
However, they prefer outdoor flowering, as they rarely bloom when planted as houseplants.
Season of Interest and Purchasing
The growing season for Corn Plants lasts from spring until October. This plant looks lovely in gardens as an ornamental plant, and it may also be kept indoors in a ceramic pot or terrarium. It requires little upkeep and is a great plant for beginners.
These amazing houseplants are available in your local nurseries and garden centers.
Growth
The Dracaena plant is a perennial shrub that grows slowly. They grow slowly from thick canes or stems that produce long, thin leaves that resemble corn stalks. This species develops in an upward pattern and may reach a height of 6 feet indoors, 15–50 feet tall, and 3–10 feet wide when grown outdoors.
Corn plants develop slowly and might take up to 5 years to mature.
Corn Plant Overview
| Scientific name | Dracaena fragrans |
| Common name/s | Corn Plant, Dracaena, Dragon Tree, Janet Craig Plant, Ribbon Plant, Striped Dragon Palm |
| Family | Asparagaceae |
| Growth Habit | Shrub |
| Height and Spread | Can have a height of up to 15 – 50 feet tall, and 3 – 10 feet wide |
| Classification based on life cycle | Perennial |
| Origin and Distribution | Native range is Africa, Sudan, Mozambique |
| Climate Zone | Generally warmer climate |
| USDA Plant Hardiness Zone | USDA Zone 10 – 11 |
| Color | Distinctive bright or dark green leaves with white-yellow stripes around gray-green centers |
Care Tips
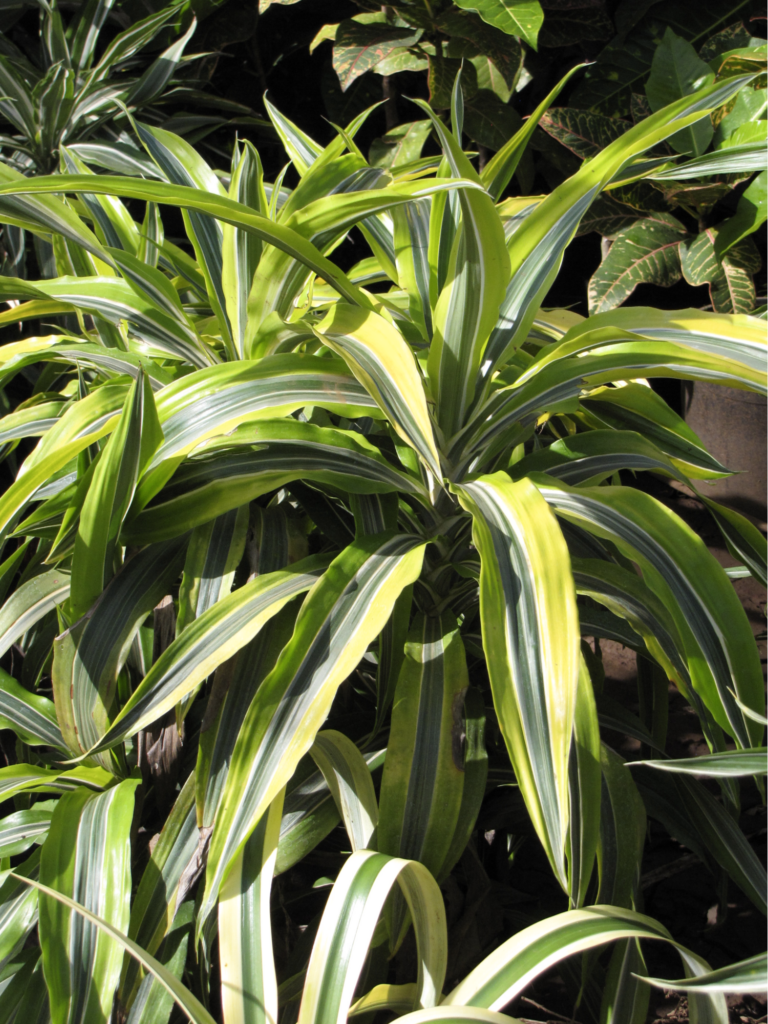

Light Requirement
Corn plants thrive indoors in medium-bright indirect light. However, it can also live under low-light settings. They look good in both natural and artificial lighting. This plant thrives in an east-facing window, although it can live in practically any place as long as it is not completely dark.
A good lighting condition will result in more intense color, richer lime-green foliage, and extended leaves.
Avoid direct sunlight as too much sun can cause sunburn and scorching of the Corn Plant’s leaves, leading to brown leaf tips.
Temperature Requirement
The Corn Plant, a native of Africa’s tropical areas, loves to thrive in an environment with a stable temperature. This plant thrives in temperatures ranging from 60 to 75 degrees Fahrenheit (16 to 24 degrees Celsius).
Additionally, keep them away from cold drafts, air conditioning, or heaters to avoid stunt growth, drooping their leaves, and leaving them limp.
Water Requirement
Corn Plants require sufficient water to grow healthy. The corn plant requires soil that is somewhat damp but not saturated. It thrives best in moist, well-draining soil.
This plant is drought tolerant and does not need to be watered frequently. However, it prefers a consistent degree of moisture, so make sure to keep the moisture level at its optimum but never excessive. Excessive watering might cause the plant’s roots to decay.
The plant is recommended to be watered once or twice every 7 to 14 days to ensure that it stays moist until the next watering.
Humidity Requirement
Corn Plants require somewhat greater amounts of humidity than the usual house plants. These plants are native to the tropics, where they flourish under normal humidity levels ranging from 40 to 50 percent. They can be capable of withstanding higher amounts but not below the optimum level.
To maintain the humidity level, use a humidifier or place the pot on a tray of water and pebbles. You may also mist the foliage on a regular basis. Any of these steps will make the environment more humid, which is ideal for growing diverse houseplant species and maintaining healthy growth and development.
Soil Requirement
A loose, loamy potting soil mixed with plenty of organic matter is the ideal choice for growing Corn Plants. This kind of mix will sustain the growing plant better. A ph level between 6.0 and 6.5 is ideal.
Corn Plant soil mix must have a proper drainage system, water retention, and aeration properties. To achieve this condition, perlite and peat moss can be added.
Fertilizer Requirement
Corn plants prefer soil with a rich organic matter content. During the growing season, Dracaena fragrans will require fertilizer to give the nutrients it requires. Therefore, it is recommended to apply a balanced houseplant fertilizer (10-10-10) NPK ratio during the growing season to stimulate growth from spring to fall.
In general, aim to feed your Corn plant once a month as too much plant food can cause chemical burn to the roots.
Space Requirement
Corn plants like a certain shade, or more specifically, semi-shade to shadow. Place this plant in a south or east-facing window to ensure it gets enough light. It may be grown in soil or pots, although it thrives in compact areas and appealing containers like terrariums.
In addition, the corn plant should be at least 18 to 24 inches apart from its neighbors.
Growing And Planting Tips
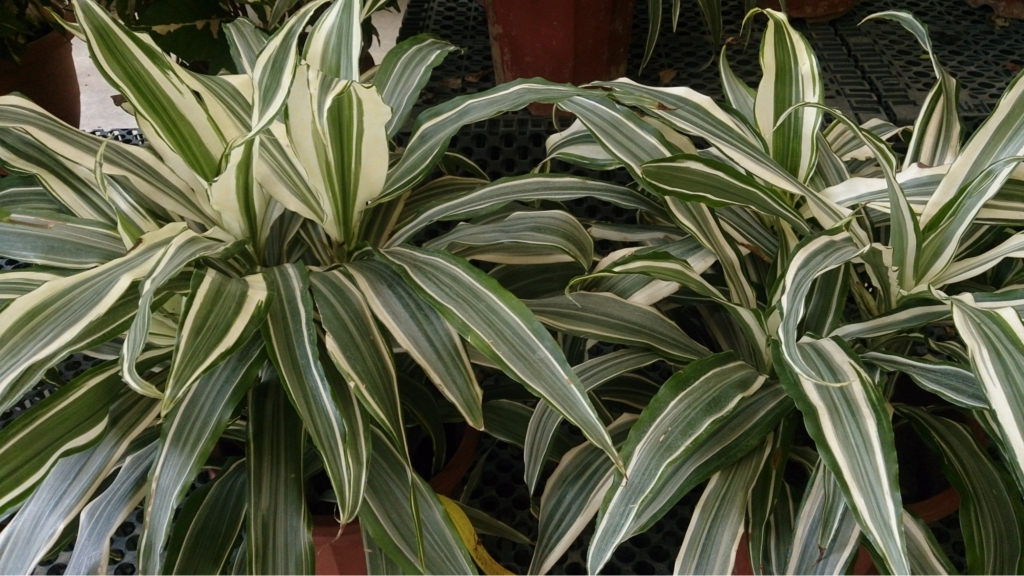

Propagation
The Corn Plant can be propagated by top cuttings or stem tip cuttings This propagation method has been proven to be an efficient way to reproduce your plant.
Below are the detailed steps on propagating your Dracaena fragrans:
Propagation by top-cuttings
Asexual reproduction is the method used by the plant Dracaena Fragrans. Stem cutting or top cutting propagation is the easiest method for reproducing corn plants.
1. Start by taking a cutting from your corn plant. Trim the stem as close to the surface as you can, with a length of around seven inches. Ensure that the cutting-edge roots have two or three leaves and at least a few nodes.
2. Dip the stem with the rooting hormone where you cut it. The cutting must be set down on moist soil.
3. When you already see a robust growth of roots, place the plant in the pot, virannium, or terracotta in a moderate area with enough indirect light.
Always remember that the newborn plant is extremely delicate, therefore you should proceed with utmost caution.
Pruning
Since the Corn Plant grows slowly, minimal pruning is needed. The lower leaves of the corn plant will start to turn yellow in around two to three years, which is the average lifespan of a leaf. Once a year, right before the growing season, trim the withering leaves with any cutting tool once they become unattractive.
You may also cut off the tips of the canes if the plant becomes too tall for the area you have available; fresh leaf buds will sprout close to the cut. Cutting extra growth and leaves can help the corn plant grow and look better by putting its energy into development.
Potting And Repotting
You may plant Dracaena fragrans in ceramic, terracotta, or other types of pots. Use a planter or container with well-draining potting soil to prevent root rot. Every year or two, aim to repot your corn plant into a new pot with fresh potting soil.
Use a pot that is 2 to 3 inches larger and deeper than the previous pot to avoid problems like overwatering and stunted growth.
Corn Plant Care
| Light | Medium to bright indirect light |
| Temperature | 60-75 degrees Fahrenheit |
| Water | Once a week, increased in summer, decreased in winter |
| Soil | Well-draining and organic, moist soil |
| Fertilization | Once a month, no fertilization needed in winter |
| Space | Minimal space, 18-24 inches apart |
| Propagation | Via stem cutting/top cutting propagation |
| Blooming | Enough sunlight and maturity needed |
| Pruning | When needed, removal of damaged and decaying leaves |
| Potting | Regular potting mix; use of perlite and peat moss recommended |
Problem And Troubleshooting

Overwatering
Overwatering is the leading cause of many corn plant problems. Yellowing leaves and stunted, sluggish development are the effects of overwatering. In addition, it may experience root rot, soggy soil, or even demise.
To lessen the effects of overwatering, think about modifying the container and soil to enable higher drainage and quicker soil drainage. Ensure your soil is airy and light and your pot have efficient drainage holes.
Underwatering
Plants that receive insufficient water or very dry air may develop dry leaf tips and edges. Insufficient watering of your plant will cause dry leaves, brown tips, leaf drops, withering, and leaf curling because of these improper growing conditions.
To fix this problem, maintain the plant’s watering schedule. Be careful not to allow the soil to become excessively moist, and give it enough of bright, indirect light, and not direct sun, to ensure its survival.
Nutrient Deficiency
When growth conditions are poor, and plants are unable to take nutrients from the soil, deficiencies can occur. Symptoms of nutrient deficiency include yellowing of the leaves, interveinal yellowing, reduced internodes, stunted plant’s growth, or aberrant color of the foliage, such as red, purple, or bronze.
The mobility of nutrients inside the plant causes these symptoms to manifest in various plant sections.
A balanced NPK is the best intervention for this problem since it contains all the necessary nutrients. You may also use lime, gypsum, calcium nitrate, or crushed eggshells as sources of calcium for crops. Epsom salts can be sprayed on crop leaves as a temporary fix for nutritional deficiencies in plants.
Flowering Problems
A mature corn plant blooms with a spray of beautiful white, pink, or purple blossoms. To ensure your plant will flower, give it the right amount of sunlight as the genes responsible for flowering is light activated. However, take note that this plant rarely yields flowers when cultivated as a houseplant.
Pests And Diseases
Corn Plant Pests And Diseases
| Common Pests/Diseases | Symptoms | Treatment And Prevention |
Common diseases include leaf spotting, root rotting, fungal diseases, stem and crown rotting. | Black or dark brown spots with yellow rim around | Do not overwater and maintain proper humidity levels. Extremely wet environments enhance fungal growth.Proper ventilation is necessary. Removal of infected plant parts to avoid spreading of disease. |
Common pests include aphids, scales, mealybugs, spider mites | Visible insects thriving on surface | Warm, soapy water can be sprayed once a month. Neem oil, herbal spray, or commercial insecticides can also be used. |
Problems With People And Animals
Toxicity
The corn plant is poisonous to dogs and cats because it contains the toxic chemical component saponin. Therefore, if consumed by animals, this plant can be lethal. According to the ASPCA, ingestion of this plant can sometimes result in vomiting with blood, anorexia, dilated pupils, sadness, and hyper-salivation in pets.
Therefore, giving the plant to pets in any form might be dangerous and should be avoided.
Dracaena Fragrans Meaning And Symbolism
The romanized version of the Ancient Greek word “drakaina,” or “female dragon,” is where the name Dracaena comes from. This name accurately describes the plant’s bold, tall, sword-shaped leaves and hardiness.
This corn plant is hailed as a lucky plant in various Asian nations. This plant also symbolizes knowledge of self and perseverance. It is said that you will be lucky if the plant blossoms in your house.
| General Meaning | Good luck |
| Symbolism | Knowledge of self and perseverance |
Landscaping And Gardening Ideas

Companion Plants
Below are some of the wonderful companions for corn plants:
1. Sweet alyssum (Lobularia maritima) – a low-growing herb that flowers at the start of the summer.
2. Snowberry (Symphoricarpos albus) – a lovely perennial shrub that looks great along large shrubs.
3. Butterfly bush (Buddleja davidii) – a fragrant shrub that is simple to cultivate and is excellent for filling in gaps in the landscape.
Related: 21 Different Types Of Corn Plants (Including Photos)
Landscaping Ideas
The popular ornamental plant Dracaena fragrans is frequently grown for hedges, living fences, and windbreaks. However, it is becoming more and more common to see this plant being used in both indoor and outdoor interior design. In any space it is in, this plant fosters a calming, pleasant environment that is intellectually pleasing.
| What To Plant With | Sweet Alyssum, Snowberry, Butterfly Bush, and other tropical plants |
| What NOT To Plant With | Basically nothing |
Conclusion
The Corn plants are popular indoor plants with distinctive foliage and lush green leaves that mimic a corn-like structure with its brilliant green leaves and woody stalks. They are versatile plants that may be cultivated indoors and valued for their low maintenance needs. Surely, the Corn Plant care makes it ideal for plant novices.
If you want to add a decorative piece to the workplace, home, or yard, then this plant is the one for you. Of course, you will be the lucky one if you have this plant!
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQS)
Are Corn Plants easy to care for?
The Corn Plants are good plants for beginners due to their low maintenance and tolerance to most of the lighting conditions. In addition, they are hardy plants; hence they can be easy to care for.
How do I get my Corn Plant to bloom?
In order for your Corn plant to bear flowers, you must give it the right amount of sunlight to activate the flowering genes that will signal your plant to bloom. The genes responsible are light-activated, hence without meeting the light requirement, it will fail to produce flowers.
Maturity is also a factor. Your plant must be mature and competent to bear flowers. So don’t expect flowers if your plant is still juvenile.
Can you overwater a Corn Plant?
Definitely, yes. Your Corn Plant is still susceptible to overwatering, especially if the soil does not drain well and the pot does not have enough drainage holes. Avoid getting your plant overwatered at all costs since it is also prone to root rotting and other bacterial and fungi diseases. As a general rule, keep your soil moist but never soggy.
Are Corn Plants toxic to humans?
Corn Plants are safe for humans; however, they are not safe for pets. Ingestion of this plant can sometimes result in vomiting with blood, anorexia, dilated pupils, sadness, and hyper-salivation in pets.
Can you propagate a Corn Plant?
Yes! Corn plants are propagated by stem or top cutting. Just cut a stem from a healthy mother plant and dip it in a rooting hormone. Allow the cut stem to develop roots in an appropriate soil mix under bright indirect lighting.
Editor’s Recommendations
Pink Syngonium: The Number 1 Care, Propagation, and Watering Guide
Monstera Peru: The Complete Care, Propagation, and Watering Guide
Peperomia Polybotrya: The Number 1 Care, Watering, and Propagation Guide